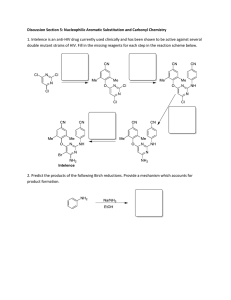
1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Okuyama & Maskill: Organic Chemistry Chapter 25: Multiple Choice Questions Results You have answered 0 out of 20 questions correctly. Your percentage score is 0%. Question 1 Which of the following statements is wrong? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: c) IR absorption is attributable to transitions between rotational energy levels of whole molecules. Feedback: For a general discussion on electromagnetic radiation and spectroscopy, see pp. 561-3. Transitions between molecular rotational energy levels are induced not by IR radiation, but by microwave radiation. Question 2 Which is the correct order of increasing wave number of the stretching vibrations of (1) C-H (alkane), (2) O-H (alcohol), (3) C=O (ketone), and (4) C≡C (alkyne)? You did not answer the question. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 1/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Correct answer: c) (3) < (4) < (1) < (2) Feedback: The stretching vibrations for C-H and O-H bonds are in the ranges 2850-2960 cm-1 and 3200-3600 cm-1, respectively, while those for C=O and C≡C are about 1700 and 2200 cm-1, as summarized on p. 565. Question 3 How many signals does the aldehyde (CH3)3CCH2CHO have in 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: b) three 1H signals and four 13C signals Feedback: We need to find non-equivalent hydrogen and carbon atoms. This aldehyde has three kinds of hydrogen and four kinds of carbon atoms. For proton and carbon chemical shifts, see pp. 572-4 and 586, respectively. Question 4 Which of hydrogens a-d in the following molecule gives a triplet signal in a normal 1H NMR spectrum? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 2/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions c) hydrogen c Feedback: A triplet signal results from the spin-spin coupling with two equivalent adjacent hydrogen atoms. For spin-spin splitting (coupling), see pp. 576-9. Question 5 Which hydrogen of 1-chloropent-2-ene shows the largest chemical (downfield) shift in its NMR spectrum? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: b) the H on either C2 or C3 Feedback: Hydrogens on unsaturated carbons generally have larger chemical shifts than those on saturated carbons (p. 547). Question 6 Which carbon of (a)-(d) of hex-3-en-2-one shows the largest (most downfield) chemical shift in the NMR spectrum? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: b) C2 Feedback: C1 and C6 are the methyl carbons while C2 is a carbonyl and C4 is a vinylic carbon. The carbonyl carbon shows the largest (most downfield) shift of the four, as summarized on p. 586. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 3/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Question 7 Which of the following statements regarding IR spectroscopy is wrong? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: a) Infrared radiation is higher in energy than UV radiation. Feedback: For electromagnetic radiation, see pp. 561-2, and for IR spectroscopy, pp. 564-8. Question 8 Which of the following statements regarding NMR spectroscopy is wrong? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: c) Chemical shifts are larger when shielding effects are greater. Feedback: For the notation of chemical shifts, see pp. 572-3, and for spin-spin splitting, see pp. 576-7. Question 9 Which of the following statements regarding mass spectrometry is wrong? You did not answer the question. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 4/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Correct answer: d) Molecular ion peaks always have even-numbered values of m/z. Feedback: The molecular mass of a molecule containing one nitrogen atom, for example, is an odd number of atomic mass units, so its molecular ion peak has an odd numbered m/z ratio; statement (d) is wrong. Question 10 Which of the following statements is wrong? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: a) A conventional mass spectrometer employs high energy UV radiation. Feedback: See pp. 589-90 for a general description of mass spectrometry. Since a conventional mass spectrometer detects positively charged species according to their abundances, small amounts of impurities do not much affect the analysis of the main compound. Question 11 Absorption of radiation in the UV range attributable to n→π* electronic transitions is characteristic of which of the following types of compounds? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: b) Unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Feedback: https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 5/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions An n→π* electronic transition is the promotion of an electron from a nonbonding into a π* antibonding orbital, so is possible only for compounds with nonbonding electrons (lone pairs) as well as a π-electron system. Question 12 Which of the following statements is wrong. You did not answer the question. Correct answer: c) Water is a good solvent for recording IR spectra of water-soluble compounds. Feedback: For an introduction to IR spectroscopy, see pp. 564-5. Solvents for spectroscopic measurements should not absorb appreciably in the relevant spectroscopic range. Water has strong IR absorption and, furthermore, the commonest IR cells are made of NaCl which is soluble in water. Question 13 Which is the correct order of increasing wave number of the stretching vibrations of (1) C-H (alkane), (2) C-H (alkene), (3) C-H (alkyne), and (4) C-H (arene)? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: d) (1) < (4) ≈ (2) < (3) Feedback: The stronger the C-H bond, the higher the frequency (and hence wavenumber and energy) of its stretching vibration. The bond strength increases in the order, C(sp3)-H < C(sp2)--H < C(sp)-H, which is the opposite order of the bond lengths (p. 35). See also Table 25.2, p. 565. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 6/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Question 14 How many signals does the unsaturated ketone (CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH=CH2 have in 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: b) six 1H signals and six 13C signals Feedback: We need to identify non-equivalent hydrogen and carbon atoms. This unsaturated ketone has six kinds of hydrogen and six kinds of carbon: note that the two hydrogen atoms on C1 are not equivalent whereas the two methyls at the other end of the molecule are. For proton and carbon chemical shifts, see pp. 572-4 and 586, respectively. Question 15 Which of the following statements in the context of 1H NMR spectroscopy is true? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: a) Arene C-H chemical shift (δ) values are greater than simple alkenes C-H chemical shift values because of the aromatic ring current. Feedback: The aromatic ring current (see p. 574) induces a magnetic field which opposes the external (applied) field in the centre of the aromatic ring but which reinforces it outside the aromatic ring where the arene C-Hs are. Consequently, a lower applied field is needed to bring the outer hydrogens into resonance than would be the case without the field induced by the aromatic ring current, and this corresponds to downfield shift (greater δ values). https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 7/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Question 16 Which carbon of (a)-(d) of hex-3-en-2-one has the smallest (most upfield) chemical shift in the NMR spectrum? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: d) C6 Feedback: C1 and C6 are methyl carbons (both sp3 hybridized) while C2 is a carbonyl and C4 is vinylic (both sp2). Of the two methyl carbons, C1 is more strongly affected (more downfield) by the carbonyl group, so the signal for C6 will be most upfield (smallest chemical shift) of the four. Question 17 Which of (a)-(d) indicates the multiplicities for hydrogens on C1, C3, and C4 of butanone attributable to spin-spin coupling in its 1H NMR spectrum. You did not answer the question. Correct answer: c) Hs on C1, singlet; Hs on C3, quartet; Hs on C4, triplet. Feedback: The proton signal splits into n + 1 peaks when the adjacent carbon has n equivalent hydrogens (p. 576). C1 is the isolated methyl, and C3 is the methylene linked to C4 (methyl) in butanone; Hs on C1, C3, and C4 are a singlet, a quartet, and a triplet, respectively. Question 18 https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 8/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Which of (a)-(d) indicates the correct order of carbon chemical shifts of the four carbons of the following compound. You did not answer the question. Correct answer: a) CMe < C2 < C3 < C1 Feedback: The chemical shift of the carbonyl carbon (C1) is the largest (most downfield), and those of the alkene carbons are the next largest (see p. 586). Of C2 and C3, the β carbon (C3) is the more strongly influenced by the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl. Question 19 Which of the following statements regarding electron-impact mass spectrometry is true? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: d) A meaningful mass spectrum can sometimes be obtained on a very small sample of an impure compound. Feedback: For the electron-impact mass spectrometric method, see pp. 589-90. A mass spectrum records relative abundances of the molecular cation and its fragment cations by their mass-to-charge ratios, m/z. The base peak corresponds to the most abundant cation which is not usually the molecular cation. Mass spectrometric signals of impurities do not normally obscure the significant peaks of the main compound; in fact, mass spectrometry is a useful technique for identifying impurities. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 9/10 1/13/22, 9:49 PM Oxford University Press | Online Resource Centre | Multiple Choice Questions Question 20 Which of the following statements regarding mass spectrometry is false? You did not answer the question. Correct answer: d) Structurally isomeric alkanes cannot be distinguished by low resolution mass spectrometry. Feedback: For mass spectra of typical compounds containing common functional groups, see pp. 590-8. Copyright © Oxford University Press, 2016. All Rights Reserved. https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/chemistry/okuyama/student/mcqs/ch25/ 10/10