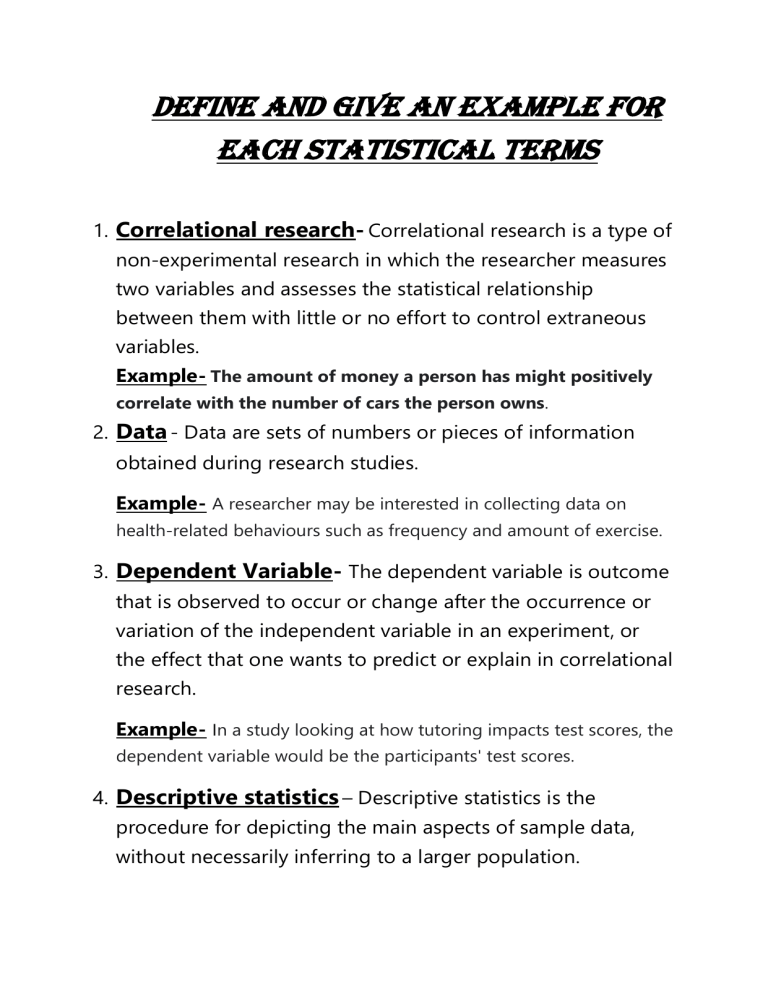
Define and give an example for each statistical teRMS 1. Correlational research- Correlational research is a type of non-experimental research in which the researcher measures two variables and assesses the statistical relationship between them with little or no effort to control extraneous variables. Example- The amount of money a person has might positively correlate with the number of cars the person owns. 2. Data - Data are sets of numbers or pieces of information obtained during research studies. Example- A researcher may be interested in collecting data on health-related behaviours such as frequency and amount of exercise. 3. Dependent Variable- The dependent variable is outcome that is observed to occur or change after the occurrence or variation of the independent variable in an experiment, or the effect that one wants to predict or explain in correlational research. Example- In a study looking at how tutoring impacts test scores, the dependent variable would be the participants' test scores. 4. Descriptive statistics – Descriptive statistics is the procedure for depicting the main aspects of sample data, without necessarily inferring to a larger population. Example- Percentages, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), measures of dispersion (range, standard deviation, variance), and correlation coefficients. 5. Independent Variables- The independent variable is the variable that is manipulated by the experimenter. Example- In an experiment on the impact of sleep deprivation on test performance, sleep deprivation would be the independent variable. 6. Inferential Statistics- Inferential statistics are broad class of statistical techniques that allow inferences about characteristics of a population to be drawn from a sample of data from that population while controlling the extent to which errors of inference may be made. Example- You might stand in a mall and ask a sample of 100 people if they like shopping at Sears. 7. Parameter-Parameter are the variables in a statistical model that is studied or used to explain an outcome or relationship. Example- The mean score on a national exam for a sample of colleges provides an estimate of this parameter in the population of colleges. 8. Population-Population is defined as total number of individuals in a given geographical area. Example- Everyone who could possibly be a participant in the study is part of the population. 9. Sample- Sample is a subset of a population of interest that is selected for study with the aim of making inferences to the population. Example- Let's say your population was every American, and you wanted to find out how much the average person earns. Time and finances stop you from knocking on every door in America, so you choose to ask 1,000 random people. This one thousand people is your sample. 10. SPSS-Statistical Package for the Social Sciences is a computer program used for statistical analysis and is also the name of the company that sells it. 11. Statistics -Statistics is the science of collecting , organizing , presenting , analysing and interpreting numerical data to assist in making more effective decisions. Example- Statistical techniques such as extreme values, mean, median, standard deviations, interquartile ranges, and distance formulas are useful in exploring, summarizing, and visualizing data. These techniques, though relatively simple, are a good starting point for exploratory data analysis. 12. Nominal Variable - Nominal variable is a variable whose possible values are unordered categories or labels. Example- Choice of college major is a nominal variable. 13. Descriptive Research -Descriptive Research is an empirical investigation designed to test pre-specified hypotheses or to provide an overview of existing conditions, and sometimes relationships, without manipulating variables or seeking to establish cause and effect. Example- A developmental psychologist who watches children on a playground and describes what they say to each other while they play is conducting descriptive research, as is a bio psychologist who observes animals in their natural habitats. 14. Qualitative Data -Qualitative Data are the information that is not expressed numerically. Example- The hair colors of players on a football team, the color of cars in a parking lot. 15. Quantitative Data -Quantitative Data are the information expressed numerically. Example - Population studies and samples to determine the prevalence of a specific condition .Statistical analysis of trends in mental health. Analysis of the frequency of certain conditions in particular families, populations, locations, and environments.