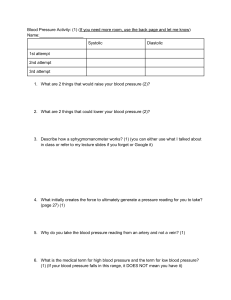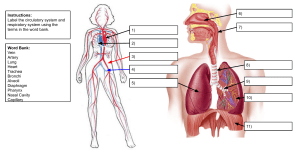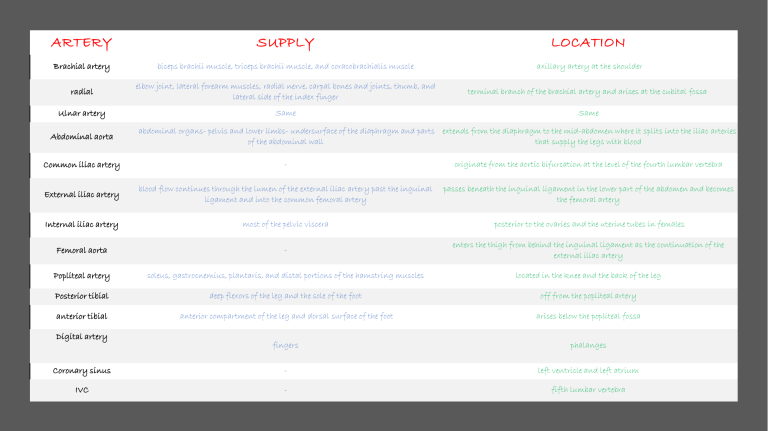
ARTERY SUPPLY LOCATION Brachial artery biceps brachii muscle, triceps brachii muscle, and coracobrachialis muscle axillary artery at the shoulder radial elbow joint, lateral forearm muscles, radial nerve, carpal bones and joints, thumb, and lateral side of the index finger terminal branch of the brachial artery and arises at the cubital fossa Ulnar artery Same Same Abdominal aorta abdominal organs- pelvis and lower limbs- undersurface of the diaphragm and parts extends from the diaphragm to the mid-abdomen where it splits into the iliac arteries of the abdominal wall that supply the legs with blood Common iliac artery - originate from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra External iliac artery blood flow continues through the lumen of the external iliac artery past the inguinal ligament and into the common femoral artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the abdomen and becomes the femoral artery Internal iliac artery most of the pelvic viscera posterior to the ovaries and the uterine tubes in females Femoral aorta - enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery Popliteal artery soleus, gastrocnemius, plantaris, and distal portions of the hamstring muscles located in the knee and the back of the leg Posterior tibial deep flexors of the leg and the sole of the foot off from the popliteal artery anterior tibial anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot arises below the popliteal fossa fingers phalanges Coronary sinus - left ventricle and left atrium IVC - fifth lumbar vertebra Digital artery veins Location Carry from TSV located on either side of the head. These veins start on the sides of the skull at a plexus. - Retromandibular vein EJV IJV Subclavian vein Brchiocephalic vein SVC cephalic Axillary vein Basilic vein Brachial vein Medial cubital vein deep vein of the face formed by the union of the superficial temporal and Carry from face and go to the heart maxillary veins begins near the mandibular angle, just below or within the substance of neck the parotid gland This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus blood from the skull, brain, superficial parts of the face, and the majority of the neck nerve continuation of the axillary vein, extends from the outer border of the first rib to upper extremities the sternal end of the clavicle located within the thorax head and neck and the arms middle mediastinum blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart In human anatomy, the cephalic vein is a superficial vein in the arm. It communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein at the elbow and is located in the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. the axillary vein is a deep vein of the upper limb that is formed by the union of the brachial and basilic veins. It starts at the lower border of the teres major muscle and ascends medially through the axilla towards the 1st rib, where it is continued by the subclavian vein medial aspect of the forearm at the wrist from the dorsal venous network of the hand- formed cephalic vein via the median cubital vein at the elbow palm of the hand from the arm, axilla and superolateral chest wall from the hand, forearm, and arm deep venous system of the upper limb axillary vein Its location is in the cubital fossa, on the anterior/flexor aspect of the elbow joint. cephalic vein + basilic Common iliac vein Great saphenous vein abdomen, at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebrae pelvis and lower limbs near the inside surface of the leg from the ankle to the groin It arises from the dorsal venous arch at the top (dorsum) of the foot and drains into the femoral vein, the main deep vein for the leg IVC fifth lumbar vertebra carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart.