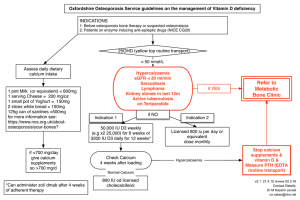
Chapter 9 Friday, November 1, 2019 10:16 Minerals → Major ○ >100 mg/day ○ Calcium ○ Phosphorus ○ Sulfur ○ Potassium ○ Sodium ○ Chloride ○ Magnesium → Trace ○ <100 mg/day ○ Iron ○ Zinc ○ Copper ○ Iodine ○ Selenium ○ Molybdenum ○ Fluoride ○ Manganese ○ Chromium → = 4% of body weight Regulatory & Structural Function → Part of hormones/enzyme → Transmit impulses → Maintain fluid balance → Support immune system → Cofactors in chemical reactions → Partner with other minerals → Bone formation/maintenance (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus) → → → → → Maintain fluid balance Support immune system Cofactors in chemical reactions Partner with other minerals Bone formation/maintenance (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus) Absorption & Bioavailability → Affected by nutrition ○ Deficiency ○ Increased need → Competition between minerals → Presence of binders ○ Phytates ○ Oxalates ○ Polyphenols ○ Others Calcium → Most abundant in the body → 99% in bone and teeth (structural, reservoir of calcium) → 1% in cells and fluids ○ Coagulation ○ Hormone secretion ○ Muscle contraction ○ Nerve transmission → Sources ○ RDA = 1000 mg/day (adults 19-50 years old) ○ UL = 2500 mg ○ Plants (reflect mineral in soil) ○ i.e. red soil in Hawaii - high in iron ○ Whole, unprocessed food ○ Animal products (dairy) ○ Tap water ○ Hard - calcium, magnesium ○ Soft - sodium ○ Leafy greens ○ Legumes ○ Supplements **High intake -- constipation, iron absorption interference, hypercalcemia ○ Soft - sodium ○ Leafy greens ○ Legumes ○ Supplements **High intake -- constipation, iron absorption interference, hypercalcemia → Blood levels managed by calcium homeostasis → Levels fall : ○ Parathyroid hormone released (from PT gland) ○ PTH stimulates active vitamin D production a. Increases calcium absorption in intestine b. Releases calcium from bone c. Decreases calcium excretion from the kidneys → Bone is constantly broken down and rebuilt for blood calcium maintenance and growth ○ osteoCLASTS cut away bone ○ osteoBLASTS build up bone → Higher peak bone density decreases osteoporosis risk → Bone Mass Phases ○ Male Peak - around 20 to 40 years; then gradual slope decrease with age ○ Female Peak - around 25 to 40 years; more dramatic loss around 50 years due to menopause; then gradual slope decrease with age Magnesium → 50 - 60% in bones → Functions ○ Transport ions for : § Muscle contraction § Impulse conduction § Maintaining heart rhythm ○ Extract energy from carbs, proteins, fats ○ Protein production ○ Vitamin D activation ○ Bone health → 60% of Americans do NOT meet recommendations → Symptoms of deficiency : rare, kidneys excrete less, body absorbs more → Increase risk of : ○ Osteoporosis ○ Atherosclerosis ○ Cancer ○ Diabetes → Increase risk of : ○ Osteoporosis ○ Atherosclerosis ○ Cancer ○ Diabetes ○ Hypertension → Sources ○ Present in small quantities in all groups → Excess intake from food = rare → Toxicity from supplements, laxatives, antacids = diarrhea, nausea, cramping