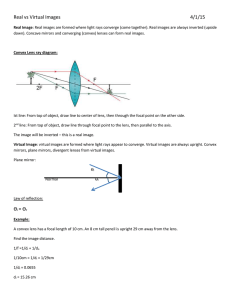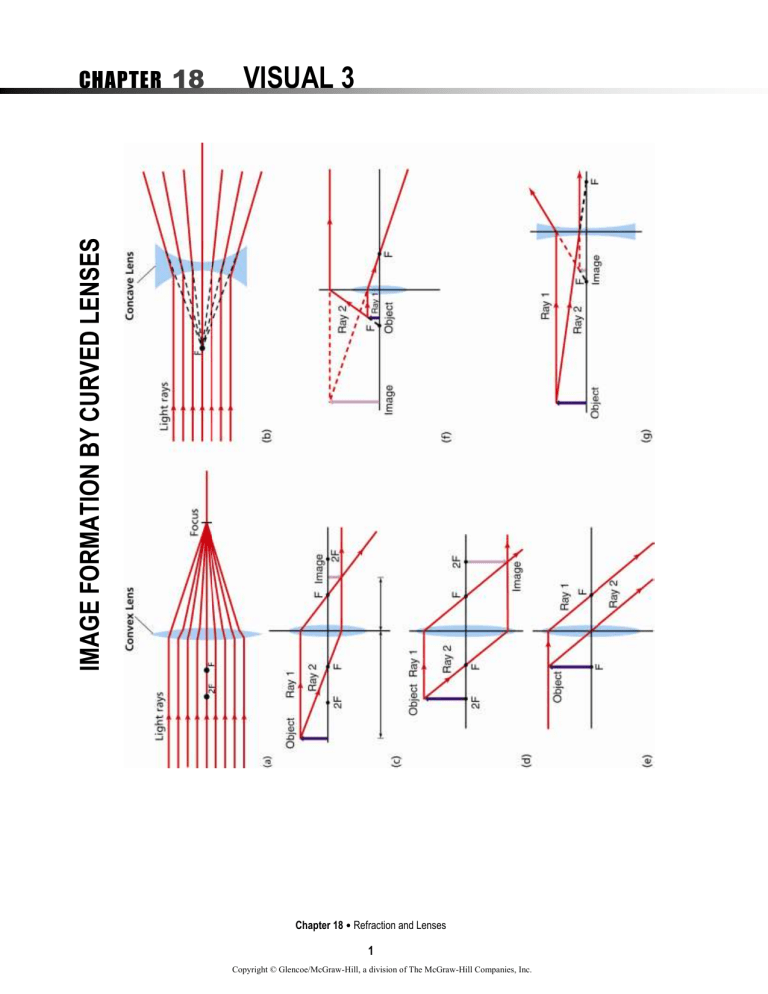
VISUAL 3 IMAGE FORMATION BY CURVED LENSES CHAPTER 18 Chapter 18 Refraction and Lenses 1 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Date __________________ Period _________________ Name ___________________________________ CHAPTER 18 VISUAL 3 IMAGE FORMATION BY CURVED LENSES 1. What type of lens is shown in Figure a? In Figure b? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does F represent? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Where is light from a very distant object focused by a convex lens? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. As the object moves from very far away to very close to F, how does the image produced by a convex lens change? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What might you do to see the images of objects further than F from a convex lens? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. When does an object’s size equal the image size for a convex lens? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What happens to the image when the object is between F and a convex lens? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What effect does a concave lens have on light rays? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What type of image is formed by a concave lens? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 18 Refraction and Lenses 2 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Visual 3 Teacher Support IMAGES FORMATION BY CURVED LENSES All numerical answers have been rounded to the correct number of significant figures. 1. Figure a is a convex, or converging, lens. Figure b is a concave, or diverging, lens. 2. F is the focal point. 3. The light is focused at the focal point. 4. It gets larger and farther from the lens. 5. Project them on a screen or position your eye where the image should be. 6. They are equal in size when the object is at 2F. 7. The image is virtual, enlarged, upright, and on the same side of the lens as the object. 8. It causes them to diverge. 9. A concave lens always forms a virtual image that is upright and smaller than the object. Chapter 18 Refraction and Lenses 3 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.