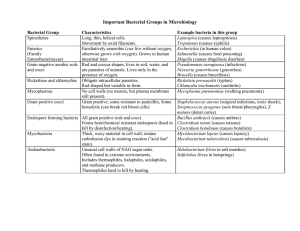
CELL WALL INHIBITORS Beta- Lactams Penicillin’s Penicillin G & Penicillin V: very old, basic penicillin’s Brand Names: › Penicillin G: Pfizerpen › Penicillin V: Pen VK • • • • • • Both are just called Penicillin now Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Used for minor cases of infection due to Gram + bacteria Narrow Spectrum antibiotic- specifically penicillinase susceptible/sensitive Penicillinase sensitive- not effective against bacteria that produce penicillinase enzymes Route and absorption: BOTH Penicillin G & V • IV • Oral- don’t take with food as it affects absorption Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: Acne and cellulitis o Peptococcus- acne Gram + Anaerobe cocci o Peptostreptococcus- acne Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Propionibacterium- acne Gram + Anaerobic rod o Streptococcus (some strains are resistant)- Mild cases of cellulitis Gram + aerobic • But also used for/ against: o Corynebacterium (usually a containment, some strains are very resistant) Gram + aerobic o Enterococcus faecalis only Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci and rods Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic rod Clostridium perfergins Gram + Anaerobic rod Clostridium tetani Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod o Neisseria meningitidis- not used against anymore Gram – aerobic cocci o Neisseria gonorrhea- not used against anymore Gram – aerobic cocci o Borrelia Burgdorferi Miscellaneous, Spirochete, Gram Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Piperacillin: Ureidopenicillin Brand Name: Generic is only form available • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Extended Spectrum antibiotic- specifically antipseudomonal Treats more Gram – and less of Gram + organisms DOES NOT TREAT STAPH AUREUS Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Penicillin resistant Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o Listeria Gram +, aerobic o Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae aerobic rod o H. influenzae (some resistance) Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species, Proteus, Citrobacter, Serratia, Providencia) Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Ticarcillin: Carboxypenicillin Brand Name: Ticar • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Extended Spectrum antibiotic- specifically antipseudomonal Treats more Gram – and some Gram + organisms REALLY good at treating PSEUDOMONAS infections Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae aerobic rod o Penicillin resistant Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o Listeria Gram +, aerobic o Gram + anaerobic cocci Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci o H. influenzae (some resistance) Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species, Proteus, Citrobacter, Serratia, Providencia) Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Ampicillin & Amoxicillin: Aminopenicillins Brand Names: › Ampicillin: Principen › Penicillin V: Amoxil • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal BROAD SPECTRUM antibiotic- PENICILLINASE SENSITIVE/SUSCEPTIBLE Penicillinase sensitive- not effective against bacteria that produce penicillinase enzymes Mainly used for Gram + coverage and a little bit of Gram – coverage Route and absorption: • Ampicillin- IV & ORAL- don’t take with food as it affects the absorption • Amoxicillin- ORAL ONLY- good to take with food Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Penicillin resistant Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o Listeria Gram +, aerobic o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + anaerobic cocci & rods Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + Anaerobic rod Closttridium perfringens Gram + Anaerobic rod Propionibacterium acnes Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod o Neisseria gonorrheae Gram – aerobic cocci o H. influenzae (some resistance) Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species, Citrobacter, Serratia, Morganella, Providencia) Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Campylobacterium Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae aerobic rod o Borrelia Burgdorferi Miscellaneous, Spirochete, Gram Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Nafcillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin: Brand Names: › Nafcillin: Unipen › Oxacillin: Bactocil • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal VERY NARROW SPECTRUM antibiotic- PENICILLINASE RESISTANT ANTISTAPHYLOCCAL infections Penicillinase resistant- effective against bacteria that produce penicillinase enzymes Gram + coverage only Route and absorption: • Nafcillin- IV ONLY due to erratic absorption • Oxacillin- IV ONLY due to erratic absorption • Dicloxacillin- ORAL ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: HEPATIC- need to dose adjust for hepatically impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Staphylococcus aureus- Methicillin sensitive (MSSA) only Gram +, aerobic o Staphylococcus epidermis- Methicillin sensitive (MSSE) only Gram +, aerobic o Streptococci Gram +, aerobic Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Amoxicillin/Clavulanate & Ampicillin/Sulbactam: Brand Names: › Amoxicillin/Clavulanate: Augmentin › Ampicillin/Sulbactam: Unasyn • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal BROAD SPECTRUM antibiotic- BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITORS Beta lactamase inhibitor- effective against bacteria that produce beta lactamase enzymes Used for Gram +, Gram -, Anaerobes Route and absorption: • Augmentin (Amoxicillin/Clavulanate)- ORAL ONLY • Unasyn (Ampicillin/Sulbactam)- IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o MSSA (produces penicillinases) Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Listeria Gram +, aerobic o Anaerobes- Gram + & Gram – Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + Anaerobic rod Closttridium perfringens Gram + Anaerobic rod Propionibacterium acnes Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacteroids GRAM – ANAEROBES Fusobacterium GRAM – ANAEROBES Prevotella GRAM – ANAEROBES o Haemophilus Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella (MCAT) Gram –, aerobic cocci o Acinetobacter (CRAB- Carbapenem Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii) Gram –, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species, Citrobacter, Serratia) E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Piperacillin/Tazobactam & Ticarcillin/Clavulanate: Brand Names: › Piperacillin/Tazobactam: Zosyn › Ticarcillin/Clavulanate: Timentin • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal BROAD SPECTRUM antibiotic- BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITOR Beta lactamase inhibitor- effective against bacteria that produce beta lactamase enzymes Used for Gram +, Gram -, Anaerobes Route and absorption: • Zosyn (Piperacillin/Tazobactam)- IV ONLY • Unasyn (Ticarcillin/Clavulanate)- IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o MSSA (produces penicillinases) Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Listeria Gram +, aerobic o Anaerobes- Gram + & Gram – Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + Anaerobic rod Closttridium perfringens Gram + Anaerobic rod Propionibacterium acnes Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacteroids GRAM – ANAEROBES rod Fusobacterium GRAM – ANAEROBES rod Prevotella GRAM – ANAEROBES rod o Enterobacteriaceae (everyone) Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Haemophilus Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci o Pseudomonas Gram –, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems CELL WALL INHIBITORS Beta Lactams Cephalosporins & Cephamycins 1st generation: Cefazolin, Cefadroxil, Cephalexin Brand Names: › Cefazolin: Ancef › Cefadroxil: Duricef › Cephalexin: Keflex • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Used for Gram + and Gram – GOOD for treating UTIs because it has high urine concentrations NOT a heavy hitter drug for MRSA or pseudomonas Route and absorption: • Cefazolin- IV ONLY due to poor oral absorption, commonly used in patients in pre-op surgery especially orthopedic surgery to cover Gram + bacteria that reside on the skin and bones such as staphylococcus bacteria • Cefadroxil- ORAL • Cephalexin- ORAL Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Staphylococcus aureus- Menthicillin sensitive (MSSA) Gram + Anaerobe cocci o Streptococcus species Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci and rods Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + Anaerobic rod Clostridium perfergins Gram + Anaerobic rod Propionibacterium acnes Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod o E. coli- most common UTI bacteria Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Proteus- CEFAZOLIN ONLY! Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins– LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 2nd generation: Cefuroxime axetil, cefuroxime, cefoxitin, cefotetan Brand Names: › Cefuroxime axetil (oral only): Ceftin › Cefuroxime (IV): Zinacef › Cefoxitin: Mefoxin › Cefotetan: Cefotan • • • • Cell wall inhibitors Bactericidal Used for Gram +, Gram –, and ANAEROBES Cefoxitin and cefotetan are both CEPHAMYCINS, which treat anaerobes so they are good for treating intrabdominal infections which are usually polymicrobial infections. Route and absorption: • Cefuroxime axetial- ORAL ONLY, the axetil compound stabilizes the antibiotic to be able to be used in oral form • Cefuroxime- IV ONLY • Cefadroxil- IV ONLY • Cephalexin- IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Staphylococcus aureus- Methicillin Sensitive Gram +, aerobic o Clostridium perfingens* (anaerobe) Clostridium perfergins Gram + Anaerobic rod o Peptostreptococcus Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o H. influenzae (including β-lactamase producers) Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella catarrhalis Gram –, aerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae (except Enterobacter) Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o o o o Bacteroides fragilis* (anaerobe) Gram – Anaerobic rods Prevotella* (anaerobe) Gram – Anaerobic rods Fusobacterium* (anaerobe) Gram – Anaerobic rods Borellia burgdorfii (cefuroxime) Miscellaneous, Spirochete, Gram Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins– LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 3rd generation: Cefdinir Brand Name: Omnicef • • • Cell wall inhibitors Bactericidal Used mostly for Gram –, but there is some Gram + coverage Route and absorption: ORAL ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus Gram +, aerobic o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus epidermidis Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species & Providencia) Gram– aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Campylobacter Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci o Haemophilus influenzae Gram -, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins– LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 3rd generation: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: Rocephin • • • • • Cell wall inhibitors Bactericidal Used for Gram +, and Gram – One of the MOST COMMON CEPHALOSPORINS you will see on the INPATIENT UNITS Used a lot to treat PNEUMONIA and UTI’s Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Staphylococcus aureus- Methicillin Sensitive (MSSA) Gram +, aerobic o Staphylococcus epidermidis- Methicillin Sensitive (MSSE) Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Propionibacterium Gram + Anaerobic rod o Clostridium perfergins Gram + Anaerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Enterobacter species) Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Campylobacter Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Acinetobacter- Gram –, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci o Borellia burgdorfii Miscellaneous, Spirochete, Gram - Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins– LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 3rd generation: Ceftazidime Brand Name: Fortaz • • • • • • Cell wall inhibitors Bactericidal Used for Gram – mostly and some Gram + and Gram + ANAEROBES This is the DRUG OF CHOICE in NEONATES VERY GOOD coverage for PSEUDOMONAS ONLY CEPHALOSPORIN THAT DOES NOT TREAT STAPH AUREUS INFECTIONS Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Streptococcus- some species has RESISTANCE Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Propionibacterium Gram + Anaerobic rod o PSEUDOMONAS*** Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae (ALL species) Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Acinetobacter- Gram –, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Campylobacter Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins– LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Aztreonam- CEFTAZIDIME ONLY Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 4th generation: Cefepime Brand Name: Maxipime • • • • • Cell wall inhibitors Bactericidal Used for Gram – mostly and some Gram + and Gram + ANAEROBES This is the DRUG OF CHOICE in NEONATES VERY GOOD coverage for PSEUDOMONAS Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Gram +, aerobic o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus epidermidis (MSSE) Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus species Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o PSEUDOMONAS*** Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae (ALL species) Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems 5th generation: Ceftaroline Brand Name: Teflaro • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Used for Gram – mostly and some Gram + and Gram + ANAEROBES GOOD for treating MRSA Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Used as salvage therapy for pneumonia Gram +, aerobic o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus species Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Propionibacterium Gram + Anaerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae (EXCEPT Citrobacter, Serratia, Salmonella, Shigella, Providencia) Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Pencillins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Cephalosporin/Beta Lactamase Inhibitors Combinations: Ceftazidime-Avibactam Brand Name: Avycaz • • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor and BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITOR BETALACTAMASE INHIBITION DUE TO AVIBACTAM New drug for resistant organisms Bactericidal May be active vs. ESBL’s and CARBAPENAMASE PRODUCING ORGANISMS Used for Gram – mostly and some Gram + and Gram + ANAEROBES Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o May be active vs. ESBL’s and CARBAPENAMASE PRODUCING ORGANISMS o PSEUDOMONAS o Streptococcus species Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Aztreonam- ONLY CEFTAZIDIME Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems Cephalosporin/Beta Lactamase Inhibitors Combinations: Ceftolozane-Tazobactam Brand Name: Zerbaxa • • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor and BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITOR BETALACTAMASE INHIBITION DUE TO TAZOBACTAM New drug for resistant organisms Bactericidal May be active vs. ESBL’s and CARBAPENAMASE PRODUCING ORGANISMS Used for Gram – mostly and some Gram + and Gram + ANAEROBES Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o May be active vs. ESBL’s and CARBAPENAMASE PRODUCING ORGANISMS o PSEUDOMONAS o Streptococcus species Gram +, aerobic o Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci o Enterobacteriaceae Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems CELL WALL INHIBITORS Beta Lactams Carbapenems Carbapenems: Doripenem, Ertapenem, Meropenem, Meropenem/Vaborbactam, Imipenem/ Cilistatin, Imipenem/Cilistatin with Relebactam Brand Names: › Doripenem: Doribax › Ertapenem: Invanz › Meropenem: Merrem › Meropenem/Vaborbactam: Vabomere › Imipenem/Cilistatin: Primaxin › Imipenem/Cilistatin with Relebactam: Recarbrio • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal Treats infections due to Gram +, Gram + ANAEROBES, Gram -, and Gram – ANAEROBES ALL CARBAPENEMS treat PSEUDOMONAS EXCEPT ERTAPENEM! Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase (ESBL) producers ARE covered Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o PSEUDOMONAS & ACINETOBACTER Gram -, NON Enterobacteriaceae Aerobic Rods o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus Aureus (MSSA) Gram +, aerobic o Streptococcus Gram +, aerobic o Enterococcus faecalis Gram +, aerobic o Most gram negative rods including Pseudomonas (except ertapenem) and Acinetobacter NOT Carbapenemase producers!!!! (Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE)/Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC) (except/ unless you have Relebactam) Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase (ESBL) producers ARE covered o GRAM + ANAEROBES & GRAM – ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Peptostreptococcus Gram + Anaerobic cocci Finegoldia Gram + Anaerobic cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + Anaerobic rod Closttridium perfringens Gram + Anaerobic rod Propionibacterium acnes Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacillus Gram + Anaerobic rod Bacteroids GRAM – ANAEROBES Fusobacterium GRAM – ANAEROBES Prevotella GRAM – ANAEROBES Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Penicillins= 11%- LOW Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems CELL WALL INHIBITORS Beta Lactams Monobactams Only Class: Aztreonam Brand Name: Azactam • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal GRAM – ONLY, DOES NOT COVER GRAM + OR ANAEROBES AT ALL! Route and absorption: IV ONLY • Can penetrate the CSF at high doses- so if patient has meningitis that is hospital acquired vs community acquired or at higher risk for more morbid pathogens, than this antibiotic is a good agent overall for patients to get it at a high dose • Normal dose: I gram • High dose: 2 grams IV every 8 hours to increase penetration in the CSF Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o PSEUDOMONAS Gram –, NON Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o Enterobacteriaceae Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 1. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 2. Steven Johnson Syndrome 3. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: ALL ABOUT THE SIDE CHAINS • Ceftazidime- has similar side chain structure so if patient has allergy to Ceftazidime, they could have an allergy to Aztreonam • Penicillins- Negligible Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems CELL WALL INHIBITORS Glycopeptides/Lipoglycopeptides Glycopeptide: Vancomycin Brand Name: Vancocin • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor- Glycopeptide Bactericidal Used for treating GRAM + and GRAM + ANAEROBES ONLY! Can treat MRSA ONLY ORAL form is DRUG OF CHOICE for C. DIFF Route and absorption: • IV- DOES NOT penetrate the GUT, can only PENETRATE the CSF in high concentration/doses • ORAL- has poor absorption but is the drug of choice for C. difficile because oral reaches the lumen of the gut, oral form also does absorb systemically Distribution: Distributes widely except into the lumen of the gut in IV form and into the CSF unless it high, concentrated doses Pharmacodynamics: • AUC/ MIC ratio • Trough levels (checked right before last dose is given) must be checked on patients to see if the antibiotic is in therapeutic range and if the drug is near or over toxicity level • Target levels for Vancomycin: MODERATE Infections: 10-15 mcg/ml o Skin infections o UTI SEVERE Infections: 15-20 mcg/ml o Endocarditis o Pneumonia o Sepsis o Bacteremia AREA OF POOR PENETRATION: 20 mcg/ml or higher o Brain o CSF Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)- Gram + aerobic o Clostridium Difficile (C.diff) Gram + aerobic- ORAL ONLY o Enterococcus species (EXCEPT VANCOMYCIN RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCUS) Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Streptococcus- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Streptopeptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Finegoldia Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Clostridium Perfringens Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Propionobacterium acnes Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Bacillus Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies- RARE 1. Rash 2. Hives 3. Anaphylaxis • N/V • HYPOTENSION with FLUSHING- seen with rapid IV, vanc has to have a certain rate at which it achieves to slow down to prevent hypotension & prevent dermatological response of Red Man’s Syndrome. Rule of thumb: for every 500 mg given, you have to infuse over 30 minutes… For example: a patient who gets 1500 mg of vancomycin, 30 minutes times 3 would give you 90 minutes of infusing it • Red Man/Red Neck- flushing of skin, redness all over the body- STOP INFUSION & GIVE BENADRYL. Infusion & rate related! • Phlebitis: inflammation of the vein- Vanco has a very low PH of about 4-5 and if infused over a long period, it might irritate the veins. Long term get a PICC line. • ***Renal Failure***- look at serum creatinine levels on daily basis or over 2 days- if you start seeing a trend, if the trend is going up for the serum creatinine level & patient is on vancomycin, it is good to check a level of vancomycin- CAN CAUSE ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY, especially with higher trough levels above theuropeutiic levels, longer time on the drug or when combined with piperacillin/tazobactam (zosyn) or an aminoglycoside Contraindications due to history of: • Hypersensitivity reactions Counseling Points to tell patients: • If infused report any chills, pain, swelling, redness at infusion site, red mans syndrome, or hypotension • Report any respiratory difficulty • May cause N/V, diarrhea • Report signs of other infections o Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections o Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections o Blood in the urine or stool • Report any change in urine output or serum creatinine- can be nephrotoxic & cause acute kidney injury, so check the level of the trough to see where levels are at or patient’s renal level. If nephrotoxic- the vancomycin level will be extremely high & the creatinine level will be elevated all due to the kidneys not processing the medication. Lipoglycopeptide: Telavancin Brand Name: Vibativ • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor- Lipoglycopeptide RARELY USED DUE TO MAJOR TOXIC EFFECTS Bactericidal Used for treating GRAM + and GRAM + ANAEROBES ONLY! Can treat MRSA Route and absorption: IV ONLY Distribution: Into most tissues INCLUDING THE LUNGS but the BRAIN is questionable so if patient has meningitis, you should not prescribe this Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)- Gram + aerobic o Enterococcus species (EXCEPT VANCOMYCIN RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCUS) Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Streptococcus- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Streptopeptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Finegoldia Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Clostridium Perfringens Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Propionobacterium acnes Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Bacillus Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Black Box Warnings o Increased mortality in Pneumonia patients with impaired renal function (CrCl ≤ 50 ml/min) Only use when benefit > risk o Nephrotoxicity o Teratogenicity: ability to cause defects in developing fetus Check for pregnancy prior to use Contraindications due to history of: • Hypersensitivity reactions Lipoglycopeptide: Oritavancin Brand Name: Vibativ • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor- Lipoglycopeptide RARELY USED DUE TO MAJOR TOXIC EFFECTS Bactericidal Used for treating GRAM + and GRAM + ANAEROBES ONLY! Can treat MRSA Route and absorption: IV ONLY- ***Given as a single dose over 3 hours*** Distribution: EXTENSIVELY DISTRIBUTED into MOST TISSUES- so good for CELLULITIS & SOFT SKIN TISSUE INFECTIONS, and can potentially can be used to treat infections of the brain Metabolism/Elimination: • NOT METABOLIZED • 1-5% EXCRETED in FECES & URINE after 2 WEEKS ADMINISTRATION • VERY BENEFICIAL FOR NON-COMPLIANT PATIENTS or RENAL/HEPATIC Patients because no adjustments needed for renal disorders or moderate to severe hepatic disorders Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)- Gram + aerobic o Enterococcus species (EXCEPT VANCOMYCIN RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCUS) Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Streptococcus- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Streptopeptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Finegoldia Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Clostridium Perfringens Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Propionobacterium acnes Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Bacillus Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Increased warfarin levels- look @ INR level & if INR is elevated long than it can be problematic. Pretty much all antibiotics can increase warfarin levels. We get about 30% of vit K from gut bacteria. If we kill bacteria, vitamin K goes down and INR go up even after stopping warfarin due to half-life. You have four clotting factors, 7, 9, 10 and 2 and some of them have half-life of up to 60 hours o Increased risk of bleeding • Prolonged aPTT (activated Partial Thromboplastin Time) o Artificial elevation • This is a 1-time dose medication so you can't stop the medication once it is given, so if patient is on warfarin, then this medication should not be prescribed because it can cause an increased risk of bleeds Contraindications due to history of: • Hypersensitivity reactions Lipoglycopeptide: Dalbavancin Brand Name: Dalvance • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor- Lipoglycopeptide RARELY USED DUE TO MAJOR TOXIC EFFECTS Bactericidal Used for treating GRAM + and GRAM + ANAEROBES ONLY! Can treat MRSA Route and absorption: IV ONLY Distribution: achieves ADEQUATE SKIN & SOFT TISSUE infections, however, the lung and brain are questionable Elimination: RENAL Elimination 33%- Dose adjust for renal impairment in patients with a creatine clearance < 30ml/min (moderate kidney disease: 30-59 ml/min) Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)- Gram + aerobic o Enterococcus species (EXCEPT VANCOMYCIN RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCUS) Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Streptococcus- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Streptopeptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Finegoldia Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Clostridium Perfringens Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Propionobacterium acnes Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Bacillus Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • Infusion related reactions- slow infusion rate • ALT elevations- hepatic enzyme elevations Contraindications due to history of: Hypersensitivity reactions CELL WALL INHIBITORS Lipopeptides Lipopeptide: Daptomycin Brand Name: Cubicin • • • • • Cell wall inhibitor- Lipopeptide Bactericidal Used for treating GRAM + Can treat MRSA/MRSE INACTIVATED BY LUNG SURFACTANT- NOT GOOD TO USE FOR PNEUMONIA Route and absorption: IV ONLY Distribution: Highly protein bound, distributes to most sites- Good for bacteremia MRSA or soft skin tissue infection. • Inactivated by surfactant in the lungs- DO NOT use for respiratory infections like pneumonia, COPD. So can penetrate the lungs but the lungs surfactant inactivates it Elimination: RENAL 60%- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)- Gram + aerobic o Clostridium Difficile (C.diff) Gram + aerobic- ORAL ONLY o Enterococcus species (EXCEPT VANCOMYCIN RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCUS) Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Streptococcus- Gram + aerobic- IV ONLY o Corynebacterium Gram + aerobic o Gram + ANAEROBES Peptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Streptopeptococcus Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Finegoldia Gram + ANAEROBIC cocci Clostridium difficile Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Clostridium Perfringens Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Propionobacterium acnes Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Bacillus Gram + ANAEROBIC rod Adverse Drug Reactions: • N/ V/ D • Constipation • Chest Pain • Rash • Myalgia: muscle pain • Can include severe reactions CPK levels recommended- CPK and CK due muscle breakdown or rhabdomyolysis. Muscle breakdown is bad for kidneys. The myoglobin gums up the kidney Contraindications due to history of: • Hypersensitivity reactions • NOT FOR USE IN PATIENTS WITH PNEUMONIA- antibiotic will be broken down and inactivated by surfactant in the lung Counseling Points to tell patients: • Report any burning, pain or redness at infusion site • Report any throat tightness or difficulty breathing • Report persistent GI upset • Report any skin rash, hives etc. • Report any new or unusual muscle pain or tingling in the extremities • Darkened urine (because of myoglobin) because drug can cause myalgia PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS Macrolides Macrolides: Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clasrithromycin Brand Names: Azactam • • • Cell wall inhibitor Bactericidal GRAM – ONLY, DOES NOT COVER GRAM + OR ANAEROBES AT ALL! Route and absorption: IV ONLY Pharmacodynamics: Time above MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)- If the drug level is kept above the MIC of the organism for 50% of the dosing interval (or longer) better killing is observed and a post antibiotic effect occurs- even after the drug is out of the system, there still is bacterial killing. Elimination: RENAL- need to dose adjust for renally impaired patients, smaller dose than given normally as well as a longer dosing interval Treatment: • Mainly used for/ against: o PSEUDOMONAS o Enterobacteriaceae Gram – aerobic rods E coli Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Klebsiella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Enterobacteriaceae species Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Proteus Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Citrobacter Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Salmonella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Serratia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Shigella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Morganella Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod Providencia Gram –, Enterobacteriaceae, aerobic rod o H. influenzae Gram -, Aerobic cocci o Moraxella Gram –, aerobic cocci o Neisseria Gram -, aerobic cocci Adverse Drug Reactions: • Allergies 4. ranging from rash to anaphylaxis 5. Steven Johnson Syndrome 6. Allergic/acute interstitial reaction • Neutropenia- low neutrophil count • N/V/D- with oral intake • Super infections 1. C. diff 2. Yeast infections of the mouth and genital area 3. UTI Cross Reactivity with other drugs: • Cephalosporins – LOW a) 1st generation= 1-10% b) 2nd generation-5th generation= <0.1% • Carbapenems= 11%- LOW • Aztreonam- NEGLIGIBLE Contraindications due to history of: • Allergic reactions- N/V/D is not a “true” allergy • Acute interstitial nephritis • Seizure disorders or renal impairment- especially if patient had a seizure with a carbapenem antibiotic • Adverse events- leukopenia Counseling Points to tell patients: • May cause N/V/D • Report rash, breathing or swallowing difficulty • Report persistent diarrhea such as c. diff- these antibiotics can kill off normal flora in the stomach that can lead to C. diff • Report changes in urinary pattern- ADR of acute interstitial nephritis • Report signs of other infections Vaginal Itching- can lead to fungal infections Sores in the mouth- can lead to fungal infections Blood in the urine or stool- could be a c.diff • Report any CNS changes- specifically seizures and carbapenems