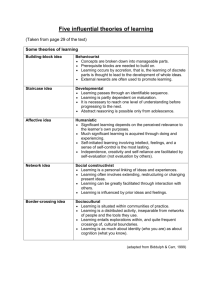
Chapter 3: Psychosocial Theories and Therapy 1. Explain the basic beliefs and approaches of the following psychosocial theories: psychoanalytic, developmental, interpersonal, humanistic, behavioral, existential and crisis intervention Psychoanalytic: Sigmund Freud o All human behavior is caused and can be explained (deterministic theory). o Believed that repressed (driven from conscious awareness) sexual impulses and desires motivate much human behavior o Dream analysis: involves discussing a client’s dreams to discover their true meaning and significance o Free association: therapist tries to uncover the client’s true thoughts and feelings by saying a word and asking the client to respond quickly with the first thing that comes to mind o Transference: occurs when the client displaces onto the therapist attitudes and feelings that the client originally experienced in other relationships o Countertransference: occurs when the therapist displaces onto the client attitudes or feelings from his or her past Developmental: Erik Erikson o Described 8 psychosocial stages of development o In each stage, the person must complete a life task that is essential to his or her well-being and mental health o Jean Piaget: Cognitive stages of development Believed that human intelligence progresses through a series of stages based on age, with the child at each successive stage demonstrating a higher level of functioning than a previous stages Interpersonal: Harry Stack Sullivan—Interpersonal and Milieu therapy o Believed that one’s personality involves more than individual characteristics, particularly how one interacts with others o Established 5 life stages of development—infancy, childhood, juvenile, preadolescence, and adolescence, each focusing on various interpersonal relationships o Milieu therapy: involved clients’ interactions with one another, including practicing interpersonal relationship skills, giving one another feedback about behavior, and working cooperatively as a group to solve day-to-day problems Humanistic theories: Maslow o Hierarchy of needs: the basic drives or needs that motivate people o Self-actualization: a person who has achieved all the needs of the hierarchy and has developed his or her fullest potential in life o Carl Rogers: Client-centered therapy Focuses on the role of the client, rather than the therapist, as the key to the healing process Behavioral theories: behaviorists believe that behavior can be changed through a system of rewards and punishments o Ivan Pavlov: Classical conditioning Behavior can be changed through conditioning with external or environmental conditions or stimuli o B.F. Skinner: Operant conditioning People learn their behaviors from their history or past experiences, particularly those experiences that were repeatedly reinforced *Believed that changing the behavior was what was important Existential theories: believe that behavioral deviations result when a person is out of touch with him or herself or the environment. *The person who is selfalienated is lonely and sad and feels hopeless o Cognitive therapy: focuses on the immediate thought processing—how a person perceives or interprets his or her experience and determines how he or she feels or behaves. o Albert Ellis: Rational emotive therapy Identified 11 “irrational beliefs” that peoples use to make themselves unhappy o Viktor Frankl: Logotherapy Based his beliefs in his observations of people in Nazi concentration camps during World War II His curiosity about why some survived and others did not led him to conclude that survivors were able to find meaning in their lives even under miserable conditions. Used in spirituality and grief counseling o Gestalt therapy: emphasizes identifying the person’s feelings and thoughts in the here and now. Believed that self-awareness leads to self-acceptance and responsibility for one’s own thoughts and feelings o Reality therapy: focuses on the person’s behavior and how that behavior keeps him or her from achieving life goals Crisis intervention: includes a variety of techniques based on the assessment of the individual. o Directive interventions: are designed to assess the person’s health status and promote problem-solving, such as offering the person new information, knowledge, or meaning o Supportive interventions: aim at dealing with the person’s needs for empathetic understanding, such as encouraging the person to identify and discuss feelings, serving as a sounding board for the person, and affirming the person’s self-worth. 2. Describe the following psychosocial treatment modalities: individual psychotherapy, group psychotherapy, family therapy, behavior modification, systemic desensitization, token economy, self-help groups, support groups, education groups, cognitive therapy, milieu therapy, and psychiatric rehabilitation Individual psychotherapy: is a method of bringing about change in a person by exploring his or her feelings, attitudes, thinking, and behavior Group psychotherapy: the goal is for members to learn about their behavior and to make positive changes in their behavior by interacting and communicating with other as a member of a group Family therapy: is a form of group therapy in which the client and his or her family members participate Education groups: goal is to provide information to members on a specific issue—for instance, stress management, medication management, or assertiveness training Support groups: are organized to help members who share a common problem cope with it Self help groups: members share a common experience, but the group is not a formal or structured therapy group Psychiatric rehabilitation: involves providing services to people with severe and persistent mental illness to help them to live in the community Systematic desensitization: can be used to help clients overcome irrational fear and anxiety associated with phobias Behavior modification: is a method of attempting to strengthen a desired behavior or response by reinforcement, either positive or negative Milieu therapy: involved clients’ interactions with one another, including practicing interpersonal relationship skills, giving one another feedback about behavior, and working cooperatively as a group to solve day-to-day problems 3. Identify the psychosocial theory on which each treatment strategy is based See answer 1 and 2 4. Identify how several of the theoretical perspectives have influenced current nursing practice An understanding of psychosocial theories and treatment modalities can help the nurse select the appropriate and effective intervention strategies to use with clients