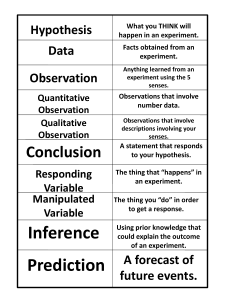
SCIENTIFIC PROCESSES Observing: Using the five senses to learn about an object or event, or to collect information about an object. quantitative - deals with numbers or amounts qualitative - deals with descriptions that cannot be expressed in numbers (using your senses) Classifying: Placing objects or events into groups based on common characteristics/attributes. Measuring: Determining the length (meters), area (A = L x W), volume (liters (liquid) OR V = L x W x H (regular shaped objects)), mass (grams) or temperature (⁰C) to describe and quantify objects. Communicating: Describing an object or event and/or sharing of ideas and results through writing and or speaking. Inferring and Predicting: Infer - Reasoning or drawing a conclusion about an object or event based upon an observation or prior knowledge Predict - making a statement or claim about what will happen in the future based on past experience or evidence Controlling Variables/Factors: Studying how attributes vary by manipulating variables. manipulated (independent) variable - a variable that has been purposely changed responding (dependent) variable - the variable that changed in response to the manipulated variable Representing data: Organizing measurements/data to make your information easier to use and interpret (graphs, tables, charts). Experimenting: Putting all the process skills in one activity. The Scientific Method Purpose/Question: What do you want to learn? Research: Find out as much about your topic as you can. Hypothesis: Predict the answer to the problem (If...then...because…). Experiment: Design a test to confirm or disprove your hypothesis. Analysis/Evaluate: Record what happened during the experiment. Conclusion: Summarize what you learned. Was your hypothesis correct or not AND why?