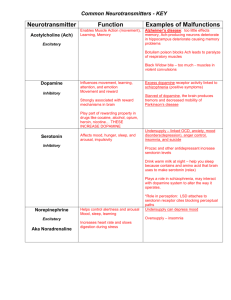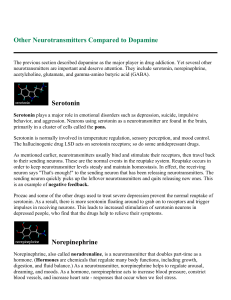
Biological and biochemical determinants of behavior Dr. Ahmed Elabwabi MD. Psychiatry Assistant professor at Albaha university The Brain The mind is considered a functional correlate of brain. Brain reaches its maximum number of synaptic connections and its greatest metabolic activity around age 3 or 4 Brain Hemispheric Hypothesis Right side of Brain: –Positive Emotions –Creative side of Brain Left side of Brain: –Role in Negative Emotions –Methodological, systematic side of Brain Neurons where the messages are delivered! Bio-chemical electrical impulses create a cascade of effects based on the message sent to various organ receptors of the body The role biochemical factors The role biochemical composition and reactions in humwn behavior • Mainly: • Genetics • Neurotransmitters. • Neurotransmitters The life of neurotransmitters In nerve endings there are sacs which contain neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter are automatically released when the electric signal reach the nerve ending. Neurotransmitter are the means of chemicals transmission between neurons. Once the chemical message is delvered one of two fates happen to neurotransmitters: – Degradation by monoamine oxidase enzyme – Reuptake to the presynaptic neurone to reture to its sacs. Categories of NTs Amino Acids – Glutamate (Glu) – GABA Biogenic Amines – Quaternary Amines Acetylcholine (Ach) – Monoamines Catecholamines – Dopamine (DA) – Norepinephrine (NE) Indolamines – Serotonin (5-HT) Categories of NTs. cont Neuropeptides –Opioid Peptides Enkephalins Endorphins Others. Neutransmitters and mental disorders Dopamine: when is in excess is related to psychosis e.g. schizophrenia Acetylecholine: is deficient is related to amnesia and dementia Norarnaline is related to depression Serotonin is related to depression Neurotransmitters and their correlation with some drugs • Dopamine - amphetamines, cocaine, ETOH • Serotonin - LSD, ETOH • Endorphins - opioids, ETOH • GABA - benzodiazepines, ETOH • Glutamate –ETOH • Acetylcholine - nicotine, ETOH Anandamide – Marijuana GABA and glutamate : The engine and the brake !! Glutamate The principal excitatory NT Biosynthesized as byproduct of cell metabolism Removed by reuptake Elevated levels neurotoxic 4 receptor types GABA (Gamma Aminobutyric Acid) • Principal Inhibitory neurotranmitter. • Biosynthesis: GAB is composed by biochemical changes to glutamate. Glu Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase (GAD) and B6 • Removed by reuptake • Has 2 receptor types GABA Drugs that bind to GABA GABAergic drugs Benzodiazepine (indirect agonist) –Probably also site for alcohol –Endogenous inverse agonist binds here Barbiturate (indirect agonist) THANK YOU