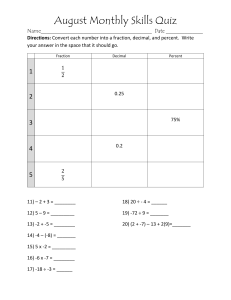
Autumn Algebra & Place Value sc Hegarty B1- Sequences I Can … Practice 1 Describe and continue a sequence diagrammatically Find the next two terms 2 Predict and check the next nth term (the nth position) What is the 20th terms? 3 Represent sequence in Tabular & graphical forms Draw this sequence in a Table and graphically 4 Continue a numerical linear sequence (arithmetic sequence)by identifying the term-to-term rule (common difference) Find the term to term rule 60, 74, 88, ___, ___ 1.5, 1.2, 0.9, ___, ___ 5 Explain the term-to-term Rule of numerical sequences in full sentences using mathematical words. How many sequences can you create beginning with 1, 2, Write the term-to-term rules in words 6 Continue numerical non-Linear sequence (geometric sequence or not with a common difference) Find the next two terms i) 1, 2, 4, 8, ___, ___ ii) 1, 3, 6, 10, ___, ___ 7 Find missing term within sequences Find the missing terms: i) 6, __, 14, __, 22, __ ii) 8000, ___, ___, 6500, ___ 8 Recognise special sequences: square numbers, cube numbers, Fibonacci sequence, triangular numbers List the first 5 cube numbers, List the first 5 Fibonacci numbers SC 1: Describe and continue a sequence diagrammatically Example add 2 more triangle to the end +3 +3 +3 add 1 triangle to each side +2 +3 • • +3 +4 +4 +5 Add 1 more triangle than previous to the right side Add 1 grey more triangle than previous to the right side Describe what is happening in the sequence and draw the next two terms How many circle, lines or squares in each term. Predict how many for the next 2 terms SC 2: Predict and check the next term Example 3, 5, 7 9 11 6, 12, 18 a) How many hexagon in each term in this sequence? b) How many will there be in the next term? 24 c) How many will there be in the 5th term? 30 d) Draw the terms to check your prediction. SC 3: Represent sequence in Tabular & graphical forms Example A sequence can be represented in multiple ways: 1 2 3 1) Complete the table a) b) Numerically Pictorial c) in a Table d) (1,4) (2,7) (3,10) 2) Complete the table and represent these sequence of a graph a) Graphically b) SC 4: Identifying the term-to-term rule (common difference) 1) Find the term-to-Term rule: Example 2) Find the term to term rule Linear Sequence have a common difference between each terms: 3) Find the term to term rule and complete the table Term-to-term rule: +4 Term-to-term ` rule -7 ` -7 11 4 ` ` -7 -7 SC 4: Continue a linear sequence 1) SC 6: Non Linear Sequence Linear Sequence: Arithmetic Sequence -6, 1, 8, 15, 22 +7 +7 +7 Non-Linear Sequence: Does not have a common difference Geometric sequence: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 2) Use the term to term rule to find the next two terms x2 x2 x2 Special sequences: Square numbers 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 +3 +5 +7 + triangle sequence 1, 3, 6, 10, 15 +2 +3 +4 +5 3) SC 7: Find missing term within a linear sequences 1) Find the missing terms Example 8 14 – 6 = 8 +3 +4 20 +6 +6 6 +4 19 - 7 =12 +6 26-14 12 ÷ 2 = 6 =12 19 - 4 = 15 11 15 +4 32 +4 12 ÷ 3 = 4 2) Use these numbers to make as many linear sequence with terms: SC 8: Special Sequences Good to know- Learn by heart Fibonacci Numbers Challenge: Find The 10th term Position to term Rule Hegarty B2- Algebraic Notation I Can … Practice 1 288 Use function machine (number) to find output Find the Output: 2 Use inverse operation on function machine to find input Find the Input: 3 157 158 Use correct algebraic notation for adding, multiplying and dividing 𝑺𝒊𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒊𝒇𝒚 𝑖) 𝑎 + 𝑎 + 𝑎 = = 4 Use function machine (algebra) to solve equations Find in the Input/output 5 Identify the functions needed to produce the outputs Find the Function: 6 155 178 Substitute values for the variables to calculate the value of the expression. Substitute n = 5 into the expression: ii) 2 × 𝑎 × b = iii) a ÷ 𝑏 Find the first three term of sequence 3n + 2 B2- Algebraic Notation I Can … Practice Solution 1 Use function machine (number) to find output Find the Output: 2 Use inverse operation on function machine to find input Find the Input: 3 Use correct algebraic notation for adding, multiplying and dividing 𝑺𝒊𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒊𝒇𝒚 𝑖) 𝑎 + 𝑎 + 𝑎 = 𝟑𝐚 ii) 2 × 𝑎 ×= 𝟐𝐚𝐛 𝒂 iii) a ÷ 𝑏 = 𝒃 Use function machine (algebra) to solve equations Find in the Input/output 4 5 Identify the functions needed to produce the outputs Find the Function: 6 Substitute values for the variables to calculate the value of the Substitute n = 5 into the expression: expression. 𝒊) 𝟓𝟐 = 𝟐𝟓 𝐢𝐢)𝟐𝟎 − 𝟓 = 𝟏𝟓 𝒊𝒊𝒊) 𝟐 × (𝟓 + 𝟒) = 𝟏𝟖 𝒊𝒗) 𝟐 × 𝟓 + 𝟖 = 𝟏𝟖 Find the first three term of sequence 3n + 2 SC 1: Use function machine (number) to find output 1. Complete the one step / two step function machine Example One step FM 2. Complete the three step function machine Two step FM 3. 4. SC 2: Use inverse operation on function machine to find input 1. Use inverse function to find the input for one step FM Example 3 2. Use inverse function to find the input for two step FM 1 (𝟓 − 𝟐) x 4 = 12 3. Write down the input z when y = 17 Sequence: multiply by 2 then add 6 Position 1 2 3 4 6 term 8 10 12 14 16 Term-to-term rule + 2 In algebra, we use particular Algebraic Notation: Good To Know notation or different calculations. Identify: True for all values of a&b SC 3: Use correct algebraic notation for + ̶ X ÷, 1) Simplifying by collecting like terms Example Collecting Like Terms 2) Find equivalent terms by simplifying Multiplying algebraic Terms 3) Simplify fractions 𝐚 𝐚 ÷𝟑= 𝟑 Dividing algebraic Terms 3÷𝐚= 𝟔×𝐚 𝟔𝐚 ÷ 𝟑 = = 𝟐𝐚 𝟑 𝟑 𝐚 4) Spot the mistake SC 3: Use correct algebraic notation for + ̶ X ÷, Match the notation on the left to the description on the right A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q 15 SC 4: Use function machine to solve equations 1. Complete the Function machine to solve these equations: Example Using Inverse Function Machine to Solve equations 2. Use Function machine to solve these equations: 3. Write down an expression for the output y when the input is 𝒙 4. Complete the function machine so that 𝒚 = 𝟒(𝒙 = 𝟓) 5. Think of a number, double it, add 4. The answer is 24. Use function machine to find the original number: 𝒙 = 𝟑𝟒 SC 5: Find the function needed for the output Find the rule Example Problem Solve to identify the function 14 3 2. Find the missing function +10 10 𝟓 × 𝟐 = 𝟏𝟎 → 𝟏𝟎 +10 = 𝟏𝟎 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟏𝟎 = Completer the function machine using inverse BIDMAS: -4 X2 𝑦=2 𝑥−4 -4 ÷2 𝑦= 𝑥 −4 5 3. Find the missing function SC 6: Substitute values for the variables to calculate the value of the expression Example 1. Evaluate these expression by substitution a =2 Replace 𝒙 with 5 2. If a= -2 and b = 6. Find the value of these expression: i) 2a + b iv) 4ab ii) 6a -b iii ) 3a – 2b v) a + 3ab vi) a² + b² 2. Find missing terms of sequence sc Hegarty B3- Equivalence I Can … 1 Understand the meaning of equality 2 Solve one step equation using + /- using family fact 3 Solve one step equation using x / ÷ using family fact 4 156 5 6 Identify like terms Understand the meaning of equivalence 157 Simplifying Collecting like term Practice SC 1: Understanding equality Equality: Both side of an equation are equal (have the same value) equal Equality: Left Side = Right Side 8+3=7 +4 8+2≠7+4 8 x 3 = 12 + 9 + 3 1) Which of these are not equal? 2) Write integers in the box to make the calculation correct. Provide 2 different solutions SC 2: Solve one step equation using + /- using family fact 1) Draw the bar model for these equations Example Addition family fact: 7 + 3 = 10 3 + 7 = 10 10 − 3 = 7 10 − 7 = 3 2) Use family fact to solve these equations 𝑥 + 14 = 20 14 + 𝑥 = 20 20 − 𝑥 = 14 𝟐𝟎 − 𝟏𝟒 = 𝒙 𝑤+9=𝑡 9+𝑤 =𝑡 𝒕 −𝒘=𝟗 𝑡−9=𝑤 3) Ken thinks of a number. He subtracts 78 from his number and gets the answer 137. Show this information as an equation and solve the equation to find Ken’s number. How else could you represent the information? SC 3: Solve one step equation using x/÷ using family fact 1) Draw the bar model for these equations Example Multiplication family fact: 4 × 6 = 24 6 × 4 = 24 24 ÷ 6 = 4 24 ÷ 4 = 6 4 × 𝑎 = 28 a × 4 = 28 28 ÷ 𝑎 = 4 𝟐𝟖 ÷ 𝟒 = 𝒂 4×𝑏 =𝑎 b×4=𝑎 𝒂÷𝒃=𝟒 𝑎÷4=6 2) Use family fact to solve these equations a) 2𝑥 = 10 𝑏) 5𝑥 = 187 𝑑) = 10 𝑒) =2 𝑐) 12 = 4𝑥 𝑓) 4 = 3) Marta thinks of a number. She divides her number by 7 and gets the answer 42 Write this information as an equation. Solve your equation to find Marta’s number. Draw a bar model 32 𝑥 SC 4: identifying like terms 1) Which term are like terms: Example To find like terms: 1) cover coefficient 2) rearrange the variables in alphabetical order. 3) If the combined variables look the same, then they 2) State which terms are like terms 𝟑𝒙𝟐 𝟑𝒙𝒚 𝟐𝒚𝒙 𝟑𝒙𝟐 𝟑𝒙𝒚 𝟐𝒙𝒚 Like terms 2) Group like terms together Equivalence: two expression have the same value (Writing the same expression in different ways) Equality verses Equivalence 𝟐 𝒙 + 𝟒 ≡ 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟖 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟒 = 𝟒𝒙 Only true when 𝒙 = 𝟏 true for all values of 𝒙 1) Each of these expression should sum to 15 m Equivalence: Writing the expression in a different way: 2) Which 2 expression are equivalent to 𝟑𝒙 + 𝟔 6 + 3𝑥 3 𝑥+2 3(𝑥 + 6) 𝒙+𝒙+𝒙+𝒙 → 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟑𝒙 → 𝒙 + 𝟒𝒙 → 𝟔𝒙 − 𝒙 3) Complete the table equivalence of substitution: If 𝒙 = 𝟒 𝒕hen 4 can replace the 𝒙 in an equation 2𝒙 + 6 2 x 𝟒 + 6 = 14 4) W𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐞 𝟒 𝐞𝐱𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐭𝐨 𝟐𝟒𝒙 + 𝟒 SC 6: Simplifying Collecting like term 1) Simplify by collecting like terms 2) Write three expressions with 5 terms that simplifies to: 𝟐𝒙 − 𝒙𝒚𝟐 + 𝟒 3) Identify which answer is correct s Hegarty B4 – Place Value Practice I Can … 1 13 45 write and represent the numbers up to million in several ways Complete these representations to show the same number 2 3 4 5 14 13 Identify place value convert integers between numeral and words work out the intervals and complete a number line round to the nearest 10, 100, 1000 Write down the value of 5 in : 305, 052, 867 Write Two hundred and three thousand, fifty-four 6 130 137 14 46 14 46 410 7 8 9 17 Round to 1 significant figure There are 2000 students in a school. What I the maximum and minimum student possible? Round to 1 sf: 2940, 0.0249 Compare and sort numbers using symbols <≤>≥=≠ Order a list of numbers Put in ascending Order: Find the range from a group of values Find the range of these numbers: 68 63 79 111 104 Find the median from the list of these numbers: 68 63 79 111 104 What as a power of 10: 1000 × 102 × 10−3 × 100 = Write in standard form: 2.5 × 106 × 2.2 × 104 = 10 409 Find the medium from a list of values 11 121 125 12 122 123 writing multiple of 10s in the form 10𝑛 writing and interpreting numbers in standard Form Example 1 403 021 603 SC 1: I can represent numbers in multiple ways Complete these representations so they all show the same number. One billion, four hundred and three million, twenty-one thousand, six hundred and three 1,403,021,603 = 1,000,000,000 + 400,000,000 + 3,000,000 + 20,000 + 1,000 + 600 + 3 Represent these numbers in multiple format a) 1 073 080 529 b) Eighty-eight million, eighty-eight thousand, five hundred and twelve c) Half a million Example Example 1 403 021 603 SC SC 1: 1: II can can represent represent numbers numbers in in multiple multiple ways ways Complete these representations so they all show the same number. Zero point 7 = 1,000,000,000 + 400,000,000 + 3,000,000 + 20,000 + 1,000 + 600 + 3 1,403,021,603 1. Represent this numbers in multiple format 2. Put in expand form 3. Complete the number bond Example 1) State the value of 6 in 630, 604.6 600,000, 600 and 6th 2) State the place value of 7 in : 7, 354, 708.172 million, hundred, hundredth (100th) 3) Write down half million more than 600, 128 500,000 + 600, 128 = 1, 100, 128 Write down the numbers that are: a) Three million more than 917 000 000 b) The sum of three hundred million and 700 000 000 c) 30 000 000 more than nine hundred and sixty million d) The difference between one billion and seventy-five million SC 2: identify place value Example SC 3: convert between numerals and words Eighty-eight million, eighty-eight thousand, five hundred and twelve 88,088,512 10, 703, 009, 009.22 Ten billion, seven hundred and 3 million, nine thousand and nine point two-two Write in figures: a) Thirty-five thousand million b) One and a half billion c) Two hundred and three thousand d) Half a million e) One billion, ten thousand and one f) Seven thousandths g) Seventeen thousandths h) Seven hundred thousandths i) Zero point three five j) Seventy-two hundredths k) Nought point nought seven l) Nought point nought three m) Two hundredths n) Fifty hundredths o) One tenth Write in words: a) 1, 234, 567. b) 1, 303, 220, 000 c) 9, 095, 002, 003 d) 23. 789 e) 0.45 f) 2.035 g) 9.10 SC 4:work out the intervals and complete a number line Fluency 1) Estimate where the arrow is Fully label the following number lines 0 20 20 0 20 0 Can you work out the values of the intervals for the following number lines 1) 00 60 60 0 0 0 60 60 0 Reasoning 1) -12 2) 3) Problem Solving Compare the two number lines below. What's the same? What's different? 1) 9 Can you work out the interval for the following number line? Give a reason for your answer. 10 Why count the number of spaces in between the marks on a number line, rather than the marks? Can you create 4 different number lines with different scales that have a start point of 0 and an end point of 30? Challenge – can you create one where the interval is a decimal? 28 0 20 2) 3) Can you create a question using a number line where the answer for the interval would be 2.5? Can you come up with 3 questions you could ask about the number line below? 7 25 Mark 7.45, 7.48 and 7.425 on the number line I can work out intervals on a number line Fluency 1) Estimate where the arrow is Fully label the following number lines 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 8 4 12 -10 30 -20 -20 -40 20 10 0 -60 0 1) Can you work out the values of the intervals for the following number lines Interval =10 Interval =20 00 10 30 40 50 60 0 20 20 40 Interval = 12 Interval = 15 0 15 30 60 45 0 24 12 Reasoning 1) -12 28 1) 3) 20 40 60 48 60 Can you create 4 different number lines with different scales that have a start point of 0 and an end point of 30? There are lots of different answers. Ask your teacher to check. Challenge – can you create one where the interval is a decimal? There are lots of different answers. Ask your teacher to check. 9 2) Both intervals are 7, but the second number line is not the 7 times table 2) 20 Problem Solving Compare the two number lines below. What's the same? What's different? 0 36 16 Can you create a question using a number line where the answer for the interval would be 2.5? Can you work out the interval for the following number line? Give a reason for your answer. There are lots of different answers. Ask your teacher to check. 10 Why count the number of spaces in between the marks on a number line, rather than the marks? The spaces give you the E.g. Fully label the number line, work out the interval etc. 3) Can you come up with 3 questions you could ask about the number line below? No, you need 2 numbers to be able to work out the interval correct interval. 7 25 0.06 0.07 0.01 0.068 0.2 0.4 0.08 0.10 0.6 Example Round to nearest 10 Round to nearest 100 SC 5:round to the nearest 10, 100, 1000 The school kitchen wants to order enough jacket potatoes for lunch. Potatoes come in sacks of 100. How many sacks do they need for 766 children? A number rounded to the nearest 10 is 550. What is the smallest possible number it could be? Example Round to 1 sf SC 6:Round to 1 significant figure Estimate the answer To one significant figure, the population of Scotland is given as five million. What is the greatest possible population of Scotland? What is the least possible population? Example SC 7:Compare and sort numbers using symbols <≤>≥=≠ 𝟔𝟒𝟏 < 𝟔𝟓𝟎𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟏 𝟔𝟒𝟓𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟒 > 𝟔𝟒𝟎𝟎. 𝟎𝟏𝟎 𝟔𝟒𝟓𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟒 ≠ 𝟔𝟓00.001 Example Arrange in order from smallest: 201, 197, 210, 192, -208 Put in ascending order: 0.5, 0.45, 0.435, 0.46, 0.501 SC 8:Order a list of numbers Solution Arrange in order from smallest: 201, 197, 210, 192, -208 Put in ascending order: 0.5, 0.45, 0.435, 0.46, 0.501 SC 8:Order a list of numbers Type equation here.Example SC 9: Find the range from a group of values SC 10:Find the median from a group of values 3 numbers with no mode, mean 7 and range 4 Find Range Find Median SC 11:writing ordinary numbers in the form 10𝑛 Fluency Write the following numbers as a power of 10 a) 100 b) 10,000 c) 1,000 d) 1,000,000 e) 0.1 f) 0.00001 g) 0.01 h) 0.0000001 e) 10−1 f) 10−3 g) 10−6 h) 100 Write the following as an ordinary number a) 103 b) 104 c) 108 d) 101 Choose the largest number from each of the following pairs of numbers a) 103 and 10,000 b) 1,000 and 104 c) 0.01 and 10−1 d) 0.1 and 10−5 Reasoning 1) Problem solving For each of the following statements, decide whether the statement is true or false. If a statement is false, explain why. a) 105 is the same as 100,000 1,000,000,000 is the same as 1010 c) 10−3 is the same as 0.01 0.0000001 is the same as 10 Fill in the question marks to make the following statements correct. a) 10? is equivalent to 100,000 b) ? is equivalent to 10−2 b) d) 1) 7 2) Convince me that a hundredth is the same as 0.01 which is the same as 𝟏𝟎−𝟐 c) 10? is equivalent to 0.0001 2) Is multiplying by 𝟏𝟎−𝟏 the same as dividing by 10? Prove your answer with some examples. 3) Is dividing by 𝟏𝟎𝟐 the same as calculating 10% of the number? Prove your answer with some examples? I can convert between powers of 10 and ordinary numbers Fluency Write the following numbers as a power of 10 a) 100 𝟐 b) 10,000 𝟒 c) 1,000 𝟑 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎 d) 1,000,000 e) 0.1 f) 0.00001 g) 0.01 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎 𝟔 𝟏𝟎 −𝟏 −𝟓 −𝟐 h) 0.0000001 𝟏𝟎−𝟕 Write the following as an ordinary number a) 103 b) 104 1,000 10,000 c) 108 d) 101 100,000,000 10 e) 10−1 f) 10−3 0.1 0.001 g) 10−6 0.000001 h) 100 1 Choose the largest number from each of the following pairs of numbers a) 103 and 10,000 b) 1,000 and 104 c) 0.01 and 10−1 Problem solving Reasoning 1) For each of the following statements, decide whether the statement is true or false. If a statement is false, explain why. True c) d) 1) Fill in the question marks to make the following statements correct. a) 10𝟓 is equivalent to 100,000 b) 0.01 is equivalent to 10−2 a) 105 is the same as 100,000 b) 10 1,000,000,000 is the same as 10 False it should be 𝟏, 𝟎𝟎𝟎, 𝟎𝟎𝟎, 𝟎𝟎𝟎 is the same as 𝟏𝟎𝟗 10−3 is the same as 0.01 c) 10−𝟒 is equivalent to 0.0001 2) False it should be 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 is the same as 0.001 0.0000001 is the same as 10 d) 0.1 and 10−5 7 False it should be 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟏 is the same as 𝟏𝟎−𝟕 2) Convince me that a hundredth is the same as 0.01 which is the same as 𝟏𝟎−𝟐 Students need to show all of their workings to convince. 3) Is multiplying by 𝟏𝟎−𝟏 the same as dividing by 10? Prove your answer with some examples. −𝟏 True 𝟏𝟎 is equivalent to 0.1. 𝟒𝟎 × 𝟎. 𝟏 = 𝟒 and 𝟒𝟎 ÷ 𝟏𝟎 = 𝟒 Is dividing by 𝟏𝟎𝟐 the same as calculating 10% of the number? Prove your answer with some 𝟐 examples? False 𝟏𝟎 is equivalent to 100 which is the same as calculating 1%. Standard Form Notes Commutative: :Can multiply in any order Put all these numbers into standard form and then write them in ascending order SC 12: working with standard form Rounding and Estimates Round the following numbers to the given decimal place. Round the following numbers to the given place value. Round the following numbers to the given significant figure. a) 0.53 (1 d.p.) a) 12 ( nrst 10) a) 58 (1 s.f.) b) 0.885 (1 d.p.) b) 6.8 (integer) b) 0.359 (1 s.f.) c) 10.085 (2 d.p.) c) 3527 (nrst 100) c) 13.489 (2 s.f.) d) 2.645 (2 d.p.) d) 85540 (nrst 1000) d) 0.00485 (2 s.f.) e) 0.999 (1 d.p.) e) 950 (nrst 1000) e) 0.106 (1 s.f.) f) 0.099 (2 d.p.) ANS f) 0.8714 (nrst 0.1) ANS f) 0.0999 (2 s.f.) ANS Rounding and Estimates Round the following numbers to the given decimal place. Round the following numbers to the given place value. Round the following numbers to the given significant figure. a) 0.53 (1 d.p.) 0.5 a) 12 ( nrst 10) 10 a) 58 (1 s.f.) 60 b) 0.885 (1 d.p.) 0.9 b) 6.8 (integer) 7 b) 0.359 (1 s.f.) 0.4 c) 10.085 (2 d.p.) 10.09 c) 3527 (nrst 100) 3500 c) 13.489 (2 s.f.) 13 d) 2.645 (2 d.p.) 2.65 d) 85540 (nrst 1000) 86000 d) 0.00485 (2 s.f.) 0.0049 e) 0.999 (1 d.p.) 1.0 e) 950 (nrst 1000) 1000 e) 0.106 (1 s.f.) 0.1 f) 0.8714 (nrst 0.1) 0.9ANS f) 0.0999 (2 s.f.) 0.1 ANS f) 0.099 (2 d.p.) 0.10 ANS mr-mathematics.com 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Hegarty skill 1 58 81 73 75 82 57 74 76 83 59 61 46 60 63 B5 – FDP I Can … Practice Representing Fraction and percentages as diagrams Converting Fractions ( 1 1 1 1 1 1 . , , , , ) 10 100 4 5 50 20 to decimal and percentages Link fraction to division Convert Complex Fractions- Decimals - Percentage- Representing fraction and decimal on number line Represent and interpret Simple pie chart (application) Identify and use equivalent fractions Sort FDP in a give order Improper Fractions Information: Representing Fraction decimals & Percentages 0 . 2 1 20 percent means 20 per 100 𝟐𝟎 𝟏𝟎𝟎 1 4 0.25 1 8 0.125 1 100 0.01 1 1000 0.001 1 Decimal 1 1 10 5 0.10 0.20 Percentage 10% 20% 24% 12.5% 1% 0.1% 100% Fraction 1.00 SC 1: Representing 10th and 100th as diagrams 1) Exmple 2) Multiple representation 3) Represent 120 hundredths using hundred square 4) 5) SC 2: Converting FDP when denominator is a factor of 100 Remember factors of 100 Fraction 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝒓𝒆𝒘𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒆: 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Fraction Bus stop division 𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒊𝒗𝒂𝒍𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝒇𝒓𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝒏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Numerator ÷ denominator Place value 𝟒𝟐𝟕𝟔 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 Percentage = numerator Percentages Decimal Percentages x 100 Examples i) Fraction Decimal Percentage Decimal ÷ 100 11 1000 9 𝑖𝑖) 20 𝟕 𝟏𝟎 𝟖𝟏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 15 𝑖𝑖𝑖) 500 𝟗 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝟐 𝟓 𝟔 𝟐𝟓 0.04 60% 𝟕 𝟐𝟓𝟎 SC 3/4: Converting FDP Division fraction Bus stop division method Fraction 𝒓𝒆𝒘𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒆: 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Place value Equivalent fraction Percentages Decimal ÷ 100 Examples: Calculate as a division and write as a fraction Decimal Percentage 𝟔𝟒𝟑 634 ÷ 4 = 𝟒 158.5 4|643.0 = 158.5 𝟐𝟔𝟑 𝟒 Fraction Division 𝟏𝟔𝟖 ≡ 𝟏𝟖𝟔 ÷ 𝟔 𝟔 186÷ 𝟔 ≡ 𝟔 | 𝟏𝟖𝟔 21 ÷ 4 81 ÷ 2 162 ÷ 4 84 ÷ 8 241 ÷ 8 2947 ÷ 7 24.1 SC 4 Representing fraction, decimal and Percentage on number line 0.1 ≡ 0.10 𝟏 𝟏𝟎 ≡ ≡ 𝟏𝟎% 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Complete the number lines SC 4 Representing fraction, decimal and Percentage on number line 0.1 ≡ 0.10 𝟏 𝟏𝟎 ≡ ≡ 𝟏𝟎% 𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Complete the number lines SC 5: Application – Pie chart What fraction is shaded a) What fraction of the kids painted? b) What fraction of the kids read? c) What percentage of the kids danced? a) What fraction of the kids painted? b) What fraction of the kids read? c) What percentage of the kids danced? Challenge SC 6: Identify and use equivalent fractions Example Simplify fraction by dividing by HCF Equivalent Fraction: multiply /divide numerator and denominator by same value Equivalent Fraction SC: 7 Comparing fraction 𝟖 × 𝟖 𝟖 ≡ 𝟒𝟎 < 𝟓 × 𝟓 ≡ 𝟏𝟓 𝟒𝟎 Put in ascending order SC 8:Order FDP Example Step 1 : Convert to decimal 0.42 0.44 0.429 decimal Step 2 : Put in order 0.42 0.429 0.44 0.5 ascending order Step 3 : Give answer in original format 42 % 𝟑 𝟕 𝟒 𝟗 0.5 original format Improper Fraction Mixed number improper fraction notes Convert to improper Fraction Convert to Mixed Number SC 9: Work with improper fraction Convert to Number Mixed Improper Fraction Mixed number Complete the number line Convert to improper Fraction Find the term-to-term rule and complete the sequence 𝟏) 𝟎. 𝟒, 𝟎. 𝟏𝟏, 𝟐) 𝟖𝟎%, 𝟔 , 𝟓 𝟏. 𝟔, 𝟐, 𝟑. 𝟏, 𝟕𝟕 , 𝟐𝟎 𝟐𝟑 𝟓 𝟒𝟕 𝟑) , 𝟐𝟎 𝟎. 𝟏𝟖, 𝟎. 𝟐𝟓 Write division as fracti Convert between FDP Shade farctions FDP on number line Compare FDP Do Now: End Point: LL) What fraction of the square is shaded? Give your answer as 3 different fraction. Which number is below LW) Complete the cycle to convert: Fraction Decimal Percentage 4 6 Fraction ↑ Percentages LM) Sort in ascending order 344.01 304.41 314.04 341.04 310.44 340.14 Decimal 0.84 𝟑 𝟒 1.205 5 4 Explain how you know What percentage of the area is shaded? SC 9:FDP Application Example Factors 100? SC: 6 Equivalent fraction Find 3 fractions that are equivalent End Point: Which number is below 4 6 0.84 𝟑 𝟒 1.205 5 4 SC: 6 Equivalent fraction SC 3: Converting Complex fractions Example Denominators is not a factor of 100 1) Use bus stop division to find decimals 0.22 … 2 = 2 ÷ 9 → 𝟗 𝟐 .𝟎 𝟎 9 2) decimal × 100 = 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒈𝒆 𝟎. 𝟐𝟐 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 = 𝟐𝟐% Fraction 1 9 1 11 2 3 1 8 3 22 decimal Percentage 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 SC 2: Converting FDP (𝟏𝟎 . 𝟏𝟎𝟎 , 𝟒 , 𝟓 , 𝟐𝟓 , 𝟐𝟎) Example Denominators = Factors of 100: 1 x 100 2 x 50 4 x 25 5 x 20 10 x 10 𝑛 1) Use equivalent fraction to write in form100 3 3 5 𝟏𝟓 ≡ × = 20 20 5 𝟏𝟎𝟎 2) When in form 𝑛 100 → 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒐𝒓 = 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒈𝒆 𝟏𝟓 = 𝟏𝟓% 𝟏𝟎𝟎 3) Convert % to decimal by ÷ 100 𝟏𝟓 ÷ 𝟏𝟎𝟎 = 𝟎. 𝟏𝟓 Fraction Percentage Decimal 1 10 1 100 1 2 = 5 10 1 20 1 4 3 4 1 25 1 2 1 50 10 =10% 100 0.1 SC 2&3: FDP conversion Example Denominator = Factors of 100: 1 x 100 2 x 50 4 x 25 5 x 20 10 x 10 SC 8: Division as fractions 1) Write as a fraction and simplify Example 𝟏𝟐 ÷ 𝟑 = 𝟒 𝑎) 32 ÷ 8 = 𝑏) 27 ÷ 3 = 𝑐) 35 ÷ 5 = d) 7 ÷ 21 = e) 6 ÷ 30 = f) 4 ÷ 36 = g) 3.5 ÷ 7 = h) 3.6 ÷ 6 = i) 15 ÷ 0.3 = ≡ 𝟏 𝟏𝟐 × 𝟏𝟐 = =𝟒 𝟑 𝟑 𝟏 ÷𝟑= 6 24 = 3 12 0.4 2 𝑐) ⇒ 5 2 . 0 = 𝟎. 𝟒 5 = 2) Write as a division and solve 9 𝑎) ⇒ 3 56 14 𝑎) 56 ÷ 8 = = =𝟕 8 2 b) 6 ÷ 24 = 𝟏 𝟑 𝟏 𝟒 1 𝑏) ⇒ 9 3 𝑐) ⇒ 5 sc Hegarty B1- Sequences I Can … Practice 1 Describe and continue a sequence diagrammatically Find the next two terms 2 Predict and check the next nth term (the nth position) What is the 20th terms? 3 Represent sequence in Tabular & graphical forms Draw this sequence in a Table and graphically 4 Continue a numerical linear sequence (arithmetic sequence)by identifying the term-to-term rule (common difference) Find the term to term rule 60, 74, 88, ___, ___ 1.5, 1.2, 0.9, ___, ___ 5 Explain the term-to-term Rule of numerical sequences in full sentences using mathematical words. How many sequences can you create beginning with 1, 2, Write the term-to-term rules in words 6 Continue numerical non-Linear sequence (geometric sequence or not with a common difference) Find the next two terms i) 1, 2, 4, 8, ___, ___ ii) 1, 3, 6, 10, ___, ___ 7 Find missing term within sequences Find the missing terms: i) 6, __, 14, __, 22, __ ii) 8000, ___, ___, 6500, ___ 8 Recognise special sequences: square numbers, cube numbers, Fibonacci sequence, triangular numbers List the first 5 cube numbers, List the first 5 Fibonacci numbers Do Now LL) End Point 0.01, 0.05, 0.09 Fill in the gaps a) find the next two terms b) Use Double line to represent sequence as fraction & percentage LW) 𝟔 𝒘𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒆 𝒂𝒔 𝒂 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒈𝒆 𝟓𝟎 LM) 𝑺𝒊𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒊𝒇𝒚 𝒆𝒙𝒑𝒓𝒆𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝒃𝒚 𝒄𝒐𝒍𝒍𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒍𝒊𝒌𝒆 𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒎𝒔 𝟒𝒙 + 𝟑𝒙𝒚 − 𝟐𝒙 − 𝟔𝒚𝒙 i) How many objects (circle, squares..) in each term 5 rectangle , 9 rectangle, 13 rectangle, ii) How many object is in the next term. 17 rectangle, iii) What would the next term look like? iv) Predict How many objects (circle, squares..) will be in the 6th term v) Describe the Sequence (use term-toterm) Add 4 rectangle to the end vi) Complete the table example Position (n) 1 Position Position (n) (n) 11 Number Number Number of.. of.. 55 of.. Rule 2 22 3 33 4 44 5 55 6 66 99 13 17 21 25 1) Find the term –to - term Rule 2) Find the next two terms: Connection to other topics 1) Use Function machine to find Rule 2) Represent the sequence on a table 3) Represent the sequence on graph End Point 0.01, 0.05, 0.09 a) find the next two terms b) Use Double line to represent sequence as fraction & percentage Hegarty B2- Algebraic Notation I Can … Practice 1 288 Use function machine (number) to find output Find the Output: 2 Use inverse operation on function machine to find input Find the Input: 3 157 158 Use correct algebraic notation for adding, multiplying and dividing 𝑺𝒊𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒊𝒇𝒚 𝑖) 𝑎 + 𝑎 + 𝑎 = = 4 Use function machine (algebra) to solve equations Find in the Input/output 5 Identify the functions needed to produce the outputs Find the Function: 6 155 178 Substitute values for the variables to calculate the value of the expression. Substitute n = 5 into the expression: ii) 2 × 𝑎 × b = iii) a ÷ 𝑏 Find the first three term of sequence 3n + 2 Solve with fact family Solve with function machine Find the value of unknown Find the value of unknown s Hegarty B4 – Place Value Practice I Can … 1 13 45 write and represent the numbers up to million in several ways Complete these representations to show the same number 2 3 4 5 14 13 Identify place value convert integers between numeral and words work out the intervals and complete a number line round to the nearest 10, 100, 1000 Write down the value of 5 in : 305, 052, 867 Write Two hundred and three thousand, fifty-four 6 130 137 14 46 14 46 410 7 8 9 17 Round to 1 significant figure There are 2000 students in a school. What I the maximum and minimum student possible? Round to 1 sf: 2940, 0.0249 Compare and sort numbers using symbols <≤>≥=≠ Order a list of numbers Put in ascending Order: Find the range from a group of values Find the range of these numbers: 68 63 79 111 104 Find the median from the list of these numbers: 68 63 79 111 104 What as a power of 10: 1000 × 102 × 10−3 × 100 = Write in standard form: 2.5 × 106 × 2.2 × 104 = 10 409 Find the medium from a list of values 11 121 125 12 122 123 writing multiple of 10s in the form 10𝑛 writing and interpreting numbers in standard Form Write the numbers then put it in order 327, 619 741,093 2, 936,081 542,730 2,357 327, 619 517,409 542,730 741,093 1,406,271 8,901,473 8,901,473 1,406,271 517,409 2,357 2, 936,081 Rounding Round to nearest Whole number: Round to 1 significant place: