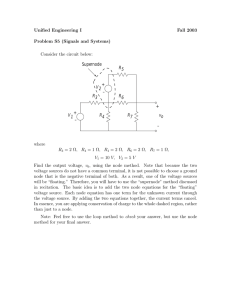
NODAL ANALYSIS -Is provides a procedure of analyzing circuits using node voltages as the circuits variables. Choosing node voltages instead of element voltages as circuit variables is convenient and reduces the number of equation one must solve simultaneously . - In nodal analysis , we are interested finding node voltages . Given a circuit with n nodes without voltage source, the nodal analysis of the circuit involves taking the following three steps. Reference Node - A reference node is indicated by any of the three symbols. THE FORMULAS: STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 NODAL ANALYSIS WITH VOLTAGE SOURCE Case 1: If a voltage source is connected between the reference node and a non-reference node, we simply set the voltage at the nonreference node equal to a voltage of the voltage source. Case 2: If the Voltage Source ( dependent or independent ) is connected between two nonreference node , the two nonreference nodes forms a generalized node or supernode. Supernode- is formed by enclosing a (dependent or independent)voltage source connected between two nonreference nodes and any elements connected in parallel with it.