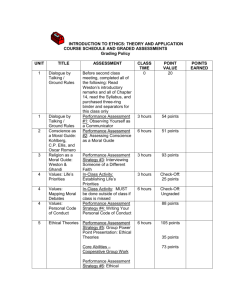
ILOILO DOCTORS COLLEGE, INC. COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES VISION MISSION CORE VALUES To be a Premiere Tertiary Instill Love for God, country and community; Integrity Educational Institution Deliver Quality Education and undertake relevant researches to ensure the growth and sustainability of the institution; Dependability Contribute to the attainment of national development goals of economic and social progress. Page 1 of 7 Compassionate Service COURSE CODE and Number: GE108 COURSE TITLE: ETHICS COURSE CREDIT: 3 UNITS CONTACT HOURS: 54 hours PRE-REQUISITE: CO-REQUISITE: COURSE CLASSIFICATION: PLACEMENT: COURSE INSTRUCTORS: Clydell S. Ofilas OBJECTIVES: At the end of the course, the student will be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Differentiate between moral and non-moral problems Describe what a moral experience is as it happens in different levels of human existence Explain the influences of Filipino Culture on the way students look at moral experiences and solve moral dilemmas Describe the elements of moral development and moral experiences Use ethical frameworks or principles to analyze moral experience Make sound judgments based on principles, facts, and the stakeholders affected Develop sensitivity to the common good Understand and internalize the principles of ethical behavior in modern society at the level of the person, society, and in interaction with the environment and other shared resources TEXTBOOK: Bulaong Jr., O., Calano, M.J., Lagliva, A., Mariano, M.N., Principe, J. D., ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation. Rex Bookstore, Incorporated, 2018. REFERENCES: - The Project Gutenberg eBook, Summa Theologica, Part I-II (Prima Pars Secundae), by Saint Thomas Aquinas, Translated by Fathers of the English Dominican Province Kant, I., Gregor, M. J., & Kant, I. (1998). Groundwork of the metaphysics of morals. Cambridge, U.K: Cambridge University Press. Kant, I., & Smith, N. K. (1929). Immanuel Kant's Critique of pure reason. Boston: Bedford. IDCCOLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES (GE108) SYLLABUS Updated (Month Year)Page 2 - - Plato. ( 1943). Plato's The Republic. New York :Books, Inc., https://faculty.mtsac.edu/cmcgruder/cmcgruder/sabbatical_aesthetics/republic.pdf http://history.as.uky.edu/sites/default/files/The%20Survival%20Lottery%20-%20John%20Harris.pdf https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/kant-moral/. https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/critique-of-pure-reason/259C2355B74458963EC285F53337AAF0 http://www.vidya-ashramvidyaorder.org/Media/I.let.03.09.pdf http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/physics.2.ii.html https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1467-839X.00054 COURSE DESCRIPTION Ethics deals with principles of ethical behaviors in modern society at the level of the person, society, and in interaction with the environment and other shared resources. (CMO 20 s 2013) Morality pertains to the standards of right and wrong that an individual originally picks up from the community. The course discusses the context and principles of ethical behavior in modern society at the level of individual, society, and in interaction with the environment and other shared resources. The course also teaches students to make moral decisions by using dominant moral frameworks and by applying a seven-step moral reasoning model to analyze and solve moral dilemmas. The course is organized according to the three (3) main elements of the moral experience: (a) agent, including context - cultural, communal, and environmental; (b) the act; and (c) reason or framework (for the act). PROGRAM OUTCOME FOR DENTAL GRADUATES aligned with COURSE OUTCOMES and PERFORMANCE INDICATORS PROGRAM OUTCOMES COURSE OUTCOMES A. Explain what is ethics and morality and their distinction. B. Identify what constitutes a moral act. C. Identify what are considered as ethical dilemmas. D. Identify the different sources of ethics and morality. E. Explain Consequential ethics F. Explain Natural law ethics. G. Explain Virtue ethics Define what ethics is and what morality is then discuss the distinction between the two concepts. Identify the requisites for an act to be considered as whether moral or not. Discuss what kind of questions can be considered as ethical questions. Provide the different sources of the two types of judgment. Explain the concept of consequentialism as discussed in the conept of utilitarianism pioneered by John Stuart Mill and Jeremy Bentham. Explain the concept of natural law, founded on Plato’s ideas and the felicifc calculus. Explain St. Thomas’ concept of virtue as the means and an end to achieve Eudaimonia as the telos of the human existence and the role of Grace of God IDCCOLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES (GE108) SYLLABUS Updated (Month Year)Page 3 Performanc e Indicators H. Explain Deontological ethics. I. Explain justice and fairness in relation to social justice. J. Show the application of ethics in relation to the Sikolohiyang Pilipino as the Divine initiative that would fulfill what man cannot. Explain the concept of categorical imperative as proposed by Immanuel Kant and emphasize, according to Kant, the autonomy of reason Synthesize what has been learned and explore how we can render justice to the society. Synthesize and apply Ethical standards to the Filipino context in reference to Sikolohiyang Pilipino KEY: I – Introduced: Basic concepts introduced; beginning skills taught (skills laboratory); P – Practiced: Concepts and principles presented with applications; actual case, skills lab, actual exposure with supervision; D – Demonstrated: I + P with skills acquisition; actual patient care including clinical scenarios; with minimal or no supervision DESIRED LEARNING OUTCOMES (after reading this chapter, the student should be able to:) Identify the ethical aspect of human life and the scope of ethical thinking; Define and explain the terms that are relevant to ethical thinking; Evaluate the difficulties that are involved in maintaining certain commonly-held notions on ethics; and Recognize and understand the interconnectedness of life in different aspects across generations Discuss the basic principles of utilitarian ethics; Distinguish between two utilitarian models: the quantitative model of Jeremy Bentham and the qualitative model of John Stuart Mill; and Apply utilitarianism in understanding and evaluating local and international scenarios. Recognize how Thomas Aquinas made use of ancient Greek concepts to provide a rational grounding to an ethical theory based on the Christian faith; Identify the natural law in distinction COURSE CONTENT/SUBJECT MATTER Ethical Dimension of Human Existence Value Sources of Authority Senses of the Self Intergenerational Responsibility Utilitarianism REFERENCE RESOURCES Time Allotted/Assessment ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Reflection paper Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Chapter Quiz Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Oposa vs. Factoran G.R. No. 101083 (224 SCRA 792) ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. “The survival lottery” by John Harris “The trolley problem” by Philippa Foot Natural Law Ethics ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. Summa Theologiae I Summa Theologiae I-II By St. Thomas of Aquinas Republic IDCCOLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES (GE108) SYLLABUS Updated (Month Year)Page 4 Prelim Exam from, but also in relation to, the other types of law mentioned by Aquinas: eternal law, human law, and diving law; and Apply the precepts of the natural law to contemporary concerns. by Plato Enneads By Plotinus Physics By Aristotle Discuss the meaning and basic principle of virtue ethics Distinguish virtuous acts from nonvirtuous acts; and Apply Aristotle’s ethics in understanding the Filipino Character. Discuss the basic principles of deontology; Apply the concepts of agency and autonomy to one’s moral experience; and Evaluate actions using the universalizability test. Virtue Ethics Identify the different factors that shape and individual in her moral decisionmaking; Internalize the necessary steps toward making informed moral decisions; Apply the ethical theories or frameworks on moral issues involving the self, society, and the non-human environment; and Contextualize learnings of ethical standards to the indigenous perspective through Enriquez’s Sikolohiyang Pilipino Synthesis ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. Nicomachean Ethics By Aristotle Deontological Ethics ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. Grundlegung zur Metaphysik der Sitten By Immanuel Kant Critique of Practical Reason By Immanuel Kant Critique of Pure Reason By Immanuel Kant ETHICS: Foundations of Moral Valuation By Bulaong et. al. Sikolohiyang Pilipino Virgilio Enriquez IDCCOLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES (GE108) SYLLABUS Updated (Month Year)Page 5 Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Reflection paper Chapter Quiz Midterm exam Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Reflection paper Chapter Quiz Class Discussion Powerpoint presentation Individual reading assignments 3 Hrs Reflection paper Chapter Quiz Midterm exam PREPARED BY: RECOMMENDING APPROVAL: FACULTY IN-CHARGE DEAN IDCCOLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES (GE108) SYLLABUS Updated (Month Year)Page 6 APPROVED BY: VICE-PRESIDENT FOR ACADEMIC AFFAIRS