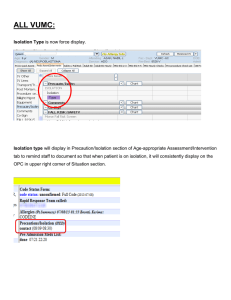
epidemiology of covid-19 IN PEDIATRIC POPULATION As of February 2021: 48,411 confirmed COVID-19 cases aged 19 years old and below 15-19 years old (40.2%) 10-14 years old (23.8%) 0-4 years old (18.5%) 5-9 years old (17.4%) Total of 210 deaths were recorded among 19 years old and below Case Fatality Rate: 0.4% Transmission • Inhalation of infected droplets • Contact of the mucosal surfaces of the eyes, nose and mouth after touching contaminated objects • Airborne transmission through aerosol-generating procedures • Transplacental transmission • Study of Stonoga et. Al tested placenta and cord blood of a stillbirth fetus and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 via PCR • Bwire et. Al reported 11 infants borth to COVID-19 positive mothers and detected IgM and IgG antibodies CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Dong et al studied 2,143 confirmed and suspected pediatric cases in China and found: Asymptomatic: 44% Mild Disease: 50.9% Moderate Disease: 38.8% Severe Case: 5.2% Critical Case: 0.6% PATHOPHYSIOLOGY SCREENING AND ASSESSMENT SCREENING A CHILD FOR COVID-19 A. Influenza-like illness (ILI) - Sudden (within 3 days) onset of fever ≥ 38°C - Sough or sore throat • Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) - ARI with onset during the previous 7 days requiring overnight hospitalization. a) Shortness of breath or difficulty of breathing; b) Severe pneumonia of unknown etiology, acute respiratory distress, or severe respiratory disease possibly due to novel respiratory pathogens (such as COVID-19) B. Exposure evaluation 1. Contact2 days before and the 14 days after the onset of symptoms of a probable or confirmed case. 2. Take note if the child resides in or has travelled within the last 14 days to areas with localized transmission or local communities under quarantine. C. Evaluate the patient’s status D. Laboratory evaluation -Pulse oximetry CXR, CBC, Inflammatory markers, ABG E. If either exposure evaluation, clinical evaluation or ancillary laboratory tests is positive, the diagnosis of COVID-19 should be considered. CLINICAL MANAGEMENT Disease Severity CLINICAL MANAGEMENT PATIENTS WITH MILD SYMPTOMS • Home Care • Appropriate supportive treatment, prevention of transmission. • Monitoring for clinical deterioration. • Isolation to contain or prevent virus transmission Isolation • Children should stay at home and be separated from other people in the household. • Well ventilated room, ideally with bathroom. • Assign one person who is in good health as primary caretaker of the child • The child should use dedicated dishes • Do not allow visitors until the child has completely recovered Isolation • Children 2 years of age and older should be properly instructed on how to wear a mask. • Children younger than 2 years old should NOT wear masks due to risk of suffocation. • Children older than 2 years old may use a face shield together with a face mask. Caregiver • Ideally, one person of good health, non-elderly. • Should always wear mask. Do not reuse. • Should weak gloves and dispose properly. Hygiene and Sanitation • Hand washing • Use disposable towel • Clean and disinfect surfaces frequently touched • Proper disposal Laundry and Disposal of Soiled Linen and Diapers • Waste bin with a lid should be placed in the child’s room. • Do not shake dirty linens; should be washed separately • Machine washing with warm water and laundry detergent is recommended. • Linens soaked in 0.05% chlorine for approximately 30 minutes • Wear disposable gloves and face masks when handling soiled items Home Therapies • Symptomatic Treatment • May start empiric antibiotics • Nebulization should be avoided unless otherwise indicated. • Vitamin D3 and Zinc from supplements may help bolster the immune system. • Steam inhalation has been shown to be ineffective. Home Therapies • Emotional and Mental Support Monitoring • The caregiver should be instructed to record the child’s symptoms • Bring the child to the nearest health care facility if symptoms worsen or if no improvement is seen in 2-3 days at home. PATIENTS WITH MODERATE, SEVERE OR CRITICAL SYMPTOMS All patients with moderate, severe or critical symptoms should be admitted. A. Inpatient Management • Full Personal Protective Equipment. • Standard, contact, and droplet precautions with eye and face protection. • Additional airborn precaution B. Diagnostics • RT-PCR- the preferred method for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection. -NPS/OPS; Saliva may be used. • Antigen Tests -Antigen tests detect the presence of viral proteins (antigens) -Relatively lower costs and faster turn around times. -Be used only for symptomatic patients, close contacts and those with history of exposure. -Sn: 80% and Sp:97% B. Diagnostics • Serologic Tests IgG/IgM had a sensitivity of *30.1% at day 1 to day 7 from the time of exposure *72.2% at 8 to 14 days *91.4% at 15 to 21 days *96% at 21 to 35 days Ancillary Laboratory Tests • Complete blood count (CBC) • Inflammatory markers - procalcitonin, D-dimer and interleukin-6 were found to be elevated. • ABG or pulse oximetry Imaging CXR-Chest x-ray • Recommended first line imaging modality in children suspected to have COVID-19 presenting with respiratory symptoms Imaging Chest CT Scan • Considered in patients with a worsening clinical course who are not responding appropriately Chest Ultrasound Pharmacologic Interventions for Children with Severe and Critical COVID-19 • Tocilizumab It is also used for the induction of the rapid reversal of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a form of cytokine storm caused by chimeric antigen T– cell (CART) immunotherapy.2 Since it can bind to the IL-6 receptor with high affinity, it can prevent IL-6 from binding to its receptor, rendering it incapable of immune damage to target cells and alleviating the inflammatory responses. DISCHARGE FROM ISOLATION AND DISCONTINUATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS • Discharge criteria for suspect, probable, and confirmed COVID-19 cases shall no longer entail repeat testing. Symptomatic • For symptomatic patients with mild symptoms: 10 days after symptom onset, inclusive of 3 days of being clinically recovered and asymptomatic • For symptomatic patients with moderate, severe or critical symptoms: 21 days from the onset of illness, inclusive of 3 days of being clinically recovered and asymptomatic DISCHARGE FROM ISOLATION AND DISCONTINUATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS • For asymptomatic immunocompetent -cases who test positive on RT-PCR and remained asymptomatic: 10 days after positive test for SARS-CoV-2. • Close contacts -who remain asymptomatic for at least 14 days from date of exposure can discontinue their quarantine without the need of any test. DISCHARGE FROM ISOLATION AND DISCONTINUATION OF TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS • For asymptomatic immunocompetent -cases who test positive on RT-PCR and remained asymptomatic: 10 days after positive test for SARS-CoV-2. • Close contacts -who remain asymptomatic for at least 14 days from date of exposure can discontinue their quarantine without the need of any test. • Follow-up in 2 to 4 weeks after discharge. • Once fully recovered, ensure that the child's immunizations are up to date. Consult the child's healthcare provider for proper scheduling.