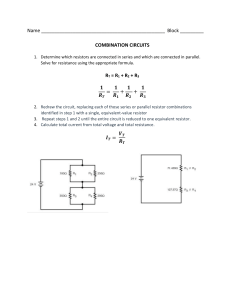
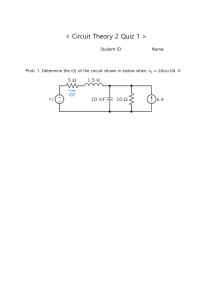
Basic Electrical Engineering & A.C. Fundamentals, Circuits and Circuit Theory 1. The power consumed in a circuit element will be least when the phase difference between the current and voltage is (A) 180° (https://www.objectivebooks.com/) (B) 90° (C) 60° (D) 0° 2. Form Factor is the ratio of (A) Average value/r.m.s. value (B) Average value/peak value (C) r.m.s. value/average value (D) r.m.s. value/peak value 3. Capacitive reactance is more when (A) Capacitance is less and frequency of supply is less (B) Capacitance is less and frequency of supply is more (C) Capacitance is more and frequency of supply is less (D) Capacitance is more and frequency of supply is more 4. Pure inductive circuit (A) Consumes some power on average (B) Does not take power at all from a line (C) Takes power from the line during some part of the cycle and then returns back to it during other part of the cycle (D) None of the above 5. Power factor of the following circuit will be zero (A) Resistance (B) Inductance (C) Capacitance (D) Both (B) and (C) 6. The double energy transient occur in the (A) Purely inductive circuit (B) R-L circuit (C) R-C circuit (D) R-L-C circuit 7. In any A.C. circuit always (A) Apparent power is more than actual power (B) Reactive power is more than apparent power (C) Actual power is more than reactive power (D) Reactive power is more than actual power 8. Magnitude of current at resonance in R-L-C circuit (A) Depends upon the magnitude of R (B) Depends upon the magnitude of L (C) Depends upon the magnitude of C (D) Depends upon the magnitude of R, Land C 9. The safest value of current the human body can carry for more than 3 second is (A) 4 mA (B) 9 mA (C) 15 mA (D) 25 mA 10. The purpose of a parallel circuit resonance is to magnify (A) Current (B) Voltage (C) Power (D) Frequency The power is measured in terms of decibels in case of (A) Electronic equipment (B) Transformers (C) Current transformers (D) Auto transformers 2. Wire-wound resistors are unsuitable for use at high frequencies because they (A) Create more electrical noise (B) Are likely to melt under excessive eddy current heat (C) Consume more power (D) Exhibit unwanted inductive and capacitive effects 3. The product of apparent power and cosine of the phase angle between circuit voltage and current is (A) True power (B) Reactive power (C) Volt-amperes (D) Instantaneous power 4. In a series resonant circuit, the impedance of the circuit is (A) Minimum (B) Maximum (C) Zero (D) None of the above 5. In series resonant circuit, increasing inductance to its twice value and reducing capacitance to its half value (A) Will change the maximum value of current at resonance (B) Will change the resonance frequency (C) Will change the impedance at resonance frequency (D) Will increase the selectivity of the circuit 6. In a loss-free R-L-C circuit the transient current is (A) Oscillating (B) Square wave (C) Sinusoidal (D) Non-oscillating 7. In a circuit containing R, L and C, power loss can take place in (A) C only (B) L only (C) R only (D) All above 8. Time constant of a capacitive circuit (A) Increases with the decrease of capacitance and decrease of resistance (B) Increases with the decrease of capacitance and increase of resistance (C) Increases with the increase of capacitance and decrease of resistance (D) Increase with increase of capacitance and increase of resistance 9. The effective resistance of an iron-cored choke working on ordinary supply frequency is more than its true resistance because of (A) Iron loss in core (B) Skin effect (C) Increase in temperature (D) Capacitive effect between adjacent coil turns 10. Skin effect occurs when a conductor carries current at _________ frequencies. (A) Very low (B) Low (C) Medium (D) High The apparent power drawn by an A.C. circuit is 10 kVA and active power is 8 kW. The reactive power in the circuit is (A) 4 kVAR (B) 6 kVAR (C) 8 kVAR (D) 16 kVAR 2. In a sine wave the slope is constant (A) Between 0° and 90° (B) Between 90° and 180° (C) Between 180° and 270° (D) No where 3. The r.m.s. value of pure cosine function is (A) 0.5 of peak value (B) 0.707 of peak value (C) Same as peak value (D) Zero 4. In a pure capacitive circuit if the supply frequency is reduced to 1/2, the current will (A) Be reduced by half (B) Be doubled (C) Be four times at high (D) Be reduced to one fourth 5. Capacitors for power factor correction are rated in (A) kW (B) kVA (C) kV (D) kVAR 6. The reactance offered by a capacitor to alternating current of frequency 50 Hz is 20 Q. If frequency is increased to 100 Hz, reactance becomes __________ ohms. (A) 2.5 (B) 5 (C) 10 (D) 15 7. For the same peak value which of the following wave will 'have the highest r.m.s. value? (A) Square wave (B) Half wave rectified sine wave (C) Triangular wave (D) Sine wave 8. The r.m.s. value of a sinusoidal A.C. current is equal to its value at an angle of ________ degrees. (A) 90 (B) 60 (C) 45 (D) 30 9. Power factor of an inductive circuit is usually improved by connecting capacitor to it in (A) Parallel (B) Series (C) Either (A) or (B) (D) None of the above 10. In the case of an unsymmetrical alternating current the average value must always be taken over (A) Unsymmetrical part of the wave form (B) The quarter cycle (C) The half cycle (D) The whole cycle 1) In a series L-C circuit at the resonant frequency the (A) Current is maximum (B) Current is minimum (C) Impedance is maximum (D) Voltage across C is minimum 2. A pure inductance connected across 250 V, 50 Hz supply consumes 100 W. This consumption can be attributed to (A) The big size of the inductor (B) The reactance of the inductor (C) The current flowing in the inductor (D) The statement given is false 3. In a parallel R-C circuit, the current always _________the applied voltage (A) Lags (B) Leads (C) Remains in phase with (D) None of the above 4. In a three-phase supply floating neutral is undesirable because it way give rise to (A) High voltage across the load (B) Low voltage across the load (C) Unequal line voltages across the load (D) None of these 5. An A.C. voltage is impressed across a pure resistance of 3.5 ohms in parallel with a pure inductance of impedance of 3.5 ohms, (A) The current through the resistance is more (B) The current through the resistance is less (C) Both resistance and inductance carry equal currents (D) None of the above 6. Inductance affects the direct current flow (A) Only at the time of turning off (B) Only at the time of turning on (C) At the time of turning on and off (D) At all the time of operation 7. The time constant of the capacitance circuit is defined as the time during which voltage (A) Falls to 36.8% of its final steady value (B) Rises to 38.6% of its final steady value (C) Rises to 63.2% of its final steady value (D) None of the above 8. Power factor of electric bulb is (A) Zero (B) Lagging (C) Leading (D) Unity 9. If a sinusoidal wave has frequency of 50 Hz with 30 A r.m.s. current which of the following equation represents this wave? (A) 42.42 sin 314 t (B) 60 sin 25 t (C) 30 sin 50 t (D) 84.84 sin 25 t 10. Capacitive susceptance is a measure of (A) Reactive power in a circuit (B) The extent of neutralization of reactive power in a circuit (C) A purely capacitive circuit's ability to pass current (D) A purely capacitive circuit's ability to resist the flow of current 1. All definitions of power factor of a series R-L-C circuit are correct except (A) Ratio of net reactance and impedance (B) Ratio of kW and kVA (C) Ratio of J and Z (D) Ratio of W and VA 2. Ohm is unit of all of the following except (A) Inductive reactance (B) Capacitive reactance (C) Resistance (D) Capacitance 3. If two sinusoids of the same frequency but of different amplitudes and phase angles are subtracted, the resultant is (A) A sinusoid of the same frequency (B) A sinusoid of half the original frequency (C) A sinusoid of double the frequency (D) Not a sinusoid 4. Form factor for a sine wave is (A) 1.414 (B) 0.707 (C) 1.11 (D) 0.637 5. All the rules and laws of D.C. circuit also apply to A.C. circuit containing (A) Capacitance only (B) Inductance only (C) Resistance only (D) All above 6. In R-L-C series resonant circuit magnitude of resonance frequency can be changed by changing the value of (A) R only (B) L only (C) C only (D) L or C 7. In an A.C. circuit power is dissipated in (A) Resistance only (B) Inductance only (C) Capacitance only (D) None of the above 8. The r.m.s. value of half wave rectified sine wave is 200 V. The r.m.s. value of full wave rectified AC. will be (A) 282.8 V (B) 141.4 V (C) 111 V (D) 100 V 9. The voltage of domestic supply is 220 V. This figure represents (A) Mean value (B) r.m.s. value (C) Peak value (D) Average value 10. The transient currents are associated with the (A) Changes in the stored energy in the inductors and capacitors (B) Impedance of the circuit (C) Applied voltage to the circuit (D) Resistance of the circuit 1. The apparent power drawn by an A.C. circuit is 10 kVA and active power is 8 kW. The reactive power in the circuit is (A) 4 kVAR (B) 6 kVAR (C) 8 kVAR (D) 16 kVAR 2. In a sine wave the slope is constant (A) Between 0° and 90° (B) Between 90° and 180° (C) Between 180° and 270° (D) No where 3. The r.m.s. value of pure cosine function is (A) 0.5 of peak value (B) 0.707 of peak value (C) Same as peak value (D) Zero 4. In a pure capacitive circuit if the supply frequency is reduced to 1/2, the current will (A) Be reduced by half (B) Be doubled (C) Be four times at high (D) Be reduced to one fourth 5. Capacitors for power factor correction are rated in (A) kW (B) kVA (C) kV (D) kVAR 6. The reactance offered by a capacitor to alternating current of frequency 50 Hz is 20 Q. If frequency is increased to 100 Hz, reactance becomes __________ ohms. (A) 2.5 (B) 5 (C) 10 (D) 15 7. For the same peak value which of the following wave will 'have the highest r.m.s. value? (A) Square wave (B) Half wave rectified sine wave (C) Triangular wave (D) Sine wave 8. The r.m.s. value of a sinusoidal A.C. current is equal to its value at an angle of ________ degrees. (A) 90 (B) 60 (C) 45 (D) 30 9. Power factor of an inductive circuit is usually improved by connecting capacitor to it in (A) Parallel (B) Series (C) Either (A) or (B) (D) None of the above 10. In the case of an unsymmetrical alternating current the average value must always be taken over (A) Unsymmetrical part of the wave form (B) The quarter cycle (C) The half cycle (D) The whole cycle 1. For the same peak value, which of the following wave has the least mean value? (A) Half wave rectified sine wave (B) Triangular wave (C) Sine wave (D) Square wave 2. The phase difference between voltage and current wave through a circuit element is given as 30°. The essential condition is that (A) Both waves must have same frequency (B) Both waves must have identical peak values (C) Both waves must have zero value at the same time (D) None of the above 3. The square waveform of current has following relation between r.m.s. value and average value. (A) r.m.s. value is equal to average value (B) r.m.s. value of current is greater than average value (C) r.m.s. value of current is less than average value (D) None of the above 4. Time constant of an inductive circuit (A) Increases with increase of inductance and decrease of resistance (B) Increases with the increase of inductance and the increase of resistance (C) Increases with the decrease of inductance and decrease of resistance (D) Increases with decrease of inductance and increase of resistance 5. In AC. circuits, laminated iron is invariably used in order to (A) Reduce eddy current loss (B) Increase heat radiation (C) Make assembly cheap and easier (D) Reduce circuit permeability 6. At __________ frequencies the parallel R-L circuit behaves as purely resistive. (A) Low (B) Very low (C) High (D) Very high 7. When an alternating current passes through an ohmic resistance the electrical power converted into heat is (A) Apparent power (B) True power (C) Reactive power (D) None of the above 8. Power factor of an electrical circuit is equal to (A) R/Z (B) Cosine of phase angle difference between current and voltage (C) Ratio of useful current to total current Iw/I (D) All above 9. In a purely inductive circuit (A) Actual power is zero (B) Reactive power is zero (C) Apparent power is zero (D) None of above is zero 10. Time constant of an inductive circuit (A) Increases with increase of inductance and decrease of resistance (B) Increases with the increase of inductance and the increase of resistance (C) Increases with decrease of inductance and decrease of resistance (D) Increases with decrease of inductance and increase of resistance 1. The peak value of a sine wave is 200 V. Its average value is (a) 127.4 V (b) 141.4 V (c) 282.8 V (d)200V Ans: a 2. Two waves of the same frequency have opposite phase when the phase angle between them is (a) 360° (b) 180° (c) 90° (d) 0° Ans: b 3. The power consumed in a circuit element will be least when the phase difference between the current and voltage is (a) 180″ (b) 90° (c) 60° (d) 0° Ans: b 4. The phase difference between voltage and current wave through a circuit element is given as 30°. The essential condition is that (a) both waves must have same frequency (b) both waves must have identical peak values (c) both waves must have zero value at the same time (d) none of the above Ans: a 5. The best place to install a capacitor is (a) very near to inductive load (b) across the terminals of the inductive load (c) far away from the inductive load (d) any where Ans: b 6. Pure inductive circuit (a) consumes some power on average (b) does not take power at all from a line (c) takes power from the line during some part of the cycle and then returns back to it during other part of the cycle (d) none of the above Ans: c 7. Inductance affects the direct current flow (a) only at the time of turning off (b) only at the time of turning on (c) at the time of turning on and off (d) at all the time of operation Ans: c AC Fundamentals 8. Power factor of the system is kept high (a) to reduce line losses (b) to maximise the utilization of the capacities of generators, lines and transformers (c) to reduce voltage regulation of the line (d) due to all above reasons Ans: d 9. In a loss-free R-L-C circuit the transient current is (a) oscillating (b) square wave (c) sinusoidal (d) non-oscillating Ans: c 10. The r.m.s. value of alternating current is given by steady (D.C.) current which when flowing through a given circuit for a given time produces (a) the more heat than produced by A.C. when flowing through the same circuit (b) the same heat as produced by A.C. when flowing through the same circuit (c) the less heat than produced by A.C. flowing through the same circuit (d) none of the above Ans: b 11. The double energy transient occur in the (a) purely inductive circuit (b) R-L circuit (c) R-C circuit (d) R-L-C circuit Ans: d 12. In the case of an unsymmetrical alternating current the average value must always be taken over (a) unsymmetrical part of the wave form (b) the quarter cycle (c) the half cycle (d) the whole cycle Ans: d 13. Pure inductive circuit takes power from the A.C. line when (a) applied voltage decreases but current increases (b) applied voltage increases but current decreases (c) both applied voltage and current increase (d) both applied voltage and current decrease Ans: a 14. In a R-L-C circuit (a) power is consumed in resistance and is equal to I R (b) exchange of power takes place between inductor and supply line (c) exchange of power takes place between capacitor and supply line (d) exchange of power does not take place between resistance and the supply line (e) all above are correct Ans: e 15. The time constant of a series R-C circuit is given by (a) R/C (b) RC2 (c) RC (d) R2C Ans: c 16. The safest value of current the human body can carry for more than 3 second is (a) 4 mA (b) 9 mA (c) 15 mA (d) 25 mA Ans: b 17. The apparent power drawn by an A.C. circuit is 10 kVA and active power is 8 kW. The reactive power in the circuit is (a) 4 kVAR (b) 6 kVAR (c) 8 kVAR (d) 16 kVAR Ans: b 18. A phasor is (a) a line which represents the magnitude and phase of an alternating quantity (b) a line representing the magnitude and direction of an alternating quantity (c) a coloured tag or band for distinction between different phases of a 3-phase supply (d) an instrument used for measuring phases of an unbalanced 3-phase load Ans: a 19. Wire-wound resistors are unsuitable for use at high frequencies because they (a) create more electrical noise (b) are likely to melt under excessive eddy current heat (c) consume more power (d) exhibit unwanted inductive and capacitive effects Ans: d 20. A pure capacitor connected across an A.C. voltage consumed 50 W. This is due to (a) the capacitive reactance in ohms (b) the current flowing in capacitor (c) the size of the capacitor being quite big (d) the statement is incorrect Ans: d B. Coulomb C. Watt D. Watt-hour (https://www.mechanicaltutorial.com) 1. In gases the flow of current is due to A. Electrons only B. Positive ions only C. Electrons and positive ions D. Electrons, positive ions and negative ions 9. Temperature coefficient of resistance is expressed in terms of A. Ohms/oC B. Mhos/ohmoC C. Ohms/ohmoC D. Mhos/oC 2. The flow of current in solids is due to A. Electrons B. Electrons and ions C. Atoms D. Nucleus 10. One newton metre is same as A. One watt B. 1 joule C. 5 joules D. 1 joule/sec 3. The minimum requirements for causing flow of current are A. A voltage source, a resistor and a switch B. A voltages source and a conductor C. A power source and a bulb D. A voltage source, a conductor an ammeter and a switch 11. Which of the following materials has the least resistivity? A. Zinc B. Lead C. Mercury D. Copper 4. An instrument which detects electric current is known as A. Voltmeter B. Rheostat C. Wattmeter D. Galvanometer 12. Which of the following can have negative temperature coefficient ? A. Compounds of silver B. Liquid metals C. Metallic alloys D. Electrolytes 5. Electric pressure is also called A. Resistance B. Power C. Voltage D. Energy 13. Which of the following method can be used for absolute measurement of resistance? A. Lorentz method B. Releigh method C. Ohm's law method D. Wheatstone bridge method 6. Which of the following ampere-second could be the unit? A. Reluctance B. Charge C. Power D. Energy 14. Which of the following does not have negative temperature co-efficient ? A. Aluminium B. Paper C. Rubber D. Mica 7. The rating of the fuse wire is always expressed in A. Ampere-hours B. Ampere-volts C. KWH D. Ampere 15. Which is the best conductor of electricity? A. Iron B. Silver C. Copper D. Carbon 8. The S.I. unit of power is A. Henry 16. The filament of an electric bulb is made of A. Carbon B. Aluminium C. Tungsten D. Nickel B. Decreases C. First increases and then decreases D. Remains constant 17. Which of the following materials has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance? A. Copper B. Aluminium C. Carbon D. Brass 25. The property of the conductor due to which it passes current is called A. Resistance B. Reluctance C. Conductance D. Inductance 18. Which of the following material has nearly zero temperature coefficient of resistance? A. Manganin B. Porcelain C. Carbon D. Copper 26. Resistance of a wire always increases if A. Temperature is reduced B. Temperature is increased C. Number of free electrons available become less D. Number of free electrons available become more 19. The substance which have a large number of free electrons and offer a resistance are called A. Insulators B. Inductors C. Semiconductors D. Conductors 27. Pure metals generally have A. High conductivity and low temperature coefficient B. High conductivity and large temperature coefficient C. Low conductivity and zero temperature coefficient D. Low conductivity and high-temperature coefficient 20. The resistance of human body is around A. 50 Ohms B. 25 Ohmes C. 250 Ohms D. 1000 Ohm's 28. The temperature coefficient of resistance of an insulator is A. Positive and independent of temperature B. Negative and independent of temperature C. Negative and dependent on temperature D. Positive and dependent on temperature 21. 1 Coulomb charge equals the charge on A. 6.24 x 1012 electrons B. 6.24 x 1014 electrons C. 6.24 x 1016 electrons D. 6.24 x 1018 electrons 29. Specific resistance of a conductor depends upon A. Dimensions of the conductor B. Composition of contactor material C. Resistance of the conductor D. Both A and B 22. The resistance of a conductor varies inversely as A. Length B. Area of cross-section C. Temperature D. Resistivity 30. Which of the following materials posses the least specific resistance? A. Aluminium B. Copper C. Silver D. Iron 23. With rise in temperature the resistance of pure metals A. Increases B. Decreases C.. First increases and then decreases D. Remains constant 31. A closed switch has a resistance of A. Zero B. About 50 ohms C. About 500 ohms D. Infinity 24. With the rise in temperature the resistance of semiconductors A. Increases 32. Who in one leg of parallel circuit is opened out the total current will A. Reduce B. Increase C. Decrease D. Become zero 33. Which of the following quantities remain the same in all parts of a series circuit? A. Voltage B. Current C. Power D. Resistance 34. Heat in a conductor is produced on the passage of electric current due to A. Reactance B. Capacitance C. Impedance D. Resistance 35. The insulation on a current carrying conductor is provided A. To prevent leakage of current B. To prevent a shock C. Both of the above D. None of the above 36. A field of force can exist only between A. Two molecules B. Two ions C. Two atoms D. Two metal particles 37. Balbs in street lighting are all connected in A. Parallel B. Series C. Series-parallel D. End to end 38. Sparking occurs when a load is switched off because the circuit has high A. Resistance B. Inductance C. Capacitance D. Impedance 39. Three 6 ohms resistors are connected to from a triangle. What is the resistance between any two corners? A. 3/2 ohm B. 6 ohm C. 4 ohm D. 8/3 ohm 40. Voltage dependent resistors are usually made from A. Charcoal B. Silicon carbide C. Nichrome D. Graphite 41. Two resistors are set to be connected in series when A. Same current passes in turn through body B. Both carry the same value of current C. Total current equals the sum of branch currents D. Some of I.R. drops equal the applied e.m.f. 42. Varistors are A. Insulators B. Non-linear resisters C. Carbon resistors D. Resisters with zero temperature coefficient 43. Insulating materials have the function of A. Preventing a short circuit between conducting wire B. Preventing an open circuit between the voltage source and the load C. Conducting very large currents D. Storing very high currents 44. The minimum charge of an ion is A. Equal to the atomic number of the atom B. Equal to the charge of an electron C. Equal to the charge of the number of electrons in an atom D. Zero 45. If the efficiency of a machine is to be high, what should be low? A. Input power B. Losses C. Ratio of output to input D. All of the above 46. For testing appliances, the wattage of test lamp should be A. Very low B. Low C. High D. Any value 47. In the case of direct current A. Magnitude and direction of current remains constant B. Magnitude and direction of current changes with time C. Magnitude of current changes with time D. Magnitude of current remains constant 48. Voltage dependent resistors are used A. For inductive circuits B. To suppress surges C. An heating elements D. As current stabilizers 49. Which of the following could be the value of resistivity of copper ? A. 1.72 × 10-4 Ω-m B. 1.72 × 10-9 Ω-m C. 1.72 × 10-6 Ω-m D. 1.72 × 10-8 Ω-m 50. Specific resistance of a substance is measured in A. Ω/m B. Ω/m2 C. Ω-m D. m/Ω 1. Ohm's law is applicable to A. Semiconductors B. Vacuum tubes C. Carbon resistors D. None of these 2. The condition for the validity of Ohm's law is that the A. Temperature should remain constant B. Current should be proportional to voltage C. Resistance must be wire wound type D. All of the above 3. Ohm's law is not applicable to A. Semiconductors B. D.C. circuits C. Small resistors D. High currents 4. Correct form of ohm's law A. I = VR B. V ∝ I C. V = IR D. Above B and C 5. Ohm's law in point form in field theory can be expressed as A. V = RI B. J = E/σ C. J = σE D. R = ρl/A 7. International ohm is defined in terms of the resistance of A. A column of mercury B. A cube of carbon C. A cube of copper D. The unit length of wire 8. Resistance of carbon filament lamp.........as the applied voltage increases. A. Increases B. Decreases C. Remains same D. None of the above 8. Four 100 W bulbs are connected in parallel across 200 V supply line. If one bulb gets fused A. No bulb will light B. All the four bulbs will light C. Rest of three bulbs will light D. Above B and C 9. Two incandescent light bulbs of 40 W and 60 W ratings are connected in series across the mains. Then A. The bulbs together consume 100 W B. The bulbs together consume 50 W C. The 60 W bulb glows brighter D. The 40 W bulb glows brighter 1. Which of the following elements of electrical engineering cannot be analyzed using Ohm’s law? a) Capacitors (https://www.sanfoundry.com) b) Inductors c) Transistors d) Resistance 2. What is constant for a charged spherical shell according to basic electrical energy? a) Electrical potential outside the spherical shell b) Electrical potential inside the spherical shell c) Electrical field outside the spherical shell d) Electrical field inside the spherical shell 3. Where does electro-static shielding occur in a charged spherical shell? a) When electrical potential outside spherical shell is zero b) When electrical potential inside the spherical shell is zero c) When electrical field outside the spherical shell d) Electrical field inside the spherical shell 4. According to the fundamentals of electrical engineering, which of these is a correct representation of peak value in an AC Circuit? a) RMS value/Peak factor b) RMS value*Form factor c) RMS value/Form factor d) RMS value*Peak factor 5. Which of these according to fundaments of electrical energy is correct about alternating current? a) Frequency is zero b) Magnitude changes with time c) Can be transported to larger distances with less loss in power d) Flows in both directions 6. How many cycles will an AC signal make in 2 seconds if its frequency is 100 Hz? a) 50 b) 100 c) 150 d) 200 7. What will be the direction of the drift velocity of electrons change with respect to the electric field? a) same as that of electric field b) opposite to that of electric field c) perpendicular to that of the electric field in positive direction d) perpendicular to that of the electric field in negative direction 8. What will be the current density of metal if a current of 30A is passed through a cross-sectional area of 0.5m2? a) 7.5 A/m2 b) 15 A/m2 c) 60 A/m2 d) 120 A/m2 9. Which of the following is correct about the power consumed by R1 and R2 connected in series if the value of R1 is greater than R2? a) R1 will consume more power b) R2 will consume more power c) R1 and R2 will consume the same power d) The relationship between the power consumed cannot be established 10. According to electrical engineering, what is zero for a charged spherical shell? a) Electrical potential outside the spherical shell b) Electrical potential inside the spherical shell c) Electrical field outside the spherical shell d) Electrical field inside the spherical shell 11. What kind of quantity is an Electric potential? a) Vector quantity b) Tensor quantity c) Scalar quantity d) Dimensionless quantity 12. In the fundamentals of electrical engineering, what do crowded lines of force indicate? a) Strong electric field b) Weak electric field c) Strong electric potential d) Weak electric potential 13. What is the direction of the electric field at a point? a) Along the line perpendicular to the electric field b) Along the line tangent to the electric field c) Electric field has no direction d) Electric field has a random direction 14. What is the magnitude of mutually induced emf, E2 in a transformer? a) directly proportional to rate of change of flux and number of secondary turns b) inversely proportional to rate of change of flux and number of secondary turns c) proportional to rate of change of flux and inversely proportional to number of secondary turns d) inversely proportional to rate of change of flux and proportional to number of secondary turns 15. Which of these will happen in a transformer when the number of secondary turns is less than the number of primary turns? a) The voltage gets stepped up b The voltage gets stepped down c) The power gets stepped up d) The power gets stepped down 16. What is the number of primary turns in a 200/1000 V transformer if the emf per turn is 10V? a) 5 b) 10 c) 20 d) 40 17. What is the equivalent resistance of the primary of a transformer with a voltage transformation ratio of 10 and primary resistance of 0.05Ω when referred to secondary? a) 0.005 b) 0.5 c) 5 d) 50 18. Who defined electric current and devised a method to measure current? a) Michael Faraday b) Andre-Marie Ampere c) Nikola Tesla d) Alessandro Antonio Volta 19. How many electrons will constitute 2 Coulombs of charge? a) 6.24 * 1018 electrons b) 12.48 * 1018 electrons c) 1.602 * 1019 electrons d) 3.204 * 1019 electrons 20. What is the number of branches in a circuit with three nodes and three loops? a) 4 b) 5 c) 6 d) 7 21. Who witnessed the effect of magnetism for the first time? a) Hans Christian Orsted b) Alexander Graham Bell c) Michael Faraday d) Gustav Robert Kirchhoff 22. Which of the following according is correct about electrical conductivity? a) It is the ratio of current density to the electric field b) It is the product of current density and electric field c) It is the ratio of the electric field to current density d) It is the reciprocal of the product of current density and electric field 23. What is responsible for the current to flow? a) Protons b) Electrons c) Nucleus d) Protons and Electrons 24. Which of the following according to KCL must be zero? a) Algebraic sum of currents in closed-loop b) Algebraic sum of power in closed-loop c) Algebraic sum of currents entering and leaving a junction d) Algebraic sum of voltages across the input and output 25. How many directions can the electric field at a point have? a) Zero b) One c) Two d) Many 26. Which of the following will happen in a transformer when the number of secondary turns is greater than the number of primary turns? a) The voltage gets stepped up b) The voltage gets stepped down c) The power gets stepped up d) The power gets stepped down 27. Which of the following is correct about the voltage transformation ratio in electrical engineering? a) Ratio of number of primary turns to the number of secondary turns b) Ratio of induced emf in secondary to induced emf in primary c) Ratio of secondary current to the primary current d) Ratio of power in primary to power in secondary 28. Which of the following according to the fundamentals of electrical engineering is correct about the induced emf in primary of transformer? a) It is the ratio of primary turns to emf induced per turn b) It is the product of primary turns and emf induced per turn c) It is the ratio of secondary turns to emf induced per turn d) It is the product of secondary turns and emf induced per turn 29. In fundamentals of electrical engineering, what current is drawn by the primary circuit of an ideal transformer when the secondary is open? a) Secondary current b) Leakage current c) Magnetizing current d) Working current 30. What does positive power in an electrical element indicate in the fundamentals of electrical energy? a) Element is absorbing power b) Element is supplying power c) Element may absorb or supply power d) Element is neither absorbing nor supplying power 31. How does induce emf in DC motor react to supply voltage? a) It will aid the supply voltage b) It will be double the supply voltage c) It will oppose the supply voltage d) It will be half of the supply voltage 32. Which of the following type of circuits in electrical engineering cannot be analyzed using Ohm’s law? a) Unilateral b) Bilateral c) Linear d) Conductors 33. Which of the following according to KVL in Fundamentals of electrical engineering must be zero? a) Algebraic sum of currents in closed-loop b) Algebraic sum of power in closed-loop c) Algebraic sum of losses in closed-loop d) Algebraic sum of voltages in closed-loop 34. Which of the following is a correct representation of average value in an AC Circuit? a) RMS value/Form factor b) RMS value*Form factor c) RMS value/Peak factor d) RMS value*Peak factor 35. Which of the following is correct about direct current? a) Magnitude is constant b) Frequency is zero c) Can be transported to larger distances with less loss in power d) Flows in one direction 36. How will the drift velocity of electrons change with the electric field? a) Increases with increase in the electric field b) Decreases with increase in the electric field c) Remains same with a decrease in the electric field d) Increases with a decrease in the electric field Series - Parallel Networks In a series circuit, which of the parameters remain constant across all circuit elements such as resistor, capacitor and inductor etcetera? a) Voltage b) Current c) Both voltage and current d) Neither voltage nor current If there are two bulbs connected in series and one blows out, what happens to the other bulb? a) The other bulb continues to glow with the same brightness b) The other bulb stops glowing c) The other bulb glows with increased brightness d) The other bulb also burns out A voltage across a series resistor circuit is proportional to? a) The amount of time the circuit was on for b) The value of the resistance itself c) The value of the other resistances in the circuit d) The power in the circuit Many resistors connected in series will? a) Divide the voltage proportionally among all the resistors b) Divide the current proportionally c) Increase the source voltage in proportion to the values of the resistors d) Reduce the power to zero What is the voltage measured across a series short? a) Infinite b) Zero c) The value of the source voltage d) Null What happens to the current in the series circuit if the resistance is doubled? a) It becomes half its original value b) It becomes double its original value c) It becomes zero d) It becomes infinity If two bulbs are connected in parallel and one bulb blows out, what happens to the other bulb? a) The other bulb blows out as well b) The other bulb continues to glow with the same brightness c) The other bulb glows with increased brightness d) The other bulb stops glowing In a parallel circuit, with a number of resistors, the voltage across each resistor is ________ a) The same for all resistors b) Is divided equally among all resistors c) Is divided proportionally across all resistors d) Is zero for all resistors The current in each branch of a parallel circuit is proportional to _________ a) The amount of time the circuit is on for b) Proportional to the value of the resistors c) Equal in all branches d) Proportional to the power in the circuit The currents in the three branches of a parallel circuit are 3A, 4A and 5A. What is the current leaving it? a) 0A b) Insufficient data provided c) The largest one among the three values d) 12A If in an alternating current circuit, resistance is 5 ohm, capacitive reactance is 12 ohm, what is the impedance? a) 5 ohm b) 10 ohm c) 12 ohm d) 13 ohm 2. If in an alternating current circuit, impedance is 26 ohm, capacitive reactance is 24 ohm, what is the resistance? a) 25 ohm b) 10 ohm c) 12 ohm d) 23 ohm 3. If in an alternating current circuit, capacitance of 30 µF is connected to a supply of 200V,50Hz. Find the current in the circuit. a) 1.38 A b) 1.89 A c) 1.74 A d) 0.89 A 4. If in an alternating current circuit, capacitance C is connected to a supply of 200V,50Hz. Current in the circuit is 1.89 A. Find the capacitance C. a) 30 µF b) 20 µF c) 10 µF d) 15 µF 5. In ac circuit, resistance 5 ohm is connected with capacitor having capacitive reactance 12 ohm. Supply of 260 V is connected to the circuit. Calculate the current in the circuit. a) 40 A b) 10 A c) 20 A d) 30 A b) 50V c) 100V d) 120V 6. In ac circuit, resistance 5 ohm is connected with capacitor having capacitive reactance 12 ohm. Supply of 260 V is connected to the circuit. Calculate the voltage across resistance. a) 300 V b) 200 V c) 240 V d) 100 V 6. Which, among the following, is the correct expression for φ. a) φ=tan-1 (XL/R) b) φ=tan-1 (R/XL) c) φ=tan-1 (XL*R) d) φ=cos-1 (XL/R) 7. In ac circuit, resistance 5 ohm is connected with a capacitor having capacitive reactance 12 ohm. Supply of 260 V is connected to the circuit. Calculate the voltage across a capacitor. a) 300 V b) 200 V c) 240 V d) 100 V A resistance of 7 ohm is connected in series with an inductance of 31.8mH. The circuit is connected to a 100V 50Hz sinusoidal supply. Calculate the current in the circuit. a) 2.2A b) 4.2A c) 6.2A d) 8.2A 2. A resistance of 7 ohm is connected in series with an inductance of 31.8mH. The circuit is connected to a 100V 50Hz sinusoidal supply. Calculate the phase difference. a) -55.1 b) 55.1 c) 66.1 d) -66.1 3. A resistance of 7 ohm is connected in series with an inductance of 31.8mH. The circuit is connected to a 100V 50Hz sinusoidal supply. Calculate the voltage across the resistor. a) 31.8V b) 57.4V c) 67.3V d) 78.2V 4. A resistance of 7 ohm is connected in series with an inductance of 31.8mH. The circuit is connected to a 100V 50Hz sinusoidal supply. Calculate the voltage across the inductor. a) 52V b) 82V c) 65V d) 76V 5. A resistance of 7 ohm is connected in series with an inductance of 31.8mH. The circuit is connected to a x V 50Hz sinusoidal supply. The current in the circuit is 8.2A. Calculate the value of x. a) 10V 7. For an RL circuit, the phase angle is always ________ a) Positive b) Negative c) 0 d) 90 8. What is φ in terms of voltage? a) φ=cos-1V/VR b) φ=cos-1V*VR c) φ=cos-1VR/V d) φ=tan-1V/VR 9. What is sinϕ from impedance triangle? a) XL/R b) XL/Z c) R/Z d) Z/R 1. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the current in the capacitor and the current in the resistor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 2. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the current in the inductor and the current in the resistor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 3. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the current in the capacitor and the current in the inductor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 4. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the current in the circuit and the voltage across the resistor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 5. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the current in the circuit and the voltage across the capacitor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 Participate in Basic Electrical Engineering Certification Contest of the Month Now! 6. _________ the resonant frequency, the current in the inductor lags the voltage in a series RLC circuit. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 7. _________ the resonant frequency, the current in the capacitor leads the voltage in a series RLC circuit. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 1. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the capacitor and the voltage across the resistor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 2. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the inductor and the voltage across the resistor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 3. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the capacitor and the voltage across the inductor is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 4. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the resistor and the current in the circuit is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 5. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the capacitor and the current in the circuit is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 Check this: Basic Electrical Engineering Books 6. In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference between the voltage across the inductor and the current in the circuit is? a) 00 b) 900 c) 1800 d) 3600 7. The current in the inductor lags the voltage in a series RLC circuit ___________ resonant frequency. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 8. The current in the capacitor leads the voltage in a series RLC circuit ___________ resonant frequency. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 9. The current in the inductor ___________ the voltage in a series RLC circuit above the resonant frequency. a) Leads b) Lags c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 10. The current in the capacitor ___________ the voltage in a series RLC circuit below the resonant frequency. a) Leads b) Lags c) Equal to d) Depends on the circuit 1. If the resonant frequency in a series RLC circuit is 50kHz along with a bandwidth of 1kHz, find the quality factor. a) 5 b) 50 c) 100 d) 500 2. What is the SI unit for quality factor? a) Hz b) kHz c) MHz d) No unit 3. What happens to the quality factor when the bandwidth increases? a) Increases b) Decreases c) Remains the same d) Becomes zero 4. What happens to the quality factor when resonant frequency increases? a) Increases b) Decreases c) Remains the same d) Becomes zero 5. Resonance frequency occurs when __________________ a) XL=XC b) XL>XC c) XL<XC d) Cannot be determined 6. The current leads the supply voltage in a series RLC circuit has its frequency _________ the resonant frequency. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Cannot be determined 7. What is the power factor of a series RLC circuit under resonance condition? a) 0 b) 1 c) Infinity d) 100 8. The current lags the supply voltage in a series RLC circuit has its frequency _________ the resonant frequency. a) Above b) Below c) Equal to d) Cannot be determined 9. What is the correct formula for quality factor? a) Q=BW*fr b) Q=BW/fr c) Q=fr/BW d) Q=fr2 1. It is preferable to connect bulbs in series or in parallel? a) Series b) Parallel c) Both series and parallel d) Neither series nor parallel Answer: b Explanation: Bulbs are connected in parallel so that even if one of the bulbs blow out, the others continue to get a current supply. 5. Batteries are generally connected in______ a) Series b) Parallel c) Either series or parallel d) Neither series nor parallel Answer: a Explanation: Batteries are generally connected in series so that we can obtain the desired voltage since voltages add up once they are connected in series. 6. In a _________ circuit, the total resistance is greater than the largest resistance in the circuit. a) Series b) Parallel c) Either series or parallel d) Neither series nor parallel Answer: a Explanation: In series circuits, the total resistance is the sum of all the resistance in the circuit, hence the total is greater than the largest resistance. 7. In a ____________ circuit, the total resistance is smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit. a) Series b) Parallel c) Either series or parallel d) Neither series nor parallel Answer: b Explanation: in a parallel circuit, the equivalent resistance=1/sum of the reciprocals of all the resistances in the circuit. Hence it is smaller than the smallest resistance in the circuit. 8. Which is the most cost efficient connection? a) Series b) Parallel c) Either series or parallel d) Neither series nor parallel Answer: a Explanation: The advantage of series-connections is that they share the supply voltage, hence cheap low voltage appliances may be used. 1) Filters are used to convert a. Pulsating dc signal into a pure dc signal b. Pure dc signal into a pulsating dc signal c. Pulsating dc signal into a pure ac signal d. Pulsating ac signal into a pure dc signal 2) The cut - in voltage for silicon and germanium are a. 0.3 V, 0.3 V b. 0.3 V, 0.7 V c. 0.7 V, 0.7 V d. 0.7 V, 0.3 V 10) 3 - point starter is used to start the a. Series motor b. Shunt motor c. Compound motor d. Only (b) and (c) 3) The P - type semiconductor impurities are also called as a. Acceptor impurities b. Donor impurities c. Either (a) or (b) d. None of these 1. There are five resistors in a given series circuit and each resistor has 6 V dropped across it. The source voltage is (A) 6 V (B) Depends on the current flow (C) Depends on the resistor values (D) 30 V Answer: Option D 4) In N - type semiconductor, the impurities added to a semiconductor are a. Trivalent b. Pentavalent c. Monovalent d. Tetravalent 5) Impurities are generally added in the pure semiconductor to a. increase the number of electrons b. increase the number of holes c. increase their conductivity d. all of these 6) If induction motor is direct switched-on then it will develop a. 1.5 times their full load torque b. 1.5 to 2.5 times their full load torque c. 2.5 times their full load torque d. 1.5 to 5 times their full load torque 7) In DOL fuses are provided to protect against a. Short circuit protection b. Over voltage c. Over current d. Over load 8) In four - point starter, the no volt release is connected across the a. Supply line through a protective resistance b. In series with field circuit through a protective resistance c. Either (a) or (b) d. None of these 9) The overload release protects the motor against a. Over voltage b. Over current c. Over load d. All of these 2. To measure the current out of the second resistor in a circuit consisting of four resistors, an ammeter can be placed (A) Between the second and third resistors (B) At the negative terminal of the source (C) Between the third and fourth resistors (D) At any point in the circuit Answer: Option D 3. The voltage at one point in a circuit is always measured relative to another point. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 4. A series circuit consists of three resistors. Two resistors are 1.2 kΩ each. The total resistance is 12 kΩ. The value of the third resistor is (A) 9,600 Ω (B) 960 Ω (C) 1.2 kΩ (D) Cannot be determined Answer: Option A 5. If you know the current anywhere in a series circuit, you know the current everywhere in a series circuit. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 6. The total resistance of a circuit is 680 Ω. The percentage of the total voltage appearing across a 47 Ω resistor that makes up part of the total series resistance is (A) 68 % (B) 47 % (C) 69 % (D) 6.91 % Answer: Option D 7. The sum of all the voltage drops around a single closed loop in a circuit is zero. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 8. All the voltage drops and the source voltage added together in a series circuit is equal to (A) The total of the voltage drops (B) The source voltage (C) Zero (D) The total of the source voltage and the voltage drops Answer: Option C 9. The total power in a certain circuit is 12 W. Each of the four equal-value series resistors making up the circuit dissipates (A) 12 W (B) 48 W (C) 3 W (D) 8 W Answer: Option C 10. A certain series circuit consists of a 1/8 W resistor, a 1/4 W resistor, and a 1/2 W resistor. The total resistance is 1200 Ω. If each resistor is operating in the circuit at its maximum power dissipation, total current flow is (A) 27 mA (B) 2.7 mA (C) 19 mA (D) 190 mA Answer: Option A 1. Two resistors are in series: a 5.6 kΩ resistor and a 4.7 kΩ resistor. The voltage drop across the 5.6 kΩ resistor is 10 V. The voltage across the 4.7 kΩ resistor is (A) 8.39 V (B) 10 V (C) 2.32 V (D) 0 V Answer: Option A (B) False Answer: Option B 5. ‘Series aiding’ is a term sometimes used to describe voltage sources of the same polarity in series. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 6. If a 24 V and a 6 V battery are series opposing, the total voltage is (A) 30 V (B) 24 V (C) 18 V (D) 0 V Answer: Option C 7. The total resistance of eight 5.6 kΩ resistors in series is (A) 8 Ω (B) 5,600 Ω (C) 4,480 Ω (D) 44,800 Ω Answer: Option D 8. In a series circuit, the individual powers are additive. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 9. The term 'series opposing' means that sources are in series with opposite polarities. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 2. A 12 V battery is connected across a series combination of 68 Ω, 47 Ω, 220 Ω, and 33 Ω. The amount of current is (A) 326 mA (B) 16.3 mA (C) 32.6 mA (D) 163 mA Answer: Option C 10. A series circuit consists of a 4.7 kΩ, a 12 kΩ, and a 2.2 kΩ resistor. The resistor that has the most voltage drop is (A) The 12 kΩ (B) The 2.2 kΩ (C) The 4.7 kΩ (D) Impossible to determine from the given information Answer: Option A 3. Two 6 V batteries are connected series aiding across two 1.2 kΩ resistors in series. Current through each resistor is (A) 5 mA (B) 10 mA (C) 0 A (D) 2.5 mA Answer: Option A 1. When one of three series resistors is removed from a circuit and the circuit is reconnected, the current (A) Increases (B) Increases by one-third (C) Decreases by one-third (D) Decreases by the amount of current through the removed resistor Answer: Option A 2. A string of five series resistors is connected across a 6 V battery. Zero voltage is measured across all resistors except R3. The voltage across R3 is (A) 0 V 4. The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the difference between the largest and smallest value resistors. (A) True (B) 1.2 V (C) 6 V (D) 0.6 V Answer: Option C 3. When a fourth resistor is connected in series with three resistors, the total resistance (A) Increases by one-fourth (B) Increases (C) Decreases (D) Remains the same Answer: Option B 4. Five resistors are connected in a series and there is a current of 3 A into the first resistor. The amount of current into the second resistor is (A) 3 A (B) 1 A (C) 4 A (D) 0.3 A Answer: Option A 5. A short in a series circuit prevents current. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 6. Two 1.5 V cells are connected series opposing across two 100 Ω resistors in series. Total current flow is (A) 15 mA (B) 5 mA (C) 2 mA (D) 0 A Answer: Option D 7. Three 680 Ω resistors are connected in series with a 470 V source. Current in the circuit is (A) 69 mA (B) 230 mA (C) 23 mA (D) 690 mA Answer: Option B (D) Four 220 Ω resistors Answer: Option A 10. A series circuit has a 24 V source and a total resistance of 120 Ω. The current through each resistor is (A) 24 mA (B) 200 mA (C) 120 mA (D) 20 mA Answer: Option B 11. A series circuit acts as a current divider. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 12. A series circuit consists of three resistors with values of 120 Ω, 270 Ω, and 330 Ω. The total resistance is (A) Less than 120 Ω (B) The average of the values (C) 720 Ω (D) 120 Ω Answer: Option C 13. The following resistors (one each) are connected in a series circuit: 470 Ω, 680 Ω, 1 kΩ, and 1.2 kΩ. The voltage source is 20 V. Current through the 680 Ω resistor is approximately (A) 60 mA (B) 30 mA (C) 6 mA (D) 300 mA Answer: Option C 14. If a 6 V and a 9 V source are connected series aiding, the total voltage is (A) 6 V (B) 9 V (C) 3 V (D) 15 V Answer: Option D 8. A series circuit acts as a voltage divider. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 15. Four equal-value resistors are in series with a 12 V battery and 13.63 mA are measured. The value of each resistor is (A) 22 Ω (B) 220 Ω (C) 880 Ω (D) 88 Ω Answer: Option B 9. Which of the following series combinations dissipates the most power when connected across a 120 V source? (A) One 220 Ω resistor (B) Two 220 Ω resistors (C) Three 220 Ω resistors Q1. The total resistance R of a _________ circuit is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Series Parallel Circuit all are correct Answer: b Short Circuit Open Circuit Bypassed Circuit All are correct Answer: b Q2. The formula of Total Series Resistance is _________________ Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 Rtotal = R1 ± R2 ± R3 Rtotal = R1 × R2 × R3 Rtotal = R1 / R2 × R3 Answer: b Q3. Three Resistances of R1=20Ω , R2=57Ω & R1=90Ω are is series then how will the total resistance? 167Ω 90Ω 57Ω 20Ω Answer: a Q4. When current flows through a resistance, electrical energy is converted into ___________ energy. Chemical Heat Light Elastic Answer: b Q5. Whenever, any machine or device connected with the ground is called______________. Grounding Earthing Answer: a Q6. Electrically isolated means that the infinite resistance between ground point. Answer: True True/False Q7. If using double subscript notation, then first letter indicates ________ and the second letter indicate reference. Measurement Increment Subscription Solution Answer: a Q8. The meaning of troubleshooting in electronics and electrical circuit is _________________. Diagnose Analyse Solution all are correct Answer: d Q9. When the current path/track damaged (means Zero Current) in a series circuit then it is called _________________. Q10. The IR voltage across each resistance is called an ___________________. IR drop Voltage drop Power drop a & b are correct Answer: d Q11. __________states that the sum of all resistor voltage drops in a series circuit equals the applied voltage. Ohm’s Law Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL) b & c are correct Answer: b Q12. In a _________Circuit, current is Same in the all part/component. Series Parallel String a & c are correct Answer: d Q13. The formula to calculate Current (I) in Series Resistance Circuit is ___________________. I = V/R I = I^2 × R I = V× R I = Vtotal / Rtotal Answer: d Q14. When components are connected in successive order is called _______________. Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Series Parallel Circuit all are correct Answer: a Q15. A combination of _________ resistances is often called string. Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Series Parallel Circuit all are correct Answer: b Q16. Total voltage (Vtotal) in Series circuit is equal to the sum of individual resistance. Answer: True True/False Extremely Low Answer: c Q17. The total power in a series circuit is the _____________ of individual powers. Sum Minus Divide Multiply Answer: a Q18. In the series circuit, high value of Resistor dissipates more power rather than low value resistor. Answer: True Q25. The resistance of the short circuit (comparing to open circuit) is _____________. Zero Maximum Infinity Low Answer: a True/False Q19. The formula to calculate the power dissipates against any Resistor is _________________. P = W/Q P = I^2 × R P = VR P = IR Answer: b Q20. When two applied voltages are connected in series-aiding mode then Vtotal will be sum of all voltages. True/False Answer: True [Series-Aiding Polarity Mode: when the plus(+) terminal of applied voltage source is connected to the negative(-) terminal of the next applied voltage source] Q21. When two applied voltages are connected in series-opposing mode then Vtotal will be sum of voltages. True/False Answer: False [Series-Opposing Polarity Mode: when the plus (+) terminal of applied voltage source is connected to the Plus (+) terminal of the next applied voltage source] Q1. A circuit in which current divided in separate path or branches is called ______________. Series Circuit Series Parallel Circuit Parallel Circuit all are correct Answer: c Q2. A common use of Parallel circuit is home wiring. True/False Answer: True Q3. Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL) applies for any number of _______ branches. Series Series Parallel Parallel ab c are correct Answer: c Q4. In the parallel circuit, total resistance is increase when more resistance are added. Answer: False Q22. If two series-opposing voltages are equal then the sum of all voltages will be _______________. Infinity Zero Equal to First Applied Voltage Equal to Second Applied Voltage Answer: b Q5. In a _________circuit, voltage is common across all components. Series Parallel String a & c are correct Answer: b Q23. The reference point in electronic schematic circuit is know as _____________ which is equal to 0 volts. Ground GND Feedback a & b are correct Answer: d Q6. A parallel circuit consists of two or more components connected in ____________. Series Parallel Series Parallel All are wrong Answer: b Q24. The resistance of an open series circuit is _____________. High Low Extremely High (Infinity) Q7. The reciprocal of resistance is ___________________. Conductance Inductance True/False Capacitance a & b are correct Answer: a Q8. The standard unit of conductance is Siemen. Answer: True Q17. A combination of parallel branches is often called a ____________. String Bank Joint a & b are correct Answer: b True/False Q9. In a Parallel circuit, the branch of lowest resistance has ___________ current. More Least Answer: a Q10. __________ states that the sum of all individual currents in a parallel circuit equals to the total current of main line. Ohm’s Law Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL) b & c are correct Answer: c Q11. The formula of Total Parallel Resistance is _________________ Rtotal = R1 × R2 / R1 + R2 1 / Rtotal = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 Rtotal = R1 + R2 a & b are correct Answer: d Q12. In the parallel circuit, the individual current in any branch is equal to the total current. Answer: False True/False Q18. How can we find the total resistance in a parallel circuit ? Ohm’s Law KCL KVL All are incorrect Answer: a Q19. How to find unknown branch resistance in any parallel circuit. Rx = R × Req / R – Req Rx = R1 + R2 Rx = 1 / R1 × R2 all are incorrect Answer: a Q20. The total power in a parallel circuit is the _____________ of individual powers. Sum Minus Divide Multiply Answer: a Q13. The total resistance R of a _________ circuit is equal to the algebraic sum of inverses of the individual resistances. Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Series Parallel Circuit all are correct Answer: a Q21. At the incident of short circuit, which component protects the circuit? Resonant Circuit Filter Fuse a & b are correct Answer: b Q14. In a parallel circuit, the smallest branch resistance will always dissipate the most power. True/False Answer: True Q22. In a Parallel Circuit , a short circuit has practically zero resistance. Answer: True Q15. If one branch of parallel circuit is open then all the other branches have same current. True/False Answer: True Q23. At the incident of short circuit, which component protects the circuit? Resonant Circuit Filter Fuse a & b are correct Answer: b 1. Three lights are connected in parallel across a 120 volt source. If one light burns out, (A) The remaining two will glow dimmer (B) The remaining two will glow brighter Q16. When one branch of parallel circuit is short then current in other branches is _______________. Maximum Zero Low Infinite Answer: b True/False (C) The remaining two will not light (D) The remaining two will glow with the same brightness as before Answer: Option D 2. Five 100 Ω resistors are connected in parallel. If one resistor is removed, the total resistance is (A) 25 Ω (B) 500 Ω (C) 100 Ω (D) 20 Ω Answer: Option A 3. There is a total of 800 mA of current into four parallel resistors. The currents through three of the resistors are 40 mA, 70 mA, and 200 mA. The current through the fourth resistor is (A) 490 mA (B) 800 mA (C) 310 mA (D) 0 A Answer: Option A 4. In a five-branch parallel circuit, there are 12 mA of current in each branch. If one of the branches opens, the current in each of the other four branches is (A) 48 mA (B) 12 mA (C) 0 A (D) 3 mA Answer: Option B 5. A set of Christmas tree lights is connected in parallel across a 110 V source. The filament of each light bulb is 1.8 kΩ. The current through each bulb is approximately (A) 610 mA (B) 18 mA (C) 110 mA (D) 61 mA Answer: Option D 6. Four resistors of equal value are connected in parallel. If the total voltage is 15 V and the total resistance is 600 Ω, the current through each parallel resistor is (A) 25 mA (B) 100 mA (C) 6.25 mA (D) 200 mA Answer: Option C 7. A sudden increase in the total current into a parallel circuit may indicate (A) A drop in source voltage (B) An open resistor (C) An increase in source voltage (D) Either a drop in source voltage or an open resistor Answer: Option C 8. Four resistors are connected in parallel. Fifteen mA flows through resistor R. If the second resistor is 2R, the third resistor 3R, and the fourth resistor 4R, the total current in the circuit is (A) 60 mA (B) 15 mA (C) 135 mA (D) 31.25 mA Answer: Option D 9. Four 8 Ω speakers are connected in parallel to the output of an audio amplifier. If the maximum voltage to the speakers is 12 V, the amplifier must be able to deliver to the speakers (A) 18 W (B) 1.5 W (C) 48 W (D) 72 W Answer: Option D 10. When a 1.6 kΩ resistor and a 120 Ω resistor are connected in parallel, the total resistance is (A) Greater than 1.6 kΩ (B) Greater than 120 Ω but less than 1.6 kΩ (C) Less than 120 Ω but greater than 100 Ω (D) Less than 100 Ω Answer: Option C 1. When an additional resistor is connected across an existing parallel circuit, the total resistance (A) Remains the same (B) Decreases by the value of the added resistor (C) Increases by the value of the added resistor (D) Decreases Answer: Option D 2. In a parallel circuit, the branch with the lowest resistance has the most current. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 3. A 470 Ω resistor, a 220 Ω resistor, and a 100 Ω resistor are all in parallel. The total resistance is approximately (A) 790 Ω (B) 470 Ω (C) 60 Ω (D) 30 Ω Answer: Option C 4. The total current divides among parallel resistors in a manner directly proportional to the resistance values. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 5. Total power in a parallel circuit is found by adding up the power of all the individual resistors. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 6. The following currents are measured in the same direction in a three-branch parallel circuit: 200 mA, 340 mA, and 700 mA. The value of the current into the junction of these branches is (A) 200 mA (B) 540 mA (C) 1.24 A (D) 900 mA Answer: Option C 7. The sum of the currents into a junction is equal to the sum of the currents out of that junction. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 8. If one of the resistors in a parallel circuit is removed, the total resistance (A) Decreases (B) Increases (C) Remains the same (D) Doubles Answer: Option B 9. Parallel resistors are connected between the same two points. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 10. An ammeter has an internal resistance of 50 Ω. The meter movement itself can handle up to 1 mA. If 10 mA is applied to the meter, the shunt resistor, RSH1, is approximately (A) 55 Ω (B) 5.5 Ω (C) 50 Ω (D) 9 Ω Answer: Option B 1. The total resistance of a parallel circuit is 50 Ω. If the total current is 120 mA, the current through the 270 Ω resistor that makes up part of the parallel circuit is approximately (A) 22 mA (B) 120 mA (C) 220 mA (D) 50 mA Answer: Option A 2. When an open circuit occurs in a parallel branch, the total resistance decreases. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 3. The currents into a junction flow along two paths. One current is 4 A and the other is 3 A. The total current out of the junction is (A) 1 A (B) 7 A (C) Unknown (D) The larger of the two Answer: Option B 4. If there are a total of 120 mA into a parallel circuit consisting of three branches, and two of the branch currents are 40 mA and 10 mA, the third branch current is (A) 50 mA (B) 70 mA (C) 120 mA (D) 40 mA Answer: Option B 5. A parallel circuit acts as a current divider. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 6. Four equal-value resistors are connected in parallel. Ten volts are applied across the parallel circuit and 2 mA are measured from the source. The value of each resistor is (A) 12.5 Ω (B) 200 Ω (C) 20 KΩ (D) 50 Ω Answer: Option C 7. The power dissipation in each of four parallel branches is 1.2 W. The total power dissipation is (A) 1.2 W (B) 4.8 W (C) 0.3 W (D) 12 W Answer: Option B 8. The total resistance for two resistors in parallel is equal to the sum of the two resistors. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 9. Five light bulbs are connected in parallel across 110 V. Each bulb is rated at 200 W. The current through each bulb is approximately (A) 2.2 A (B) 137 mA (C) 1.8 A (D) 9.09 A Answer: Option C (B) 6 V (C) 12 V (D) 5.7 V Answer: Option D 10. In a certain three-branch parallel circuit, R1 has 12 mA through it, R2 has 15 mA through it, and R3 has 25 mA through it. After measuring a total of 27 mA, you can say that (A) R3 is open (B) R1 is open (C) R2 is open (D) The circuit is operating properly Answer: Option A 2. In a certain five-step R/2R ladder network, the smallest resistor value is 1 kΩ. The largest value is (A) Indeterminable (B) 2 kΩ (C) 10 kΩ (D) 20 kΩ Answer: Option B 11. Addition of resistors in parallel increases total resistance and decreases total current. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 12. The following resistors are in parallel across a voltage source: 220 Ω, 470 Ω, and 560 Ω. The resistor with the least current is (A) 220 Ω (B) 470 Ω (C) 560 Ω (D) Impossible to determine without knowing the voltage Answer: Option C 13. The number of current paths equals the number of resistors in parallel. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 14. Three 47 Ω resistors are connected in parallel across a 110 volt source. The current drawn from the source is approximately (A) 2.3 A (B) 780 mA (C) 47 mA (D) 7.06 A Answer: Option D 15. Six resistors are in parallel. The two lowest-value resistors are both 1.2 kΩ. The total resistance (A) Is less than 6 kΩ (B) Is greater than 1.2 kΩ (C) Is less than 1.2 kΩ (D) Is less than 600 Ω Answer: Option D 1. A voltage divider consists of two 100 kΩ resistors and a 12 V source. What will the output voltage be if a load resistor of 1 MΩ is connected to the output? (A) 0.57 V 3. A voltage divider consists of two 68 kΩ resistors and a 24 V source. The unknown output voltage is (A) 12 V (B) 24 V (C) 0 V (D) 6 V Answer: Option A 4. A certain Wheatstone bridge has the following resistor values: R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 720 Ω, and R4 = 2.4 kΩ. The unknown resistance is (A) 24 Ω (B) 2.4 Ω (C) 300 Ω (D) 3,000 Ω Answer: Option D 5. A certain circuit is composed of two parallel resistors. The total resistance is 1,403 Ω. One of the resistors is 2 kΩ. The other resistor value is (A) 1,403 Ω (B) 4.7 kΩ (C) 2 kΩ (D) 3,403 Ω Answer: Option B 6. Using Kirchhoff's voltage law, you can find the voltages across certain parts of a series-parallel circuit. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 7. Using the current-divider formula, you can find the current in any branch of a series-parallel circuit. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 8. Two 3.3 kΩ resistors are in series and this series combination is in parallel with a 4.7 kΩ resistor. The voltage across one of the 3.3 kΩ resistors is 12 V. The voltage across the 4.7 kΩ resistor is (A) 24 V (B) 12 V (C) 0 V (D) 6 V Answer: Option A 9. Two 1.2 kΩ resistors are in series and this series combination is in parallel with a 3.3 kΩ resistor. The total resistance is (A) 138 Ω (B) 1,389 Ω (C) 5,700 Ω (D) 880 Ω Answer: Option B 10. A certain voltage divider consists of three 1 kΩ resistors in series. Which of the following load resistors will have the least effect on the output voltage? (A) 1 MΩ (B) 100 kΩ (C) 1 kΩ (D) 330 Ω Answer: Option A 1. The parallel combination of a 470 Ω resistor and a 680 Ω resistor is in series with the parallel combination of four 2 kΩ resistors. The total resistance is (A) 1,650 Ω (B) 1,078 Ω (C) 77.8 Ω (D) 778 Ω 01. Answer: Option D 2. The parallel combination of a 470 Ω resistor and a 1.5 kΩ resistor is in series with the parallel combination of five 1 kΩ resistors. The source voltage is 50 V. The percentage of the load current through any single 1 KΩ resistor is (A) 25 % (B) 20 % (C) 100 % (D) 50 % Answer: Option B 3. A smaller-value load resistor will cause the output voltage to change more than a larger-value one. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 4. A galvanometer is a meter that measures small amounts of voltage. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 5. A 12 kΩ resistor, a 15 kΩ resistor, and a 22 kΩ resistor are in series with two 10 kΩ resistors that are in parallel. The source voltage is 75 V. Current through the 15 kΩ resistor is approximately (A) 14 mA (B) 1.4 mA (C) 5 mA (D) 50 mA Answer: Option B 6. The parallel combination of a 470 Ω resistor and a 1.2 kΩ resistor is in series with the parallel combination of three 3 kΩ resistors. A 200 V source is connected across the circuit. The resistor with the most current has a value of (A) 470 Ω or 1.2 kΩ (B) 3 kΩ (C) 470 Ω (D) 1.2 kΩ Answer: Option C 7. To derive 18 V and 12 V from a 24 V supply requires a voltage divider with three taps. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 8. The higher the range setting, the less the internal resistance and the greater the load effect of the voltmeter on a circuit. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 9. The internal resistance of a 20,000 ohm/volt voltmeter set on its 5 V range is (A) 20,000 Ω (B) 100,000 Ω (C) 200,000 Ω (D) 1,000,000 Ω Answer: Option B 10. On which of the following voltage range settings will a voltmeter present the minimum load on a circuit? (A) 1 V (B) 50 V (C) 500 V (D) 1,000 V Answer: Option D 1. A certain voltage divider consists of two 12 kΩ resistors in series. Which of the following load resistors will have the most effect on the output voltage? (A) 1 MΩ (B) 24 kΩ (C) 18 kΩ (D) 12 kΩ Answer: Option D 2. Three 10 kΩ resistors are connected in series. A 20 kΩ resistor is connected in parallel across one of the 10 kΩ resistors. The voltage source is 24 V. The total current in the circuit is (A) 900 μA (B) 9 mA (C) 90 mA (D) 800 μA Answer: Option A 3. A Wheatstone bridge is often shown in a "diamond" configuration. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 4. A Wheatstone bridge consists of four resistors in parallel. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option B 5. The internal resistance of a 30,000 ohm/volt voltmeter set on its 50 V range is (A) 15,000 Ω (B) 150,000 Ω (C) 1,500,000 Ω (D) 15,000,000 Ω Answer: Option C 6. The parallel combination of a 6.8 kΩ resistor and a 10 kΩ resistor is in series with the parallel combination of a 2.2 kΩ resistor and a 1 kΩ resistor. A 100 V source is connected across the circuit. The resistor(s) with the greatest voltage drop is (are) (A) 6.8 kΩ (B) 2.2 kΩ (C) 6.8 kΩ and 10 kΩ (D) 2.2 kΩ and 1 kΩ Answer: Option C 7. A resistor ladder network is a special type of series-parallel circuit. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 8. A 6 V battery output is divided down to obtain two output voltages. Three 2.2 kΩ resistors are used to provide the two taps. The two output voltages are (A) 2 V, 4 V (B) 2 V, 2 V (C) 2 V, 6 V (D) 4 V, 6 V Answer: Option A 9. A balanced Wheatstone bridge consists of an RV of 3,500 Ω, an R2 of 200 Ω, and an R3 of 680 Ω. The value of RUNK is (A) 680 Ω (B) 1,029 Ω (C) 200 Ω (D) 880 Ω Answer: Option B 10. Two equal-value resistors in series will divide the source voltage equally. (A) True (B) False Answer: Option A 1. The lines of force are said to be a) Real b) Imaginary c) Drawn to trace the direction d) Not significant Answer: c Explanation: The lines drawn to trace the direction in which a positive test charge will experience force due to the main charge are called lines of force. They are not real but drawn for our interpretation. 2. Electric flux density in electric field is referred to as a) Number of flux lines b) Ratio of flux lines crossing a surface and the surface area c) Direction of flux at a point d) Flux lines per unit area Answer: b Explanation: Electric flux density is given by the ratio between number of flux lines crossing a surface normal to the lines and the surface area. The direction of D at a point is the direction of the flux lines at that point. 3. The electric flux density is the a) Product of permittivity and electric field intensity b) Product of number of flux lines and permittivity c) Product of permeability and electric field intensity d) Product of number of flux lines and permeability Answer: a Explanation: D= εE, where ε=εoεr is the permittivity of electric field and E is the electric field intensity. Thus electric flux density is the product of permittivity and electric field intensity. 4. Which of the following correctly states Gauss law? a) Electric flux is equal to charge b) Electric flux per unit volume is equal to charge c) Electric field is equal to charge density d) Electric flux per unit volume is equal to volume charge density Answer: d Explanation: The electric flux passing through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by that surface. In other words, electric flux per unit volume leaving a point (vanishing small volume), is equal to the volume charge density. 5. The Gaussian surface is a) Real boundary b) Imaginary surface c) Tangential d) Normal Answer: b Explanation: It is any physical or imaginary closed surface around a charge which satisfies the following condition: D is everywhere either normal or tangential to the surface so that D.ds becomes either Dds or 0 respectively. 1. Divergence theorem is based on a) Gauss law b) Stoke’s law c) Ampere law d) Lenz law Answer: a Explanation: The divergence theorem relates surface integral and volume integral. Div(D) = ρv, which is Gauss’s law. 2. The Gaussian surface for a line charge will be a) Sphere b) Cylinder c) Cube d) Cuboid Answer: b Explanation: A line charge can be visualized as a rod of electric charges. The three dimensional imaginary enclosed surface of a rod can be a cylinder. 3. The Gaussian surface for a point charge will be a) Cube b) Cylinder c) Sphere d) Cuboid Answer: c Explanation: A point charge is single dimensional. The three dimensional imaginary enclosed surface of a point charge will be sphere 9. Gauss law cannot be used to find which of the following quantity? a) Electric field intensity b) Electric flux density c) Charge d) Permittivity Answer: d Explanation: Permittivity is constant for a particular material(say permittivity of water is 1). It cannot be determined from Gauss law, whereas the remaining options can be computed from Gauss law. 10. Gauss law for magnetic fields is given by a) Div(E) = 0 b) Div(B) = 0 c) Div(H) = 0 d) Div(D) = 0 Answer: b Explanation: The divergence of magnetic flux density is always zero. This is called Gauss law for magnetic fields. It implies the non-existence of magnetic monopoles in any magnetic field 1. Gauss law can be used to compute which of the following? a) Permittivity b) Permeability c) Radius of Gaussian surface d) Electric potential Answer: c Explanation: Gauss law relates the electric flux density and the charge density. Thus it can be used to compute radius of the Gaussian surface. Permittivity and permeability are constants for a particular material. 6. Gauss law can be evaluated in which coordinate system? a) Cartesian b) Cylinder c) Spherical d) Depends on the Gaussian surface Answer: d Explanation: The Gauss law exists for all materials. Depending on the Gaussian surface of the material, we take the coordinate systems accordingly. Suppose if the material is a coaxial cable, the Gaussian surface is in the form of cylinder. Thus we take Cylinder/Circular coordinate system. 7. Gauss law cannot be expressed in which of the following forms? a) Differential b) Integral c) Point d) Stokes theorem Answer: d Explanation: Gauss law can be expressed in differential or point form as, Div (D)= ρv and in integral form as ∫∫ D.ds = Q = ψ . It is not possible to express it using Stoke’s theorem. 8. The tangential component of electric field intensity is always continuous at the interface. State True/False. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Consider a dielectric-dielectric boundary, the electric field intensity in both the surfaces will be Et1 = Et2, which implies that the tangential component of electric field intensity is always continuous at the boundary. 9. The normal component of the electric flux density is always discontinuous at the interface. State True/False. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: In a dielectric-dielectric boundary, if a free surface charge density exists at the interface, then the normal components of the electric flux density are discontinuous at the boundary, which means Dn1 = Dn2. 10. With Gauss law as reference which of the following law can be derived? a) Ampere law b) Faraday’s law c) Coulomb’s law d) Ohm’s law Answer: c Explanation: From Gauss law, we can compute the electric flux density. This in turn can be used to find electric field intensity. We know that F = qE. Hence force can be computed. This gives the Coulomb’s law. 1. Gauss law is applicable for_________ a) Point charge b) Sheet charge c) Line charge d) Point, sheet and line charge Answer: d Explanation: Gauss law states that the total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by that surface. Hence it is applicable for all point, surface and volume. 2. “Total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by that surface divided by permittivity”. This is the statement for? a) Gauss law b) Lenz law c) Coloumb’s law d) Faraday’s law Answer: a Explanation: Total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by that surface divided by permittivity is the statement for Gauss law because among the four laws, Gauss law deals with electric flux. 3. Electric flux density is a function of_______ a) Volume b) Charge c) Current d) Voltage Answer: b Explanation: Electric flux density is the charge per unit area. Hence it is a function of charge and not any of the other values. 4. As charge increases, what happens to flux density? a) Increases b) Decreases c) Remains constant d) Becomes zero Answer: a Explanation: Electric flux density is the charge per unit area. The expression for flux density is: D=Q/A. Electric flux is directly proportional to charge, hence as charge increases, electric flux also increases. 5. As area increases, what happens to electric flux density? a) Increases b) Decreases c) Remains constant d) Becomes zero Answer: b Explanation: Electric flux density is the charge per unit area. The expression for flux density is: D=Q/A. Electric flux is inversely proportional to area, hence an area increases, electric flux decreases. 6. Which, among the following, is the correct expression for electric flux density? a) D=epsilon*E b) D=epsilon/E c) D2=epsilon*E d) D=epsilon*E2 Answer: a Explanation: Electric flux density is directly proportional to the electric field, epsilon(permittivity of free space) being the constant of proportionality. Hence D=epsilon*E. 7. Strength of the electric field is ___________ a) Directly proportional to the force applied b) Inversely proportional to the force applied c) Directly proportional to the square of the force applied d) Inversely proportional to the square of the force applied Answer: a Explanation: Electric field intensity is the force per unit charge, hence it is directly proportional to the force applied. 1. Materials which easily allow the passage of electric current are known as ______ a) Insulators b) Conductors c) Dielectrics d) Semi-conductors Answer: b Explanation: Conductors are materials(mostly metals), which freely allow the passage of electrons through it. If electrons can flow freely through a material, it implies that even current can flow freely through that material since current is the rate of flow of electrons. 2. A wire of length 2m and another wire of length 5m are made up of the same material and have the same area of cross section, which wire has higher resistance? a) Both have equal resistance b) The 2m wire has higher resistance c) The 5m wire has higher resistance d) The value of resistance cannot be determined from the given data Answer: c Explanation: Resistance is directly proportional to the length of the wire, hence as the length of the wire increases, resistance increases. 3. A wire having an area of cross section = 10sqm and another wire having an area of cross section= 15sqm, have the same length and are made up of the same material. Which wire has more resistance? a) Both have equal resistance b) The 10sqm wire has higher resistance c) The 15sqm wire has higher resistance d) The value of resistance cannot be determined from the given data Answer: b Explanation: Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section. As an area of cross-section increases, resistance decreases. Hence the 10sqm wire has a higher resistance than the 15sqm wire. 4. Which of the following statements are true with regard to resistance? a) Resistance is directly proportional to a length of the wire b) Resistance is directly proportional to an area of cross section of the wire c) Resistance is inversely proportional to the length of the wire d) Resistance is inversely proportional to the resistivity of the wire Answer: a Explanation: The expression for resistance is: Resistance=Resistivity*length of wire/ area of cross section of the wire. Hence resistance is directly proportional to length 8. Calculate the ratio of the resistivity of 2 wires having the same length and same resistance with area of cross section 2m2 and 5m2 respectively. a) 5:7 b) 2:7 c) 2:5 d) 7:5 Answer: c Explanation: Resistivity = R*A/L Since resistance and length of the two wires are same so resistivity is directly proportional to area of cross section. Ratio of area is 2:5 so the ratio of resistivity is also 2:5. 9. Which of the following statements are true with regard to resistivity? a) Resistance depends on the temperature b) Resistance does not depend on the temperature c) Resistivity depend on the length d) Resistivity depend on area of cross section Answer: a Explanation: Resistivity is material property. It depends only on temperature. For the same material with different length and area, resistivity remains the same until temperature remains constant In a series circuit with unequal resistances A. The highest resistance has the most of the current through it B. The lowest resistance has the highest voltage drop C. The lowest resistance has the highest current D. The highest resistance has the highest voltage drop Answer: Option D Resistance of a material always decreases if A. Temperature of material is decreased B. Temperature of material is increased C. Number of free electrons available becomes more D. None of the above is correct Answer: Option C 1. Which of the following is the correct expression for the Schrödinger wave function? a) iℏdΨdt=−iℏ2m∂Ψ∂x+UΨ b) iℏdΨdt=−iℏ2m∂2Ψ∂x2+UΨ c) iℏdΨdt=−iℏz2m∂Ψ∂x+UΨ d) iℏdΨdt=−iℏz2m∂2Ψ∂x2+UΨ Answer: d Explanation: The correct expression for the Schrödinger wave equation is iℏdΨdt=−iℏz2m∂2Ψ∂x2+UΨ. Schrodinger equation is a basic principle in itself. 2. For a quantum wave particle, E = _____________ a) ℏ k b) ℏ ω c) ℏ ω/2 d) ℏ k/2 Answer: b Explanation: The Energy of a wave particle is given as ℏ ω while the momentum of the particle is given as ℏ k. These are the desired relation. 3. Schrodinger Wave equation can be derived from Principles of Quantum Mechanics. a) True b) False Answer: b Explanation: Schrodinger equation is a basic principle in itself. It cannot be derived from other principles of physics. Only, it can be verified with other principles. 4. Which of the following can be a wave function? a) tan x b) sin x c) cot x d) sec x Answer: b Explanation: Out of all the given options, sin x is the only function, that is continuous and single-valued. All the rest of the functions are either discontinuous or double-valued. 5. Which of the following is not a characteristic of wave function? a) Continuous b) Single valued c) Differentiable d) Physically Significant Answer: d Explanation: The wave function has no physical significance. It merely helps in determining the state of a particle. It is the square of the wave function that has a physical significance *) Any wave function can be written as a linear combination of _________________ a) Eigen Vectors b) Eigen Values c) Eigen Functions d) Operators Answer: c Explanation: A wave function describes the state of a particle. It does not have a physical significance. Moreover, it can be written as a linear combination of Eigen functions, i.e., Ψ(x) = AF(x) + BG(x). *) The Schrödinger is a differential equation. a) True b) False Answer: b Explanation: The Schrodinger wave equation generated is a partial differential equation. It is a basic principle in itself and cannot be derived from other principles of physics. There are two types of partial differential equation time dependent form and steady-state form. share pairs of valence electrons. A metallic bond is formed between a cloud of free electrons and the positively charges ions in a metal. In ionic and covalent bonds, the valence electrons play a critical role in forming the bond. Atoms achieve a stable electronic configuration by transferring and sharing electrons. As a result, the bonds become stable with well-defined strength and energy. Ionic bond The ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds join metals to non-metals. Covalent bond The covalent bond is also called a shared bond. These bonds join non-metals to non-metals. Metallic bonds Metallic bonds are the chemical bonds that join metals to metals. Ionic Bond vs. Covalent Bond vs. Metallic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Metallic Bond A metal and a nonmetal Two nonmetals or a nonmetal and a metalloid Positively charged ions and negatively charged electron cloud Sharing pairs of electrons Electrostatic attraction between the delocalized electron cloud and positively charged metal ions No Yes – Electro negativity difference between atoms High (>2) Low (<0.1) for nonpolar compounds and intermediate (0.1 – 2) for polar compounds Electro negativity does not play any role Isomerism Nondirectional Directional Nondirectional Physical state of compounds Solid at room temperature Liquid or gas at room temperature Solid at room temperature Physical properties High melting and boiling points Low melting and boiling points High melting and boiling points Solubility Dissociate into ions in solution Retain their molecular identity in solution Some metals react vigorously with water, while others do not Occurs between Formation Formation between atoms of the same element Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are different types of chemical bonds. An ionic bond is formed when one atom donates valence electrons to another atom. A covalent bond is formed when both the atoms Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions Conductivity Low in solid-state, but becomes high in molted state and solutions Low, except conducting polymers High Examples Sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium iodide (KI) Methane (CH4) and water (H2O) Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) Ionic bond formation depends on the arrangement of __________ a) molecule b) atom c) lattice d) kernal Answer: c Explanation: Lattice of the crystalline compound is the arrangement of positive and the negative ions inside a substance. It is dependent on the ease of formation of ionic bonds as per Kossel and Lewis Ionic bond formation. 1. A chemical bond formation that involves the complete transfer of electrons between atoms is _______ a) ionic bond b) covalent bond c) metallic bond d) partial covalent bond Answer: a Explanation: Ionic bond, which is otherwise known as electrovalent bond forms between two atoms by the transfer of electrons between them. It generates oppositely charged ions. Positively charged ions are mostly metals and the vice-versa. 2. Formation of a compound through ionic bond ______ the ionization energy of the metal ion. a) does not depends on b) depend on c) is independent regarding d) may or may not depend on Answer: b Explanation: For the formation of the ionic bond, the metal ion has to overcome to energy for the removal of an electron from its outer shell in order to become a cation, that is ionization energy. Therefore Formation of a compound through ionic bond depends on the ionization energy of the metal ion. 4. Electron gain enthalpy may be ________ a) exothermic b) endothermic c) both exothermic and endothermic d) always zero Answer: c Explanation: Electron gain enthalpy is the enthalpy change for an atom in the ground state to gain an electron. In the case of an exothermic reaction, the value of electron gain enthalpy is negative, which means that it is releasing energy and vice-versa when it’s positive. 5. Ionic bonds easily form when electron when ionization energy of the metallic atom is _____ comparatively. a) negative b) constant c) more d) less Answer: d Explanation: The rate of formation of an ionic bond mainly depends on the tendency to become cation and anion from their original ground states. The tendency is maximum for metallic atoms whose ionization energy is less than the other atoms. 6. What is the energy that is released upon the formation of an ionic compound known as? a) Ionization energy b) Lattice energy c) Electron gain enthalpy d) Electro positivity Answer: b Explanation: When the ions are combined to form an ionic compound that is a crystalline solid, a certain amount of energy is released and this is known as the lattice energy. Solubility, volatility, and hardness can be predicted from lattice energy 1. The number of electrons in the outer shell A) isotope B) atomic mass C) ion D) valence 2. These elements don't bond with other elements because their outer shell is filled. A) Inert gases B) metals C) none of the answers are correct D) noble solids 3. Most atoms adopt one of three simple strategies to achieve a filled shell. Which of the following is NOT one of these strategies. A) they keep their own electrons B) they give away electrons C) they accept electrons D) they share electrons 4. Which of the following is NOT a type of chemical bond? A) Metallic B) Covalent C) Ionic D) Valence 5. In ionic bonding A) electrons are shared B) Two answers are correct C) Electrons are given away D) Electrons are accepted 6. In ionic bonding electrical forces between same charged ions holds the atoms together. A) True B) False 7. In metallic bonding... A) A couple of atoms share their electrons with each other. B) Bonding takes place between positively charged areas of one atom with a negatively charged area of another atom. C) One atom takes the outer shell electrons from another atom. D) Some electrons are shared by all the atoms in the material. 8. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of metals. A) conducts electricity B) Malleable C) Shiny luster D) Brittle/Shatters easily 9. In covalent bonding A) Some electrons are shared by all the atoms. B) A couple of atoms share their electrons with each other. C) Bonding takes place between positively charged areas of one molecule with a negatively charged area of another molecule. D) One atom takes the outer shell electrons from another atom. 10. Which element forms the basis for organic chemistry A) carbon B) all of the above C) hydrogen D) oxygen 11. These help hold molecules together. A) Hydrogen Bonds B) All of the above. C) Polarization D) Van der Waals Forces 12. Polarization of a bond.... A) occurs when electrons spend more time with one atom in the molecule than another. B) occurs when molecules get near magnetic North or South Poles. C) occurs when molecules move to opposite sides (poles) of a cell. D) occurs when atoms move to opposite sides (poles) of the molecule. 13. Hydrogen bonds are.... A) formed when one atom takes an electron from another atom. B) strong bonds C) are found between the sides of the DNA double helix D) help to determine shape and function of molecules 14. Van der Waals Forces are a result of... A) molecules coming close to one another creating a weak force between these molecules B) One molecule taking electrons from another C) None of the above D) Molecules sharing electrons 15. O2 is an example of what type of bonding A) Hydrogen B) Metallic C) Covalent D) Ionic 16. When two or more metal elements are combined they form an... A) bronze B) brass C) alloy D) covalent bond What theorem replaces a complex network with an equivalent circuit containing a source voltage and a series resistance? A. Multinetwork B. Norton C. Thevenin D. Superposition Answer: Option C What is the power dissipated by R2, R4, and R6? A. P2 = 417 mW, P4 = 193 mW, P6 = 166 mW B. P2 = 407 mW, P4 = 183 mW, P6 = 156 mW C. P2 = 397 mW, P4 = 173 mW, P6 = 146 mW D. P2 = 387 mW, P4 = 163 mW, P6 = 136 mW Answer: Option A *) If the load in the given circuit is 120 komega.gif , what is the loaded output voltage? A. 4.21 V B. 15.79 V C. 16 V D. 19.67 V Answer: Option B In a series–parallel circuit, individual component power dissipations are calculated using: A. individual component parameters B. a percent of the voltage division ratio squared C. total current squared multiplied by the resistor values D. a percent of the total power depending on resistor ratios Answer: Option A The current flowing through an unloaded voltage divider is called the: A. resistor current B. load current C. bleeder current D. voltage current Answer: Option C When a Wheatstone bridge is in a balanced condition, the center voltmeter in the bridge will read: A. twice the source voltage B. the same as the source voltage C. zero volts D. half the source voltage Answer: Option C When a load is connected to a voltage divider, the total resistance of the circuit will: A. decrease B. double C. increase D. remain the same Answer: Option A What is the total resistance of the given circuit? When placed into a circuit, how are electronic components usually connected? A. positive terminal to positive terminal B. in parallel C. as a combination of series and parallel D. in series Answer: Option C If the load in the given circuit is 12kohm, what is the loaded output voltage? A. 92 omega.gif B. 288 omega.gif C. 17.7 omega.gif D. 128 omega.gif Answer: Option A What are the branch currents I2 and I3? A. I2 = 4 mA, I3 = 2 mA B. I2 = 4.5 mA, I3 = 2.5 mA C. I2 = 2.5 mA, I3 = 1.5 mA D. I2 = 5.5 mA, I3 = 3.5 mA Answer: Option C If the load in the given circuit is open, what is the unloaded output voltage? A. 0V B. 4V C. 16 V D. 20 V Answer: Option C A. 5.88 V B. 14.12 V C. 16 V D. 17.14 V Answer: Option B If a Wheatstone bridge is balanced, a voltmeter in the center of the bridge will read: A. the same as the source voltage B. half the source voltage C. zero volts D. twice the source voltage Answer: Option C The first goal to accomplish in analyzing a complex series-parallel circuit is to A. equate all parallel components B. equate all series components C. solve for all the voltage drops D. solve for the total current and resistance Answer: Option D If R1 is in series with parallel connected to R2 and R3, what happens to total current if R2 opens? A. increases B. decreases C. remains the same D. cannot tell Answer: Option B How much current is flowing through R1 in the given circuit? A. 0.3 A B. 0.15 A C. 0.5 A D. 0.68 A Answer: Option C Components or combinations of components with common currents, in a series–parallel circuit, are in: A. parallel with each other B. series with each other C. either series or parallel with each other D. none of the above Answer: Option C What determines if resistor connections are in series, parallel, or series–parallel? A. the voltage source B. the power source C. resistance D. current flow Answer: Option D If R1 is in series with a parallel combination of R2, R3, and R4, when the resistance value of R2 increases, the voltage across R3 will A. increase B. decrease C. remain the same D. Cannot tell Answer: Option A A Wheatstone bridge can be used to determine an unknown A. current B. resistance C. power D. voltage Answer: Option B In a series–parallel circuit consisting of R1 and R2 in series and connected in parallel with R3, if R1 opens, then R2's voltage will: A. increase B. decrease C. remain the same D. cannot tell Answer: Option B An electric heater draws 3.5 A from a 110 V source. The resistance of the heating element is approximately A. 385 B. 38.5 C. 3.1 D. 31 Answer: Option D If 750 µA is flowing through 11 k of resistance, what is the voltage drop across the resistor? A. 8.25 V B. 82.5 V C. 14.6 V D. 146 V Answer: Option A A resistor is connected across a 50 V source. What is the current in the resistor if the color code is red, orange, orange, silver? A. 2 mA B. 2.2 mA C. 214 mA D. 21.4 mA Answer: Option B Approximately how many milliamperes of current flow through a circuit with a 40 V source and 6.8 k of resistance? A. 27.2 mA B. 59 mA C. 5.9 mA D. 590 mA Answer: Option C How much resistance is required to limit the current from a 12 V battery to 3.6 mA? A. 3.3 k B. 33 k C. 2.2 k D. 22 k Answer: Option A When the frequency of the source voltage decreases, the impedance of a parallel RC circuit A. increases B. decreases C. does not change D. decreases to zero Answer: Option A In a parallel RC circuit, there is 100 mA through the resistive branch and 100 mA through the capacitive branch. The total rms current is A. 200 mA B. 100 mA C. 282 mA D. 141 mA Answer: Option D An ac circuit consists of a resistor and a capacitor. To increase the phase angle above 45°, the following condition must exist: A. R = XC B. R > XC C. R < XC D. R = 5XC Answer: Option C A resistor and a capacitor are in series across a 20 V ac source. Circuit impedance is 4.33 k. Current flow in the circuit is A. 9.2 mA B. 92 mA C. 4.6 mA D. 460 mA Answer: Option C When the frequency of the voltage applied to a series RC circuit is increased, the phase angle A. increases B. decreases C. remains the same D. becomes erratic Answer: Option B In a series RC circuit, when the frequency and the resistance are halved, the impedance A. doubles B. is halved C. is reduced to one-fourth D. cannot be determined without values Answer: Option D When the frequency of the voltage applied to a series RC circuit is decreased, the impedance A. increases B. decreases C. remains the same D. doubles Answer: Option A A 1.5 k resistor and a coil with a 2.2 k inductive reactance are in series across an 18 V ac source. The power factor is A. 564 B. 0.564 C. 6.76 D. 55.7 Answer: Option B To increase the current in a series RL circuit, the frequenc A. should be increased B. should be decreased C. should be constant D. cannot be determined without values Answer: Option B A 1.2 k resistor is in series with a 15 mH coil across a 10 kHz ac source. The magnitude of the total impedance is A. 152.6 B. 1,526 C. 1,200 D. 942 Answer: Option B When the frequency is decreased, the impedance of a parallel RL circuit A. increases B. decreases C. remains constant D. is not a factor Answer: Option B When the frequency of the voltage applied to a series RL circuit is decreased, the impedance A. decreases B. increases C. does not change D. cannot be determined without values Answer: Option A In a parallel RL circuit, there are 3 A rms in the resistive branch and 3 A rms in the inductive branch. The total rms current is A. 6A B. 424 mA C. 4.24 A D. 42.4 A Answer: Option C When the resistor voltage in a series RL circuit becomes less than the inductor voltage, the phase angle A. increases B. decreases C. is not affected D. cannot be determined Answer: Option A Which of the following power factors results in less energy loss in an RL circuit? A. 1 B. 0.8 C. 0.4 D. 0.2 Answer: Option D When the frequency of the voltage applied to a series RL circuit is increased, the phase angle A. decreases B. increases C. does not change D. cannot be determined without values Answer: Option B If a load is purely inductive and the reactive power is 12 VAR, the apparent power is A. 0 VA B. 12 VA C. 6 VA D. 24 VA Answer: Option B If the frequency is halved and the resistance is doubled, the impedance of a series RL circuit A. doubles B. halves C. remains constant D. cannot be determined without values Answer: Option D In a series RLC circuit that is operating above the resonant frequency, the current A. lags the applied voltage B. leads the applied voltage C. is in phase with the applied voltage D. is zero Answer: Option A A 15 resistor, a 220 H coil, and a 60 pF capacitor are in series across an ac source. What is the bandwidth of the circuit? A. 138 MHz B. 10,866 Hz C. 1,907 Hz D. 138 kHz Answer: Option B A 12 resistor, a 40 F capacitor, and an 8 mH coil are in series across an ac source. The resonant frequency is A. 28.1 Hz B. 281 Hz C. 2,810 Hz D. 10 kHz Answer: Option B If the resistance in parallel with a parallel resonant circuit is reduced, the bandwidth A. disappears B. becomes sharper C. increases D. decreases Answer: Option D A 90 resistor, a coil with 30 of reactance, and a capacitor with 50 of reactance are in series across a 12 V ac source. The current through the resistor is A. 9 mA B. 90 mA C. 13 mA D. 130 mA Answer: Option D If the value of C in a series RLC circuit is decreased, the resonant frequency A. is not affected B. increases C. is reduced to zero D. decreases Answer: Option B A 24 resistor, an inductor with a reactance of 120 , and a capacitor with a reactance of 120 are in series across a 60 V source. The circuit is at resonance. The voltage across the inductor is A. 60 V B. 660 V C. 30 V D. 300 V Answer: Option D To tune a parallel resonant circuit to a higher frequency, the capacitance should be A. increased B. decreased C. left alone D. replaced with inductance Answer: Option B In a certain series resonant circuit, VC = 125 V, VL = 125 V, and VR = 40 V. The value of the source voltage is A. 125 V B. 250 V C. 290 V D. 40 V Answer: Option D A 33 half-watt resistor and a 330 half-watt resistor are connected across a 12 V source. Which one(s) will overheat? A. 33 B. 330 C. both resistors D. neither resistor Answer: Option D When the pointer of an analog ohmmeter reads close to zero, the resistor being measured is A. overheated B. shorted C. open D. reversed Answer: Option B A certain appliance uses 350 W. If it is allowed to run continuously for 24 days, how many kilowatthours of energy does it consume? A. 20.16 kWh B. 201.6 kWh C. 2.01 kWh D. 8.4 kWh Answer: Option B A power supply produces a 0.6 W output with an input of 0.7 W. Its percentage of efficiency is A. 8.57% B. 42.85% C. 4.28% D. 85.7% Answer: Option D At the end of a 14 day period, your utility bill shows that you have used 18 kWh. What is your average daily power? A. 1.286 kWh B. 12.85 kWh C. 535 kWh D. 252 kWh Answer: Option A A 15 V source is connected across a 12 resistor. How much energy is used in three minutes? A. 938 Wh B. 0.938 Wh C. 56.25 Wh D. 5.6 Wh Answer: Option B A 120 resistor must carry a maximum current of 25 mA. Its rating should be at least A. 4.8 W B. 150 mW C. 15 mW D. 480 mW Answer: Option B If you used 400 W of power for 30 h, you have used A. 1.3 kWh B. 13.3 kWh C. 1.2 kWh D. 12 kWh Answer: Option D A 6 V battery is connected to a 300 load. Under these conditions, it is rated at 40 Ah. How long can it supply current to the load? A. 1h B. 200 h C. 2,000 h D. 10 h Answer: Option C If you used 600 W of power for 60 h, you have used A. 36 kWh B. 3.6 kWh C. 10 kWh D. 1 kWh Answer: Option A The power rating of a carbon-composition resistor that is to handle up to 1.2 W should be A. 2W B. 1W C. 5W D. 0.5 W Answer: Option A If it takes 400 ms to use 12,000 J of energy, the power is A. 30 kW B. 30 W C. 3W D. 300 kW Answer: Option A Three hundred joules of energy are consumed in 15 s. The power is A. 2,000 W B. 2W C. 20 W D. 200 W Answer: Option C How much continuous current can be drawn from a 60 Ah battery for 14 h? A. 42.8 A B. 428 A C. 4.28 A D. 4.2 A Answer: Option C When the current through a 12 k resistor is 8 mA, the power is A. 7.68 mW B. 768 mW C. 7.68 W D. 76.8 W Answer: Option B A 68 resistor is connected across the terminals of a 3 V battery. The power dissipation of the resistor is A. 132 mW B. 13.2 mW C. 22.6 mW D. 226 mW Answer: Option A Potential energy due to gravity is depends upon acceleration due to gravity, mass and the distance above a surface. True False Answer: True The energy possessed by a body due to its position is called: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Mechanical Energy Electrical Energy Answer: Potential Energy Which one of the following is not a form of energy? Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Work Current Answer: Current When an object falls freely towards the ground, then its total energy ____. increases first increases then decreases remains constant decreases Answer: remains constant What are the two factors that affect kinetic energy? time and energy power and mass mass and speed time and work Answer: mass and speed A bulb has a power of 200W. What is the energy dissipated by it in 5 minutes? a) 60J b) 1000J c) 60kJ d) 1kJ Answer: c Explanation: Here, Power = 200w and time = 5min. E=Pt => E= 200*5= 1000Wmin=60000Ws= 60000J= 60kJ. 1. Ohm's law is applicable to A. Semiconductors B. Vacuum tubes C. Carbon resistors D. None of these Answer: D. None of these 2. The condition for the validity of Ohm's law is that the A. Temperature should remain constant B. Current should be proportional to voltage C. Resistance must be wire wound type D. All of the above Answer: A. Temperature should remain constant 3. Ohm's law is not applicable to A. Semiconductors B. D.C. circuits C. Small resistors D. High currents Answer: A. Semiconductors 5. Ohm's law in point form in field theory can be expressed as A. V = RI B. J = E/σ C. J = σE D. R = ρl/A Answer: C. J = σE Four 100 W bulbs are connected in parallel across 200 V supply line. If one bulb gets fused A. No bulb will light B. All the four bulbs will light C. Rest of three bulbs will light D. Above B and C Answer: C. Rest of three bulbs will light 10. Two incandescent light bulbs of 40 W and 60 W ratings are connected in series across the mains. Then A. The bulbs together consume 100 W B. The bulbs together consume 50 W C. The 60 W bulb glows brighter D. The 40 W bulb glows brighter Answer: D. The 40 W bulb glows brighter Ohm’s law is not applicable to which of the following options? Dc circuits High currents Small resistors Semi-conductors Answer: Semi-conductors When the length of the conductor is doubled and the area of cross-section remains the same then its resistance ____. will be doubled remains the same will become half will increase by four times Answer: will be doubled