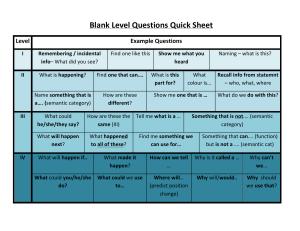
Common General Knowledge Questions & Answers Let us discuss few common general knowledge questions and answers that may really help kids. sponsored by Faspe.info & AnswerKeyHUB.com semantic memory A type of memory containing organized, factual knowledge of the world, including word meanings. episodic memory A category of long-term memory that involves the recollection of specific events, situations and experiences. category A set of objects that belong together. concept The mental representation of a category. feature comparison model A model proposing that items are categorized by matching the item's features to defining category features. defining features The set of traits necessary to make objects acceptable members of a category. characteristic features The set of traits that are descriptive of but not essential to objects in a given category. sentence verification technique An experimental procedure, used for studying memory, in which participants are given simple sentences typicality effect Finding that people reach judgments faster when an item is a typical member of a category, rather than an unusual member (nonprototype). prototype A mental image or best example of a category, to which new items can be compared as a quick and easy method for including/excluding items from a category. prototype approach An approach to semantic memory in which a person decides whether an item belongs to a category by comparing that item with a prototype prototypicality The degree to which a particular member of a category matches the prototype for that category. graded structure The fact that category members vary in how well they represent a category (some are more prototypical than others). semantic priming effect The finding that people respond faster to an item if it was preceded by an item with similar meaning. family resemblance In the prototype approach, the concept that each example has at least one attribute in common with some other example of the concept. superordinate-level categories Higher level, more general categories. basic-level categories Moderately specific categories. subordinate-level categories Lower level, more specific categories. expertise Consistently superior performance on a set of tasks for a domain, achieved by deliberate practice over a period of atleast 10 years. exemplar The specific examples of a concept stored in memory. network models A model of semantic memory that proposes a net-like organization of concepts in memory, with many interconnections. The meaning of a particular concept depends on the concepts to which it is connected. Collins and Loftus network model Semantic memory is organized in terms of net-like structures, with numerous interconnections. When people retrieve information, activation spreads to related concepts. node In the parallel distributed processing approach, the location of each neural activity, interconnected in a complex fashion with many other such locations. link The element that connects a particular concept node with another concept node. spreading activation The process through which activity in one node in a network flows outward to other nodes through associative links. ACT-R (Automated Components of Thought-Rational) A series of network models that attempts to account for all of cognition, including memory, learning, spatial cognition, language, reasoning, and decision-making. declarative knowledge One's knowledge about facts and things. proposition The smallest unit of knowledge that can be judged either true or false.