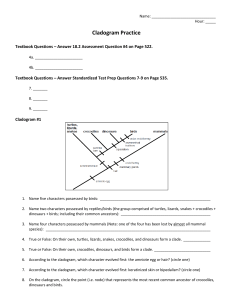
Name ___________________________________________________________________________________ Per __________ CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships. Sometimes a cladogram is called a phylogenetic tree (though technically, there are minor differences between the two). In the past, biologists would group organisms based solely on their physical appearance. Today, with the advances in genetics and biochemistry, biologists can look more closely at individuals to discover their pattern of evolution, and group them accordingly - this strategy is called EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION CLADISTICS is form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called DERIVED CHARACTERS. PART I - Analyze the Cladogram Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character. Note: this cladogram was created for simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives. 1. ______ Wings 2. ______ 6 Legs 3. ______ Segmented Body 4. ______ Double set of wings 5. ______ Jumping Legs 6. ______ Crushing mouthparts 7. ______ Legs 8. ______ Curly Antennae PART II - Create Your Own Cladogram To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, if the characteristic is present, place a (1) in the box. If the characteristic is not present, place a (0) in the box. Based on that chart, create a cladogram like the one pictured above. DRAWING OF YOUR CLADOGRAM: Cells Slug Catfish Frog Tiger Human Backbone Legs Hair Opposable Thumbs CLADOGRAM PRACTICE Use this cladogram to answer the questions below. birds dinosaurs crocodiles turtles, lizards, snakes mammals 11 10 9 amphibians 8 6 fish 5 7 4 3 2 ?? Key: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. vertebrate tetrapod amniotic egg hair or fur produces milk warm blooded scaly skin parental care bipedalism asymmetrical feathers warm-blooded (avian) 1 1. According to the cladogram, what characteristic do all of these organisms have in common? _______________________ 2. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of birds? ______ a. amniotic egg b. scaly skin c. hair or fur d. parental care e. tetrapod 3. What organism is the closest relative to birds? ___________________________________ 4. What characteristic(s) do crocodiles and mammals share? ___________________________________________ 5. What derived character distinguishes crocodiles from lizards? ____________________________________________ 6. What characteristics are common only to mammals? ____________________________________________________ 7. Which derived character(s) distinguishes birds and dinosaurs? _____________________________________________ 8. What derived character(s) do fish and amphibians share? __________________________________________________ 9. Who is more closely related… birds and crocodiles or birds and amphibians? Explain. ___________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. What type of organism would fit best in the box with the question marks? Explain what trait it would have. __________________________________________________________________________________________________