Uploaded by
Francis Kababa Cruz Kaumba
Common Lab Apparatus & Uses: Chemistry Equipment Guide
advertisement

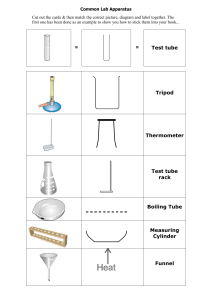
Chemistry Common Laboratory Apparatus and its Uses Many types of apparatus are used for scientific work in laboratories. however, we have compiled all possible common and comprehensive lists of 20 laboratory apparatus and their uses. they enable us to carry out experiments successfully and make accurate measurements or observations. all common laboratory apparatus should be drawn in outline only and in their correct proportions. 50 common Laboratory Apparatus/ Lab Equipment List: Alcohol burner Aspirator Bunsen burner Beakers Burette Barometer Burette clamp Buchner funnel Balance scale Conical or titration flask Crucible tong Condenser china dish (Evaporating Dish) Crucible with cover Chart Clay Triangles Desiccator Dry-cell battery Dropper Dissecting set Erlenmeyer flask Funnel Forceps Flat bottomed flask Filter paper Friability tester Glass funnel Glass tubing Indicator Iron stand Iron Clamp Iron ring Litmus paper Level Measuring cylinders Microscope Mortar and pestle Measuring flasks Magnifier Magnet No of weights pH meter Pulley Pipette Protractor Pipet Bulb Rubber stopper Reagent bottle Ring Clamp Rubber tubing Stand bath Spatula Syringe Stirring rod Separatory funnel Stethoscope Stopwatch Speedometer Test tube rack Tripod Tripod stand Test tube holder Test tube stand Telescope Test tube brush Tuning fork Tape Thermometer Tongs Wire gauze Wash bottle Watch glass NOW! Some of the items of common laboratory apparatus used in the laboratory are shown below. Names and functions of the apparatus used in the laboratory are: Bunsen burner A Bunsen burner is a source of heat or mechanical appliances for which absolute safety is required while using Bunsen Burner. it is linked to a flammable gas source. Mostly a knob is used to adjust the gas flow amount and a pivot collar that manages airflow. Both the knob and collar must be adjusted to get an excellent flame for heating things. Tripod stand It is usually made of stainless steel or Aluminium having three supporting legs. The apparatus to be heated is placed on the tripod stand. It is mainly used to support or hold the beakers or flasks during the experiments. A Bunsen burner is placed underneath the tripod stand due to its height. Wire Gauze It is the iron wire gauze piece posted with asbestos in the center. It is placed on the tripod stand so that the flame does not touch the glass apparatus directly, reducing the danger of its breaking. Test Tubes A test tube is a glass tube with one end closed and the other end open. The closed-end is in a round shape. Test tubes are used in laboratories to hold small samples. They are mainly used for qualitative comparison and assessment. A very commonplace to see test tubes is the biochemistry lab. When large numbers of the sample are needed to be compared and tested, these test tubes are used to make this easier. They are also easily covered or capped with a glass or rubber stopper. Safety Tip: Never heat a covered or capped test tube. Beakers Beakers are a very common laboratory instrument and are widely useful in the laboratory as a reaction container. they are also used for holding liquid and solid samples or catch liquids from different titrations or filtrates from filtering operations. A beaker is a simple can in most labs. It is used for heating, stirring, and mixing chemicals. Most beakers have spouts on their rims to easy pouring. uses of Beakers in laboratory They also usually have lips around their rims and markings to measure the volume of liquid they contain. They are not a piece of proper equipment to measure liquids. Beakers are available in a wide range depending on their sizes, such as 50cm3, 100cm3, 250cm3, or 500cm3 are available. Beaker Tongs Have you ever needed to grab something hot? Or pick up a beaker that is heavy and full of liquid? If so, then these beaker tongs are perfect for your needs! They are made out of stainless steel with silicone grips at the ends. These tongs will allow you to safely handle anything in your lab without getting burned or spilling your experiment! Titration flasks It is also known as a Conical Flask. The Erlenmeyer flask was titled in 1861, after its inventor. It has a slim neck and widens toward its base. This allows easy swirling and mixing of the flask without too much possibility of spilling. The narrow opening also allows the use of a glass or rubber stopper. It can comfortably be clamped to a ring stand as well as shaken or heated easily. Once again, the numberings on the side are meant mainly for estimation not for precision. Safety Tip: A significant safety tip here is to never heat the flask while it is covered. This causes pressure build-up that results in an explosion. Funnels A lab funnel is also like any other funnel but it was specially designed to be used in a laboratory. They are made up of glass or plastic and have either a long stem or a short stem, depending on the purpose, they are needed for. There are a lot of sizes that can be chosen depending upon the amount of liquid that needs to go through them easily and quickly. Funnels are of different sizes 3cm, 5cm, 8cm etc. Evaporating Dish (China Dish) It is a small dish made of porcelain used for evaporating and concentrating the dilute solutions. It is available in different sizes. Graduated or Measuring cylinders This is an essential measuring tool for the volume of any liquid. There are a lot of markings, up and down the whole length of the container with special increments. Graduated cylinders are of many sizes. The smaller they are in size or diameter, the more exact or accurate the volume measurements will be. When reviewing the volume from a graduated cylinder, you will consider that the liquid seems to have some indentation. The liquid around the edges of Graduated Cylinders will be higher than the liquid in the center. This is known as a meniscus. Keep the cylinder at a leveled surface to properly read the volume. They are also available in different sizes 5cm3, 10cm3, 20cm3, 50cm3, 100cm3 and 1000cm3. Stirring Rod A stirring Rod or glass stirring rod is used for mixing and stirring different chemicals. it is made up of solid glass (borosilicate or ) having rounded edges slightly thick and longer than a soda water straw. Stirring Rods are often 10 to 45 cm long with almost a half-centimeter in diameter. it is also available in the triangular paddle, flat paddle, or round button shape. Measuring flasks OR Volumetric flasks A volumetric flask is a round flask with a flat bottom and long neck. Volumetric Flask is used to measure the exact volume of liquids. There is a short line on the neck that hints at how far to fill the flask. Special caps are available that will not let anything in or out through the flask. These are available in different sizes i.e., 100cm3, 250cm3, 500cm3 and 1000 cm3. Just Remember: The temperature affects the volume; therefore always avoid using liquids that will vary in temperature (for example hot water that will cool). Buret Burets are often used for the addition of a precise and accurate volume of liquids. with the use of burets, you can measure or determine the volume of liquids up to nearly 0.01 mL. These are normally attached to a ring stand with a clamp. A buret is also like a glass tube that is open from the top and becomes a narrow pointed opening at the bottom side. Right above the bottom opening; there is a stopcock. This stopcock can be turned to control the released amount of liquid. There are also certain markings along the length of the buret that indicates the volume of any liquid present in them. A buret is especially used for the extremely accurate addition of liquids. By slightly adjusting the stopcock, the amount of releasing liquid can be slowed down to a single drop every few seconds. Buret is one of the most accurate tools in the laboratory. To determine the added amount of liquid in solution, write down the readings, how much is present initially in the buret. Then when you were finished adding liquids, write down how much liquid is left. Now, Subtract the final amount of liquid from the initial amount and you have the exact volume of liquid that is added. Forceps Forcep is derived from the Latin word forcipes used for holding and grasping small objects in laboratories. they are used when things are picked up in bulk or when large fingers are unable to collect little and tiny things. besides this, “forceps” is a very common word in the medical field. in the common world, forces are referred to different names like pliers, tweezers, clip, stongs, or clamps, etc. basically there are two major types of forceps: 1. Non-disposable forceps 2. Disposable forceps Pipettes as Laboratory Apparatus There is a large variety of pipettes that are designed to accomplish many specific goals. However, they all are for measuring the exact volume of liquids and then placing liquids into the other containers. Generally available sizes are 10cm3, 20cm3 and 25cm3. Thermometer The temperature of a substance is measured using a thermometer. The temperature in the laboratory is usually measured in units of degrees Celsius (˚C). Striker The Bunsen burner is lightened by the striker. Watch glasses A watch glass circular convex or concave rounded piece of the glass often used to hold a small amount of solid or liquid, to evaporate a liquid, while being weighed, and for many other purposes. Watch Glasses are also used for different purposes like evaporation. it can also work as a lid for a beaker to prevent dust from entering a beaker. in the chemistry Lab, two types of Watch glasses are used such as glass watch glasses and plastic watch glasses. both types have various sizes and varieties in the market. the glass type is more famous than the plastic type. Most glass type is reused and plastic-type are disposable i.e., for one-time use. Pipet Bulb Pipet Bulb is used to draw different liquids into the pipet. Iron stand It is used for hanging (thermometer), clamping/holding (burette, round bottom flask, etc.). Ring Clamp ring clamp is used with a ring stand to hold different types of glassware like funnel or beaker. Wash Bottle Nowadays polythene wash bottles are used in the laboratory for storing distilled water for various operations such as transferring precipitates from a container to the filter paper or washing the precipitates. When the bottle is pressed with hand, water comes out through the jet in the form of a fine stream. Flat bottomed – Florence flasks, AKA boiling flasks It is also known as a boiling flask. Florence flask contained a round bottom with a long neck. It is used for holding liquids and can easily be heated and swirled. It can also be capped by glass or rubber stoppers easily. Once again, safety edict that this flask never is heated when covered or capped with a stopper. It build-up pressure and can result in an explosion. Scoopula Scoopula is often used to transfer solids to different locations. Erlenmeyer Flasks you can use an Erlenmeyer flask to place liquid samples or to catch filtrates as a laboratory apparatus. Utility Clamp Utility Clamp resembles a couple of scissors often used to secure glassware to a ring stand. it has a screw in the middle that is used to widen the adjustments between two-prong. ring stand or retort stand is attached to it. round laboratory glassware is held e.g flasks and beakers etc. with the help of Utility Clamp. there are three major parts of Utility Clamp: clampdown 2-prong adjust metal rod Ring Stand Ring Stand is helpful as a laboratory apparatus for holding or clamping different lab glassware so that it does not fall down. Droppers they have been used for the addition of liquids/solutions in the shape of drops. Test tube stand It is made of wood, polythene, or steel on which test tubes can be placed in an upright position. Test Tubes are normally held in a test tube rack. Test Tube Racks are specifically designed for this purpose. If these test tubes become risky to touch with bare hands (in a case due to heat or some other reason); test-tube tongs are used to move them. Test Tube Clamp On a recent trip to the laboratory, I was able to see and learn about an incredible invention: the test tube clamp. This product is so cool because it can be used as a stand to hold up your test tubes without spilling any liquid. The clamp also has two clamps that can be used as handles for carrying around multiple test tubes at once. The best part of this invention is that it saves both time and space in labs because scientists no longer need as many lab hands or other furniture such as stands. It’s amazing how one simple tool could make such a huge difference in research! Clay Triangles as Laboratory Apparatus the use of Clay Triangles is seen as very rare but here we can’t miss an opportunity to describe every single opportunity to discuss every apparatus. Clay Triangles are placed on a ring that is attached to a stand that provides support to funnel, evaporating dish or crucible, etc. Balance Ballance is Used to measuring different small masses. Crucible The word “crucible” brings to mind images of fiery molten metal, the beating heart of a furnace. The crucible is an instrument used in chemistry laboratories for heating substances until they melt or vaporize. It can also be used for cooling heated material by removing it from the fire and submerging it in water. But why did this device get its name? Well, when materials are heated slowly over time, impurities will separate out and rise to the top – like what happens with metals during smelting. Crucible Tongs The crucible tongs are a laboratory apparatus that is used to take the hot metal from the furnace into the mold. It’s an important tool for a chemist, and it can be made using one of two different methods: forging or casting. Alcohol Burner alcohol burner is an important part of laboratory equipment. it is used to produce an open flame using alcohol as a burning source. Syringe A syringe is an apparatus in the chemistry laboratory used for measuring out liquids. It also has many other uses in the medical field that are outside of this blog post’s scope. List of Measurement Equipment used in Laboratory MASS Triple beam balance Centigram balance Platform balance Analytical balance TEMPERATURE Alcohol thermometer Mercury thermometer Digital thermometer VOLUME Burette Florence flask Beaker Graduated cylinder Pipette Distilling flask Erlenmeyer Volumetric flask Dropper Lab Instruments and Tools Name List in Laboratory Microscope Graduated Cylinder Test Tube Volumetric Flask Bunsen Burner Thermometer Florence Flask Some common SAFETY EQUIPMENT used in lab-ware Eyewash Mask Goggles Safety shower Gloves Lab-Grown Fire extinguisher Fire blanket Fume hood Spill neutralizer First aid kit DIFFERENT EQUIPMENT USED FOR ANALYSIS in Laboratory Apparatus CHROMATOGRAPHY IC HPLC GC SPECTROSCOPY XRFS OES AAS UV/VIS AES FT-IR What are some HEAT SOURCES used in the Common laboratory apparatus? Alcohol lamp Bunsen burner Hotplate General instructions for Using Common laboratory apparatus Conduct yourself in a responsible manner at all times in the laboratory. Always wear a lab coat and safety goggles in the lab. Girls must use scarves and close hair when working in the laboratory. Never work alone in the laboratory. Do not bring eatables in the laboratory. Never taste or smell any compound or gas, to smell gases always waft the fumes or gas towards your nose. You must report immediately on an accident or breakage. Develop a habit to put things back at their proper place after use. Do not mix the chemicals. Always take care of yourself and your calls fellows while working in the laboratory. Do not work on chemicals for which you do not have instructions. Read the FIRST-AID instructions. Conclusion In order to work with chemicals, chemists must have the right apparatus. The lab needs a fume hood for safety and ventilation, as well as a laboratory sink and drainboard. Chemists also need equipment like scales and balances for weighing chemicals or samples of materials; beakers, flasks, and test tubes for mixing solutions; Bunsen burners and hot plates for heating substances; measuring cylinders and pipettes for transferring liquids from one container to another; thermometers to measure temperature changes in substances over time; pH meters to measure acidity levels in solutions; graduated cylinders or burets for measuring volumes of liquid (liters/milliliters); pressure gauges such as manometers or vacuum gauges used in atmospheric chemistry experiments. 15 Comments Torri at Thanks to the great guide Reply stitch onsie at I think the admin of this web site is genuinely working hard for his website, for the reason that here every data is quality based material. Reply Dawood at We always try for quality based material. Thank You for Comments. Enjoy. Reply sloth onsie at I’ll immediately clutch your rss feed as I can not to find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me recognise so that I may subscribe. Thanks. Reply Admin at We have no E-Mail Subscription Link or Newsletter Service yet. please, bookmark our website. Thanks of comment! Reply edius eustace at Ilove it Reply Renate at I spent a lot of time to find something like this Reply Admin at We hope that it fulfill your needs. Thank You. Reply Lola Joyce at Judging what I read, I could say the information was accurate. But judging what I didn’t read.. shouldn’t there be things like tubes and pipes? Part of the basics ain’t they? Reply admin at the question is, they are the part of laboratory apparatus or not? if yes then they should be on the list. thanx Reply Mohammad Asif at Great work Sir. keep it up. Reply admin at Thank you so much sir, Reply Seyi stanley at Thanks sir Reply tanveer hussain at welcome Reply Yusuf at Great and real facts. Keep it up. Reply