chapter 10.1 Glembocki 2017
advertisement

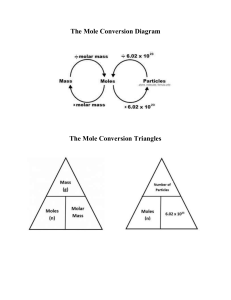
10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > REVIEW Which is larger I? or I1- ? Name each particle. 1 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Chapter 10 Chemical Quantities 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter 2 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > I can… Perform dimensional analysis to convert between units Recall Avogadro’s number Apply Avogadro’s number to determine the number of representative particles in a substance Calculate representative particles moles Calculate moles representative particles Determine molar mass of a substance 3 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Measuring Matter Chemistry is a quantitative science. • you perform calculations that relate quantities of the reactants in a chemical reaction to quantities of the products. pair case Six pack gross dozen 4 ream Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Measuring Matter Each of these different ways to measure apples can be equated to a dozen apples. • By count: 1 dozen apples = 12 apples • By mass: 1 dozen apples = 2.0 kg apples • By volume: 1 dozen apples = 0.20 bushel apples These are approximations for average-sized apples. 5 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A MeasureSample Problem 10.1 > ment of Matter Finding Mass from a Count What is the mass of 90 average-sized apples if 1 dozen of the apples has a mass of 2.0 kg? 6 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A MeasureSample Problem 10.1 > ment of Matter 1 Analyze List the knowns and the unknown. Use dimensional analysis to convert the number of apples to the mass of 90 apples. KNOWNS number of apples = 90 apples Conversion factors 12 apples = 1 dozen apples 1 dozen apples = 2.0 kg apples 7 UNKNOWN mass of 90 apples = ? kg Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.1 2 Calculate Solve for the unknown. Multiply the known by conversion factors. The conversion factor used should cancel the previous unit 90 apples × 1 dozen apples 2.0 kg apples = 15 kg apples × 1 dozen apples 12 apples 1 The unit “apples” cancels the previous unit 8 The unit “dozen apples” cancels the previous unit Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measure> ment of Matter If 0.20 bushel is 1 dozen apples and a dozen apples has a mass of 2.0 kg, what is the mass of 0.56 bushel apples? KNOWNS volume of apples = 0.56 bushel apples Conversion factors 12 apples = 1 dozen apples 1 dozen apples = 2.0 kg apples 0.20 bushel = 1 dozen apples UNKNOWN mass of 0.56 bushel apples = ? kg 9 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measure> ment of Matter If 0.20 bushel is 1 dozen apples and a dozen apples has a mass of 2.0 kg, what is the mass of 0.56 bushel apples? 0.56 bushel 1 10 1 dozen 0.20 bushel 2.0 kg = 5.6 kg 1 dozen Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > COPY THIS Assume 2.0 kg of apples is 1 dozen and that each apple has 8 seeds. How many apple seeds are in 14 kg of apples? Known – 14 kg apples Conversion factors: 2.0 kg apples = 1 dozen 1 apple = 8 seeds Unknown: seeds? 11 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Assume 2.0 kg of apples is 1 dozen and that each apple has 8 seeds. How many apple seeds are in 14 kg of apples? 14 kg 1 12 1 dozen 12 apples 2.0 kg 1 dozen 8 seeds = 672 seeds 1 apple Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > What Is a Mole? Matter is composed of atoms, molecules, and ions. • These is an extremely large number of them in a small sample of a substance so counting these particles is not practical. 13 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > What Is a Mole? Think about counting eggs. • It’s easier when the eggs are grouped into dozens. • A dozen is a specified number (12) of things. 14 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > What Is a Mole? Counting with Moles Chemists also use a unit that is a specified number of particles, most often atoms or molecules. • The unit is called the mole. • A mole (mol) of a substance is 6.022 × 1023 representative particles of that substance • The number of representative particles in a mole and is called Avogadro’s number, 6.022 × 1023 TED Ed TV 15 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > If you had a mole of doughnuts, they would cover the entire Earth in a doughnut-layer five miles deep. 16 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > If you had a mole of basketballs, you could create a new planet the size of the Earth! 17 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > If you received a mole of pennies on the day you were born, and spent a million dollars a second until you died at 100, you’d still have over 99.99% of your money in the bank! 18 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Counting with Moles The term representative particle refers to atoms, molecules, or formula units. • The representative particle of most elements is the atom. 19 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > What Is a Mole? Counting with Moles However, seven elements exist normally as diatomic molecules: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2. I Have NO Bright or Clever Friends – you must memorize the diatomic elements • The representative particle of these elements is the molecule. • For ionic compounds, such as calcium chloride, the representative particle is the formula unit, CaCl2. 20 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > What Is a Mole? Counting with Moles A mole of any substance contains Avogadro’s number of representative particles, or 6.022 × 1023 atoms, ions, molecules or formula units 21 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > COPY THIS Write the correct representative particle (atom , molecule or formula unit) for each of the following. H2O molecule formula unit KI diatomic molecule O2 Ag atom 22 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Daily Question – give 3 ideas on the words “dozen” and “mole”. 23 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.2 Converting Number of Atoms to Moles Magnesium is a light metal used in the manufacture of aircraft, automobile wheels, and tools. How many moles of magnesium is 1.25 × 1023 atoms of magnesium? 24 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.2 1 Analyze List the known and the unknown. KNOWN number of atoms = 1.25 × 1023 atoms Mg Conversion factor 1 mol Mg = 6.022 × 1023 atoms Mg UNKNOWN moles = ? mol Mg 25 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.2 2 Use DIMESIONAL ANALYSIS to Solve for the unknown. 1. Write known over 1 2. Drag and drop - unit and chemical symbol 1.25 × 1023 atoms Mg 1 1 mol Mg 6.022 × 1023 atoms Mg = 0.208 mol Mg Why does this answer have three significant figures? 26 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.3 Converting: Moles Atoms or molecules Propane is a gas used for cooking and heating. How many atoms are in 2.12 mol of propane (C3H8)? 27 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A MeasureSample Problem 10.3 > ment of Matter 1 Analyze List the knowns and the unknown. The desired conversion is: moles → molecules → atoms. KNOWN number of moles = 2.12 mol C3H8 Conversion factors 1 mol C3H8 = 6.022 × 1023 molecules C3H8 1 molecule C3H8 = 11 atoms (3 carbon and 8 hydrogen atoms) UNKNOWN number of atoms = ? atoms 28 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.3 2 Use DIMESIONAL ANALYSIS to Solve for the unknown. 1. Write known over 1 2. Drag and drop - unit and chemical formula 2.12 mol C3H8 1 6.022 × 1023 molecules C3H8 1 mol C3H8 11 atoms 1 molecule C3H8 = 1.40 × 1025 atoms Why does the answer have three significant figures? 29 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Counting Atoms in a Molecule 30 30 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > 1 molecule (NH4)3PO4 3 N atoms 31 31 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > 1 molecule (NH4)3PO4 12 H atoms 32 32 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > 1 molecule (NH4)3PO4 1 P atom 33 33 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > 1 molecule (NH4)3PO4 4 O atoms 34 34 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > In 1 Mole of (NH4)3PO4 There are: •3 moles of N •12 moles of H •1 mole of P •4 moles of O 35 35 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > How is a mole: similar to a dozen? related to chemical formulas? Subscripts in a chemical formula can indicate _____________ or ______________ . (2 ideas) 36 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Learning Targets: I can… • Determine molar mass of an element or compound • Calculate moles to grams • Calculate grams to moles 37 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > All conversions go first to mole. 1 mole 38 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Molar Mass The Mass of a Mole of an Element The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is the mass of a mole of the element. The mass of 1 mole of an element is its molar mass. For consistency, we will round all masses of elements on the periodic table to 2 decimal places. • For carbon, the molar mass is 12.01 g. • For atomic hydrogen, the molar mass is 1.01 g. 39 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > • Why are the atomic masses on the periodic table not whole numbers? • masses shown on the periodic table are weighted averages of the masses for all of the isotopes of elements • What is the atomic mass of an element on the periodic table expressed in grams? • The mass of 1 mole of that element. 40 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Molar Mass The Mass of a Mole of an Element 1 mol of sulfur atoms = 32.07 g 1 mol of carbon atoms = 12.01 g 1 mol of iron atoms = 55.85 g This figure shows one mole of carbon, sulfur, and iron. 41 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A MeasureMolar Mass > ment of Matter The Mass of a Mole of an Element • The molar mass of an element contains 1 mol or 6.022 × 1023 atoms of that element. • 1 mole of an element has the mass listed on the periodic table in grams 42 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > • How many atoms are contained in the molar mass of an element? • 6.022 x 1023 atoms 43 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Molar Mass The Mass of 1 Mole of a Compound To calculate the molar mass of a compound: • determine the number of grams of each element • then add the masses of all the elements in the compound. 44 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Molar Mass The Mass of a Mole of a Compound Find the molar mass of SO3 • the mass of sulfur (S) is 32.07 g • The mass of three atoms of oxygen: • (O): 3 × 16.00 g = 48.00 g • Molar mass of SO3 is 32.07 g + 48.00 g = 80.07 g • 1 mole of SO3 has a mass of 80.07 g. • This is the mass of 6.022 x 1023 molecules of SO3. 45 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter Molar Mass > The Mass of a Mole of a Compound 1 mol of paradichlorobenzene (C6H4Cl2) molecules (moth crystals) = 147.00g 1 mol of glucose (C6H12O6) molecules (blood sugar) = 180.00 g 1 mol of water (H2O) molecules = 18.02 g 46 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.4 Calculating the Molar Mass of a Compound The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) provides sufficient energy to launch a rocket. What is the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide? 47 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Sample Problem 10.4 2 Calculate Solve for the unknown. Add the results. mass of 1 mol H2O2 = 2.02 g H + 32.00 g O = 34.02 g molar mass of H2O2 = 34.02 g/mol 48 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Find the molar mass of PCl3 mass of 1 mol P = 30.97 g P mass of 3 mol Cl = 35.45 g x 3 = 106.35 Cl molar mass of PCl3 = 66.42 g/mol 49 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > END OF 10.1 50 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. . 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter > Glossary Terms • mole (mol): the amount of a substance that contains 6.02 × 1023 representative particles of that substance • Avogadro’s number: the number of representative particles contained in one mole of a substance; equal to 6.02 × 1023 particles • representative particle: the smallest unit into which a substance can be broken down without a change in composition, usually atoms, molecules, or ions • molar mass: a term used to refer to the mass of a mole of any substance 51 Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. .