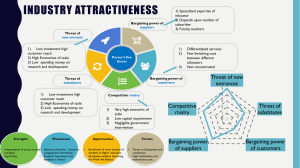
EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT CENTRAL LUZON STATE UNIVERSITY College of Business Administration and Accountancy Department of Business Administration Focuses on identifying and evaluating trends and events beyond the control of a single firm. OBJECTIVES ✓ Describe how to perform an External Assessment ✓ Discuss the Industrial Organization ✓ Explain the Forces present in a competitive environment ✓ Identify the Key External Forces ✓ Develop an EFE Matrix and CPM POLITICAL External FIRM LEGAL Political factors result from the processes and actions of government bodies that can influence the decisions and behavior of firms. Government Policies Trading Policies Monetary/Tax Policies Political Factors Corruption Consumer Confidence Inflation rate Interest rate Unemployment Economic Factors Economic factors in a firm’s external environment are largely macroeconomic, affecting economy-wide phenomena. Sociocultural factors capture a society’s cultures, norms, and values of the population within which the organization operates Ethnic/religious factors Health and Lifestyle Life Cycle Socio-cultural Factors Population growth Filipino: Close family ties Virtual kumustahan E-numan session Health and Lifestyle Lifecycle Bachelor Empty Nest 1 and 2 Newly married couple Full Nest 1,2,3 Solitary Survivor 1 and 2 Population Growth Technological factors pertain to innovation in technology and the regulations surrounding technology Technological Development Research Development Information System Technological Consumer access to technology It involves issues such as the natural environment, global warming, and sustainable economic growth. Weather Climate change Environmental regulations Environmental Environmental issues Legal factors include the official outcomes of political processes as manifested in laws, mandates, regulations, and court decisions—all of which can have a direct bearing on a firm’s profit potential. Environmental Law Consumer protection Legal Factors Data Privacy Act Tariff laws • Republic Act 8749 Philippine Clean Air Act Of 1999 • Ra 9275 Philippine Clear Water Act • Republic Act 6969 Toxic Substances, Hazardous And Nuclear Waste Control Act Of 1990. ... • Presidential Decree 1586 Environmental Impact Statement (Eis) Of 1978. • Ra 9512 Environmental Education Act Of 2008 RA 7394 (Consumer Act of the Philippines of 1991) THREAT OF NEW ENTRANT THREAT OF SUBSTITUTE COMPETITIVE RIVALRY BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIER BARGAINING POWER OF BUYER Threat of New Entrant The possibility that the profits of established firms in the industry may be eroded by new competitors. Bargaining Power of Buyer The threat that buyers may force down prices, bargain for higher quality or more services, and play competitors against each other. Bargaining Power of Supplier The threat that suppliers may raise prices or reduce the quality of purchased goods and services. Threat of Substitute The threat of limiting the potential returns of an industry by placing a ceiling on the prices that firms in that industry can profitably charge without losing too many customers to substitute products. Intensity of Rivalry among Competitors The threat that customers will switch their business to competitors within the industry. This strategyformulation tool summarizes and evaluates the major opportunities and threats in the functional areas of a business Key External Factors Opportunities • Opportunities are the chances exist in the external environment, it depends firm whether the firm is willing to exploit the opportunities or may be they ignore the opportunities due to lack of resources. Threats • Threats are always evil for the firm, minimum no of threats in the external environment open many doors for the firm. Maximum number of threats for the firm reduce their power in the industry. Steps in Developing the EFE Matrix 1. List key external factors as identified in the external-audit process. 2. Assign a weight that ranges from 0.0 (not important) to 1.0 (allimportant) to each factor. 3. Assign a rating between 1 and 4 to each key external factor to indicate how effectively the firm’s current strategies respond to the factor, where 4 = the response is superior, 3 = the response is above average, 2 = the response is average, and 1 = the response is poor. 4. Multiply each factor’s weight by its rating to determine a weighted score for each variable. 5. Sum the weighted scores for each variable to determine the total weighted score for the organization. Identifies a firm’s major competitors and its particular strengths and weaknesses in relation to a sample firm’s strategic position. Critical Success Factor • Critical success factors are extracted after deep analysis of external and internal environment of the firm. • Obviously there are some good and some bad for the company in the external environment and internal environment. • The higher rating show that firm strategy is doing well to support this critical success factors and lower rating means firm strategy is lacking to support the factor. EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT CENTRAL LUZON STATE UNIVERSITY College of Business Administration and Accountancy Department of Business Administration