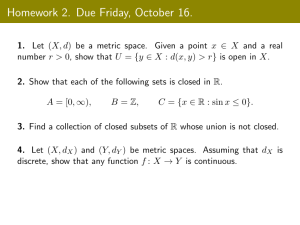
Question 1 What RF metric is often used at the output radio to indicate the output power level? Select one: a. mW b. SNR c. RSSI d. dBi Question 2 0 dBm is equal to 1 Watt Select one: True False Question 3 The metric ………. is absolute and the metric ………. is relative mW dB Question 4 What is defined as the difference between the signal strength and the noise floor? Select one: a. RCPI b. dBm c. RSSI d. SNR Question 5 What is defined as the output power from the radiating antenna including the gain of the antenna? Select one: a. EIRP b. SNR c. Intentional Radiator d. RSSI ANSWERS Question 1 What RF metric is often used at the output radio to indicate the output power level? a. mW Milliwatt (mW) is often used at the transmitter to indicate output power. dBm is also used at this point. The correct answer is: mW Question 2 0 dBm is equal to 1 Watt False 0 dBm is actually equal to 1 mW. The correct answer is 'False'. Question 3 The metric …mW... is absolute and the metric …dB... is relative mW is an absolute metric as is dBm. However, dB is relative as is dBi and dBd. The correct answer is: The metric [mW] is absolute and the metric [dB] is relative. Question 4 What is defined as the difference between the signal strength and the noise floor? d. SNR The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is the difference between the signal and the noise floor. With a noise floor of -95, for example, and a signal of -72, the SNR is 23 dB. The correct answer is: SNR Question 5 What is defined as the output power from the radiating antenna including the gain of the antenna? c. Intentional Radiator The Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) is the theoretical power that is delivered by an intentional radiator to an imaginary isotropic antenna that would produce an even distribution of RF power with the same amplitude actually experienced in the preferred direction of the actual antenna. How’s that for a technical definition. To make it simpler, it’s the output power from the intentional radiator (output power from the transmitter plus any gains or losses leading up to the connection point of the antenna) plus the directional gain provided by the antenna. The correct answer is: EIRP