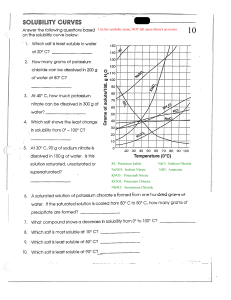
TOMSK POLYTECHNIС UNIVERSITY ENGLISH FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Teacher’s Book Recommended for publishing as a study aid by the Editorial Board of Tomsk Polytechnic University Draftsmen T.S. Petrovskaya, I.E. Rymanova, A.V. Makarovskikh Tomsk Polytechnic University Publishing House 2012 МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «НАЦИОНАЛЬНЫЙ ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКИЙ ТОМСКИЙ ПОЛИТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ» АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК ДЛЯ ИНЖЕНЕРОВ-ХИМИКОВ Книга для преподавателя Рекомендовано в качестве учебного пособия Редакционно-издательским советом Томского политехнического университета Авторы-составители Т.С. Петровская, И.Е. Рыманова, А.В. Макаровских Издательство Томского политехнического университета 2012 3 УДК 811.111:66(075.8) ББК Ш143.21-923+Ш143.21-91 А64 А64 Английский язык для инженеров-химиков. Книга для преподавателя: учебное пособие / авторы-сост.: Т.С. Петровская, И.Е. Рыманова, А.В. Макаровских; Томский политехнический университет. – Томск: Изд-во Томского политехнического университета, 2012. – 59 с. Книга для преподавателя, входящая в учебно-методический комплекс по профессиональному английскому языку «English for Chemical Engineers», содержит ответы к заданиям, а также методические рекомендации по эффективной организации учебного процесса. Предназначена для преподавателей, обучающих студентов химико-технологического направления, изучающих английский язык на основе многоуровневого подхода. УДК 811.111:66(075.8) ББК Ш143.21-923+Ш143.21-91 Рецензенты Кандидат педагогических наук, доцент декан факультета иностранных языков ТГПУ И.Е. Высотова Кандидат филологических наук доцент кафедры ЛиП ИМОЯК ТПУ Д.Ф. Мымрина © Составление. ФГБОУ ВПО НИ ТПУ, 2012 © Петровская Т.С., Рыманова И.Е., Макаровских А.В., составление, 2012 © Обложка. Издательство Томского политехнического университета, 2012 4 CONTENTS Unit 1 Engineering career……………………………………………………………..……6 Unit 2 Engineering education……………………………………………………………..10 . Unit 3 Are you good for this job?........................................................................................11 Unit 4 Engineering ethics…………………………………………………………………14 Unit 5 Company structure and corporate culture…………………………………………19 Unit 6 Chemical engineering……………………………………………………………...24 Unit 7 Objects of chemical engineering…………………………………………………..26 Unit 8 Functions and applications of chemical objects…………………………………...30 Unit 9 Chemical industry markets………………………………………………………...33 Unit 10 Materials in chemical industry…………………………………………………...41 Unit 11 Technological process in chemical industry: tools and equipment ……………...44 Unit 12 Safety at work…………………………………………………………………..47 Unit 13 Resource saving………………………………………………………………….50 Unit 14 Waste disposal……………………………………………………………………52 Unit 15 Innovations in chemical engineering…………………………………………….55 5 UNIT 1 Engineering Career Before you start Divide the class into groups of 3 or 4 SS (students). Give the groups one minute to list as many achievements in engineering as they think are the most important for the mankind. Elicit their achievements with the whole class and write the most popular on the board. Quotation Get the SS to read the quotation. Put SS in pairs or small groups and tell them to define the stages of any engineering activity: o a figment of the imagination o a plan on paper o realization in material (stone, metal or energy) o jobs/homes o raising the standard of living o adding to the comforts of life Ask SS whether they agree or disagree with the quotation and invite comments on this statement. Starting up 1 Possible answers: manufacture, design, to apply/application, to build, achievement, to create, contribution, process, etc. 2 1) E 2) H 3) D 4) C 5) F 6) B 7) G 8) A 3 Possible answers: aerospace, agricultural, biomedical, environmental, geological, metallurgical, mining, nuclear, petroleum, etc. 4 Individual SS’ answers Reading 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 1) c 2) e 3) a 4) f 5) h 6) b 7 1) F 2) F 3) T 7) d 8) g 4) T Tapescript: texts A, B, C (Course Book) 6 5) T 8 contribution – smth that you give or do in order to help smth be successful to apply – to use smth such as a method, idea, or law in a particular situation, activity, or process lab coat – a piece of clothing with long sleeves that is worn over your clothes to protect them plaid [plæd] – a pattern of crossed lines and squares, used especially on cloth man-made – made by people = artificial (not natural) rapidly = quickly/fast to modify – to make small changes to smth in order to improve it and make it more suitable or effective input – ideas, advice, money or effort that you put into a job or activity in order to help it succeed (+ into/to) efficient – if smb or smth is efficient, they work well without wasting time, money or energy. (internal) thermostat – an instrument used for keeping a room or a machine at a particular temperature adhering (n), to adhere – to stick firmly to smth (+ to) to graduate – to obtain a degree, especially a first degree, from a college or university (+ from) to enhance – to improve smth 9 1) contribution 2) principles 3) to solve 4) image 5) theorems 10 1) in 2) at 3) into 4) in 6) to modify 7) to undertake 8) process 9) depletion 10) engineers 11) major 12) outside 13) interests 14) computer 15) environment 5) into 6) on/off 7) to 8) with 11 1) applies 2) accomplishments 3) rapidly 9) with 10) on 11) up 12) to 4) had input into 5) potable 6) graduating Professional Language development 12 machine [mə'∫i:n] machinery [mə'∫i:nəri] mechanics [mi'kæniks] mechanic [mi'kænik] mechanical [mi'kænikl] technical ['teknikl] technician [tek'ni∫n] science ['saiəns] scientific [,saiən'tifik] scientist ['saiəntist] chemistry ['kemistri] chemical ['kemikl] chemist ['kemist] technology [tek'nɔlədʒi] 7 13 Subject 1) engineering 2) mechanics 3) science 4) technology 5) chemistry 14 1) e 2) i 3) j 15 1) D 2) C 16 People & Jobs engineer mechanic scientist technician chemist 4) a 5) m 6) d 7) n 8) b 9) c 3) B 4) A 1) knowledge 2) highest 3) creativities Thing engine machine 10) f 11) l 12) g 5) A 6) B Adjective engineering mechanical scientific technical chemical 13) k 14) h 7) C 8) D 4) complicated 5) implies 6) calculations 7) insufficient 8) paid 9) basis 9) D 10) C 10) typical 11) inventive 12) discovery Speaking 17 Individual SS’ answers 18 a) 1) Petroleum Engineer 2) Electrical Engineer 3) Civil Engineer 4) Mechanical Engineer 5) Biomedical Engineer 6) Aerospace Engineer b), c) Individual SS’ answers 19 Individual SS’ answers 20 Civil engineering Activity planning, designing and operating planning, designing and constructing producing, delivering designing, testing and analyzing Products/services provided synthetic rubber and fiber, breweries and distilleries buildings, dams, airports, water and wastewater treatment and distribution systems, mass transit systems, roads, bridges and drainage systems electricity, telecommunications, cable, electronics, control systems, and digital systems machines, structures and devices including cars, pumps, heating, ventilation and cooling systems, combustion systems and sports equipment (such as bicycles and skis) 8 Electrical engineering Mechanical engineering Chemical engineering Industries it can be met in chemical, petrochemical, foodprocessing, forestry and pharmaceutical different kinds of building (e. g. houses, buildings, bridges, etc.) biomedical engineering and digital signal processing metallurgy and materials; machine design; systems engineering; plant design; construction, and operation; environmental engineering Advantages producing new kind of materials in different fields (medicine, industry, agriculture, etc.) and new kinds of fuel different kinds of building creating opportunities for all engineering activities creating opportunities for all engineering activities Disadvantages harmful for humans and nature; polluting environment destroying nature harmful influence when in excess exceeding consumption of natural resources Project work 21 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 22 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 9 UNIT 2 Engineering Education Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 1) school 2) university 3) engineering society 4) Bachelor’s Degree 3 (a) 1) civil 2) petroleum 5) Master’s Degree 6) PhD 3) mechanical 4) electrical 5) education 6) chemical (b) Possible answer: RAEE – Russian Association for Engineering Education It is recommended to ask SS to find any information as a home task. Reading 4 1) c 2) d 3) e 4) b 5) f 6) a 5 1) G 2) F 3) E 4) D 5) C 6) B 7) A 6 Individual SS’ answers Professional language development 7 5-evaluation 1-granted 6-professional 2-undergone 7-ability 3-knowledge 4-theoretical 8-independently 8 6-science 1-equip 7-advance 2-specialty 3-undergraduates 8-industry 4-application 9-combine 10-capabilities 5-grant Speaking 9 Individual SS’ answers Project work 10 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 11 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 10 UNIT 3 Are you good for this job? Quotation Ask SS what is more important in the job they have: personal qualities or qualifications. Ask them to read the quotation. Ask SS if they agree. If they have different opinions, run a brief class discussion. Starting up 1 Divide the class into small groups of three to five SS. Ask SS to work through the list of factors in considering candidates for jobs, choosing the seven most important ones, and agreeing on a ranking. Allow five minutes or so. Get them to compare and discuss their rankings. 2 Individual SS’ answers Reading 3 Individual SS’ answers 4 Individual SS’ answers 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 Individual SS’ answers 7 Individual SS’ answers 8 1) h 2) I 3) f 4) a 5) j 6) c 7) e 8) d 9) b 10) g 9 Individual SS’ answers Professional language development 10 1-appropriate experience 2-applied mathematics 3-potential solutions 4-core contradiction 5-full-scale production 11 Knowledge & Understanding 6-prototypes 7-reduce the risk 8-forensic engineering 9-careful analysis 10-establish the cause An Engineer should be able to demonstrate: • Specialist knowledge • Business and Management techniques • Understanding of professional and ethical responsibilities • Understanding of the impact of engineering solutions on society • Awareness of relevant contemporary issues 11 Intellectual Abilities An Engineer should be able to demonstrate: • The ability to solve engineering problems, design systems etc. through creative and innovative thinking • The ability to apply mathematical, scientific and technological tools • The ability to analyse and interpret data and, when necessary, design experiments to gain new data • The ability to maintain a sound theoretical approach in enabling the introduction of new technology • The ability to apply professional judgement, balancing issues of costs, benefits, safety, quality etc. • The ability to assess and manage risks Practical Skills An Engineer should be able to: • Use a wide range of tools, techniques, and equipment (including software) appropriate to their specific discipline • Use laboratory and workshop equipment to generate valuable data • Develop, promote and apply safe systems of work General Transferable Skills An Engineer should be able to: • Communicate effectively, using both written and oral methods • Use Information Technology effectively • Manage resources and time • Work in a multi-disciplinary team • Undertake lifelong learning for continuing professional development Qualities An Engineer should be: • Creative, particularly in the design process • Analytical in the formulation and solutions of problems • Innovative, in the solution of engineering problems • Self-motivated, • Independent of mind, with intellectual integrity, particularly in respect of ethical issues • Enthusiastic, in the application of their knowledge, understanding and skills in pursuit of the practice of engineering Speaking 12 - Get SS, individually, to read the categories: intelligence and ability, emotional stability and conscientiousness. - Ask a couple of individual SS if they agree with the categories. 12 - Ask if any SS would like to suggest any other categories. If SS do have other categories to suggest, write them on the board. - Divide the class into pairs or groups of three. - Tell SS to work together to sort the fourteen adjectives into the three categories. - When most pairs have finished, go through the exercise with the class, writing the solution on the board. intelligence/ability: bright; astute; clever; sharp; slow emotional stability: calm; easy-going; moody; neurotic; quick-tempered conscientiousness: reliable; hard-working; punctual; responsible Ask SS to add as many extra words to each category as they can in two minutes. Get SS to call out their extra words and write them on the board in the appropriate category in the table you drew earlier. For follow up, elicit the names of five famous people from SS and write them on the board. In pairs, SS decide which of the adjectives apply to each person. When most pairs have finished, ask some SS what they decided. Alternatively, get each S to write down the name of a famous person. If you have a large class, divide it into groups of five or six SS. In turns, SS describe the personality of the celebrity they have thought of to the other members of their group without saying his/her name. The others try to guess who they are describing. 13 Individual SS’ answer 14 a) Individual SS’ answers b) Individual SS’ answers 15 Prepare cards with different situations to select a candidate for a position. Rate the candidate on his or her (1) character, (2) interpersonal dealings, (3) communications ability, (4) organizational capability, (5) balance between family and work, (6) technical skills, and (7) leadership ability. Get SS to choose one card. Get SS to work in groups of 3 or 4 and role play a situation to choose the right person at the meeting of a Board of Directors of a Chemical Corporation. Writing 16 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : design, content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, register and format. 13 UNIT 4 Engineering Ethics Before you start Write the following questions on the board: Is it worse to steal from another person than to steal from a shop? Is it always wrong to lie? If you knew your brother was selling drugs would you tell the police? Hold a class vote on each of the three questions – yes or no. Divide the class into groups to discuss the questions. Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers a) Business ethics are theories about conduct and values which take account of the moral responsibilities a business has to the community it exists in, to its employees and to its customers. b) A code of ethics/good practice is a written document laying down ethical ways of working for the personnel of a company. Engineering ethics is the study of moral issues and decisions confronting individuals and organizations involved in engineering and the study of related questions about moral conduct, character, ideals and relationships of people and organizations involved in technological development (Martin and Schinzinger, Ethics in Engineering). 2 Individual SS’ answers 3 Individual SS’ answers 4 1) highest standards 2) impact 3) impartiality 4) welfare 5) standard of professional behaviour 6) ethical conduct Reading 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 Individual SS’ answers 7 integrity – the quality of being honest and strong about what you believe to be right to acknowledge – to admit or accept that smth. is true or that a situation exists to distort – to report smth. in a way that is not completely true or correct; to change a situation from the way it would naturally be detriment – harm or damage dignity – the ability to behave in a calm controlled way even in a difficult situation (with dignity) to strive – to make a great effort to achieve smth. sustainable – able to continue without causing damage to the environment; able to continue for a long time 14 to deceive – to give someone a wrong belief or opinion about smth. to disclose = to reveal (to make smth. publicly known) supplier – a company or person that provides a particular product to obtain = to get advancement = promotion (progress or development in your job) indemnification – payment someone money because of loss, injury or damage that they have suffered negligence – failure to take enough care over smth. that you are responsible for accomplishment = achievement to justify = to give an acceptable explanation for smth. that other people think is unreasonable 8 1) acknowledge 2) detriment 3) expense 4) serve 5) affairs 9 1) with 2) on 3) from 4) with 6) notify 7) ethical 8) private 9) evaluate 10) duplicate 5) without 6) in 7) in; with 8) on 9) under 10) with 11) with/to 12) in Listening 10 Individual SS’ answers 11 1) F 2) T Tapescript 3) T (I = Interviewer, CB = Claire Bebbington) I Why should companies be ethical or what are the advantages of a company in behaving ethically? CB Mm. I think the whole issue of ethics is a very complex one. Companies are made up of people. Multinationals are made up of many different nationalities. I think that companies are part of society and as such they should reflect society's standards. Companies, especially multinational ones, do have responsibilities in the world and should try to be a positive influence and I think if a company is not ethical, then it will not survive as a company. I Should a company have a code of ethics? CB I think from my point of view it's useful on two counts. Firstly, it makes a commitment to certain good behaviour and so it's a way of communicating the importance of good behaviour to all of it's employees and partners. Secondly, if a company has a code of ethics and spends time communicating it, it docs actually contribute to it's ethical behaviour. If you express these things in writing, especially, then you can be held accountable for them. This tends to mean that you are much more likely to act on them as well. I think following up that code is difficult. People tend to have different ethical standards, and defining the term 'ethics' can I think be a problem. But I think generally to express what your ethics are is a positive thing to do. 15 12 1) ‘Firstly, it makes a commitment to certain good behaviour and so it’s a way of communicating the importance of good behaviour to all of its employees and partners.’ 2) ‘If you express these things in writing, especially, then you can be held accountable for them.’ 13 a) ‘When does a facilitation payment become a bribe?’ Tapescript (I = Interviewer, CB = Claire Bebbington) I What kinds of moral dilemmas do large companies face? Can you think of any examples? CB I think if you were to look at any company's ethical code you would usually find in it a section about offering bribes and this can be an area where I think people can get themselves into hot water. Facilitation payments are part of doing business in many countries, and bribes are something which most companies are not going to want to get involved in. Bui when does a facilitation payment become a bribe? And that is a question that can be quite difficult to answer. I Can you think of an example where a facilitation payment is clearly a facilitation payment and not a bribe? CB I think that there are many examples. When you are paying consultants to make introductions to new business contacts, obviously the reason you choose these consultants is because they are well placed to give that kind of advice in a particular country. And you're paying for that introduction. I Can you give an example of a facilitation which is closer to a bribe? CB I would say size is important. Sometimes facilitation payments are out of proportion to the kind of business that you are expecting to win. I think there are many instances. Also, you have to be careful with issues such as nepotism. b) The example she gives of a facilitation payment is ‘When you are paying consultants to make introductions to new business contacts, obviously the reason you choose these consultants is because they are well placed to give that kind of advice in a particular country.’ She also points out that the size of the payment is an issue: ‘Sometimes facilitation payments are out of proportion to the kind of business that you are expecting to win.’ This may be an indication that something greater is at stake. c) Individual SS’ answers A facilitation payment is money paid to speed a process along, but one which is not actually a bribe because it is done openly. However, it may not be part of any official procedure. For example, a supermarket wishing to build a new store in a district where there is resistance may offer to make a donation to the local school. A multinational eager to impress a local politician may offer political financing in a deal which is – superficially at least – entirely separate from the business at hand. A bribe happens in secret, but the line between the two is not always clear, particularly when, for instance, political parties may be under no legal obligation to divulge the names of their donors. 16 14 1. Engineers shall hold paramount the safety, health and welfare of the public and shall strive to comply with the principles of sustainable development in the performance of their professional duties. (try to satisfy) 2. Engineers shall perform services only in areas of their competence. (fulfill) 3. Engineers shall issue public statements only in an objective and truthful manner. (distribute) 4. Engineers shall act in professional matters for each employer or client as faithful agents or trustees, and shall avoid conflicts of interest. (conscientious) 5. Engineers shall build their professional reputation on the merit of their services and shall not compete unfairly with others. (quality) 6. Engineers shall act in such a manner as to uphold and enhance the honor, integrity, and dignity of the engineering profession and shall act with zero-tolerance for bribery, fraud, and corruption. (maintain and improve) 7. Engineers shall continue their professional development throughout their careers, and shall provide opportunities for the professional development of those engineers under their supervision." (give) Professional language development 15 1) crooked 2) compensation 3) disclosure 4) a whistleblower 5) a bribe 6) integrity 16 1) law –abiding 2) a slush fund 3) industrial espionage 5) a bribe 4) a whistleblower 6) integrity 17 boycott breach break commit falsify impose companies contracts crimes documents laws regulations sanctions 18 accuse somebody of offering bribes charge somebody with breaking guidelines prosecute somebody for selling dangerous goods sentence somebody to three years in prison sue somebody for damages 19 a) defraud discredit misinform mislead misrepresent mistreat misuse products overbook overcharge overprice undermine 17 b) defraud a company / consumers / customers / people discredit a company / people misinform consumers / customers / people / staff mislead consumers / customers / people / staff misrepresent facts mistreat consumers / customers / people / staff misuse information overbook seats overcharge consumers / customers / people overprice goods undermine confidence / people 20 1) b 2) c 3) a 4) c 5) b 18 Speaking 21 Individual SS’ answers 22 Individual SS’ answers 23 Individual SS’ answers 24 Individual SS’ answers 25 Individual SS’ answers Pay SS’ attention to the following useful language. Write it on the board: There are several ways we could deal with this. Let’s look at the pros and cons… Let’s look at this from a different angle. It might be worse… Let’s think about the consequences of… The best way forward is to… So the next thing to do is… To encourage maximum language use, try to throw in some provocative options (e. g. appoint a private detective to break into the rival’s premises and assemble evidence; confront them directly; threaten to go to the press). Project work 26 Individual SS’ works Writing 27 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 19 UNIT 5 Company Structure & Corporate Culture Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 1) buying, selling, marketing and production 2) information technology, telecommunications, film, and car manufacture 3) multinationals 4) operate 5) a parent or holding company 6) subsidiaries 3 1) YARA 3 e 2) HXK 2 c 3) BASF 4 a 4) Dow 5 b 5) HARDEX 1 d 4 Individual SS’ answers 5 (New Insights into business unit1 key vocabulary) Introduce the topic by asking students to present a typical company structure, writing their ideas on the board in the form of a chart. This could be a famous local company or one they have worked for. This will help students visualise the structure of a company and generate vocabulary they already know. Ask students to read through the Key vocabulary section and introduce the organisation chart, presenting the hierarchy from top to bottom, allowing students to comment on how it compares to their own diagram. Ensure that students understand the words in bold. Ask them to fill the gaps in the exercise below after listening to the record. 1) The shareholders 5) Board of Directors 2) management 6) Chairperson or President 3) workforce 7) Managing Director or Chief Executive Officer 4) organization chart 8) Senior managers or company officers 6 shareholders → chairperson (board of directors) → managing director → senior management → middle management → workforce Reading 7 Individual SS’ answers 8 1) B 2) E 3) A 4) C 5) D 9 Individual SS’ answers Professional language development 10 Encourage students to use a monolingual dictionary to check their answers. Copy the table onto the board and elicit students' answers. Mark on word stress and drill if necessary. Point out that advertisement is often shortened. Find out if students know to what (ad, advert). 20 Nouns 1 production, product 2 providers, provision 3 development 4 marketing, market 5 advertisement Verbs produce provide develop market advertise 11 1) market 3) develop 5) production 2) product 4) market 6) advertise 12 1. annual general meeting (AGM); 8. stock exchange; 2. personal assets; 9. sleeping partner; 3. board of directors; 10. sole trader; 4. public limited company; 11. business partner; 5. private limited company; 12. company directors; 6. unlimited liability; 13. board meeting; 7. business debts; 14. personal liability 13 1) partnership 2) public limited company 3) corporation 4) sole owner, freelancer 5) limited company 14 a) manager e) management b) organization f) organize c) managing g) managerial d) organizational 15 a) Human Resources/Personnel d) Production b) Sales and Marketing e) Finance c) Research and Development 16 a) Production b) Human Resources/Personnel c) Finance d) Sales and Marketing 17 1) in….of 2) to; for e) Office f) Research and Development g) Human Resources/Personnel h) Production 3) with; with 4) to 18 There is not a big difference between customers and clients and sometimes both can be used. In general, people in shops are usually customers, while businesses and professional people like lawyers and accountants have clients. 1) owner; director 7) supplier 2) Chief Executive Officer 8) leader 3) boss 9) colleague 4) shareholder 10) opposite number 5) investor 11) manager 6) customer 21 Speaking 19 Types of company Role of leader/ manager Role of everyone Function of organization Most commonly found in … Type of company Incubator are treated with scepticism. The function of the organisation is to enable people to fulfil their potential. Sweden Typical of new start-ups and partnerships Guided Missle set clear objectives Everyone is equal and there is as little formal hierarchy as possible. Everyone is equal, while having different roles. The organisation may break up or alter when its goals have been achieved. the USA, Canadaand the UK Typical of large, decentralised companies. Family is seen as a father-figure Everyone is valuable Decisions are made at the top. Typical of small and medium-sized firms. Eiffel Tower Leaders are distant. Everyone is replaceable The organisation functions because everyone obeys the rules. Spain, Italy, Greece, France, Belgium, Japan and Singapore France, Germany, Austria and the Netherlands. Tapescript (‘Reward’ Upper-intermediate Business Resource Pack, unit 2) 22 Typical of large, mature companies. — The Incubator — The function of the organisation is to enable people to fulfil their potential. Relationships grow between people as they work on tasks together. Leaders are treated with scepticism. A high value is placed on creativity. Change can be fast and spontaneous. There is an emotional commitment to the work being done. Managers are enthusiastic. Everyone is equal and there is as little formal hierarchy as possible. Most commonly found in Sweden. Typical of new start-ups and partnerships: doctors, consultants, lawyers. — The Family — There are strong relationships between people at work. The leader is seen as a fatherfigure. Differences in status between people are seen as natural. Everyone is valuable. Decisions are made at the top. The main types of reward and punishment are the approval and disapproval of superiors. People can act together because they understand each other and the organisation. A high value is placed on loyalty to the company and to superiors. Most commonly found in Spain, Italy, Greece, France, Belgium, Japan and Singapore. Typical of small and medium-sized firms. — The Guided Missile — Everyone is equal, while having different roles. The organisation is oriented to performing tasks and achieving goals. People must do whatever it takes to achieve the goals of the organisation. The organisation may break up or alter when its goals have been achieved. Individual contributions are recognised and lead to pay rises or promotion. Managers set clear objectives. A high value is placed on practicality. People take a pride in their professionalism. Most commonly found in the USA, Canada- and the UK. Typical of large, decentralized companies. - The Eiffel Tower — There are explicit definitions of roles and relationships. Authority belongs to roles, not to the people who occupy them. Everyone is replaceable. People have a strong sense of duty and responsibility. The organisation functions because everyone obeys the rules. Decisions are made at the top. The hierarchy is complex and is described formally. Leaders are distant. Most commonly found in France, Germany, Austria and the Netherlands. Typical of large, mature companies. 20 Individual SS’ answers 23 21 Individual SS’ answers Card A You are a Production Manager. And you are a member of the work group of the company. Your task is to prepare the information of your department for designing an advertising brochure. Present your ideas and participate in discussion. Card B You are a Finance Manager. And you are a member of the work group of the company. Your task is to prepare the information of your department for designing an advertising brochure. Present your ideas and participate in discussion. Card C You are a Sales & Marketing Manager. And you are a member of the work group of the company. Your task is to prepare the information of your department for designing an advertising brochure. Present your ideas and participate in discussion. Card D You are a Human Resources Manager. And you are a member of the work group of the company. Your task is to prepare the information of your department for designing an advertising brochure. Present your ideas and participate in discussion. Card E You are a R&D Manager. And you are a member of the work group of the company. Your task is to prepare the information of your department for designing an advertising brochure. Present your ideas and participate in discussion. Card F You are a supervisor of the work group for designing an advertising brochure. Your task is to start, manage and finish the meeting. Explain the idea, encourage discussion and make the conclusion. Project work 22 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 23 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 24 UNIT 6 Chemical Engineering Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 Individual SS’ answers 3 1) engineering 2) physical science 3) chemistry 4) physics 5) mathematics 6) materials 7) chemicals 8) research & development 9) chemical engineer Reading 4 1) chemicals 2) mechanical 3) raw materials Tapescript: texts A, B, C (Class Book) 5 1) It is true that chemical engineers are comfortable with chemistry and mathematics, physics and the engineering art. 2) Chemical engineers should use such necessary skills as design, testing, scale-up, operation, control, and optimization, and require a detailed understanding of the various "unit operations", such as distillation, mixing, and biological processes. 6 chemicals – substances used in chemistry or produced by a chemical process marriage – the relationship or connection between smb or smth narrow specialist – someone who knows a lot about a particular subject, or is very skilled at it versatile – to be versatile is to have many different skills prominent = important raw materials – substances that are in a natural state and not treated or prepared for use to encompass – to include a wide range of ideas, subjects, etc. conversion – when smth changes form from one to a different one to utilize = to use 7 1) range 2) ties 3) valuable 4) conversions 8 1) with 2) from 5) to overcome 6) universal 7) understanding 8) recognized 3) upon 4) between 9) branches 10) to utilize 5) of 6) on Professional language development 9 1) E 3) A 5) G 2) D 4) F 6) B 7) into 8) at 7) I 8) J 25 9) to 10) in 9) C 10) H 10 1) chemical processes 2) chemical reactions 3) refining 4) manufacture 5) solvents 6) organic 7) polymers 8) elastomers 9) oleochemicals 10) explosives 11 1) a variety of rewarding careers 2) 3) food or plastics industries for example 4) a major role 5) processes to prevent 6) by increasing 7) 8) 12 1) reactions 2) resistant 3) separated 7) liquids 8) developing 9) located 4) distillation 5) instruments 6) specifications Speaking 13 Individual SS’ answers 14 a) 1) F 2) A 3) G 4) B 5) H 6) C 7) I 8) D 9) J 10) E b) Individual SS’ answers 15 Individual SS’ answers Project work Hotlist is a list of websites necessary for making web tasks. 16 Individual SS’ hotlists 17 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 18 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : design, content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, register and format. 26 UNIT 7 Objects of chemical engineering Starting up 1 Area 654900 Chemical Technology of Inorganic Substances and Materials Specialty 250200 Chemical Technology of Inorganic Substances 250300 Technology of Electrochemical Production Facilities 654900 Chemical Technology of Inorganic Substances and Materials Major Technology of Basic Inorganic Synthesis Technology of Mineral Fertilizers Functional Electroplating Corrosion and Protection of Metals 251000 Chemical TechChemical Technology of Solid Elecnology of Monocrystals, tronic Materials Materials and Products of Electronic Engineering Technology of Monocrystals Technology of Precious Stones Area 655000 Chemical Technology of Organic Substances and Fuels Specialty 250100 Chemical Technology of Organic Substances Major Technology of Basic Organic and Petrochemical Synthesis Technology of Fine Organic Synthesis Technology of Organic Coloring Agents Technology of Surfactants and Synthetic Detergents Technology of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Compounds 250400 Chemical Engineering of Natural Energy Products and Carbon Materials 251500 Chemical Technology of Synthetic Biologically Active Substances Technology of Cosmetics Technology of Solid Energy Products Technology of Carbon and Composite Materials Technology of Oil and Natural Gases Chemistry and Technology of Bioactive Substances Technology of Medicinal Preparations Technology of Biomedical Preparations 27 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Technology of Basic Inorganic Synthesis Technology of Mineral Fertilizers Corrosion and Protection of Metals Technology of Basic Organic and Petrochemical Synthesis Technology of Solid Energy Products Technology of Carbon and Composite Materials Technology of Oil and Natural Gases Chemistry and Technology of Bioactive Substances Technology of Biomedical Preparations Technology of Refractory Materials 2 Individual SS’ answers 3 Possible answer: There are definite objects in chemical manufacturing. They are materials and equipment which are combined in technical process to manufacture products. So, the main object of chemical engineering is the final product. 4 Possible answers: Raw Materials: aluminium, copper, diamond, sand, iron, etc. Equipment: boiler, reactor, turbine, generator, pump, test tube, flask, etc. Products: aircraft, electrical wire, bridges, etc. Reading 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 1) B 2) E 7 Raw materials Products Chemical producers 8 3) A 4) F 5) G 6) C oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, minerals polymers and plastics, especially polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate, polystyrene and polycarbonate, rubber, textiles, apparel, refined oil products, pulp and paper, primary metals BASF, Dow, Shell, Bayer, INEOS, ExxonMobil, DuPont, Mitsubishi (a) Company Country Headquarters BASF Germany Ludwigshafen Dow Chemical the USA Midland, Mich. 28 Products chemicals, plastics, petrochemicals, etc. chemicals, plastics, agricultural products Chemical sales, billions $53,2 $46,3 The Netherlands/ The UK Shell Chemicals Rotterdam/ London Bayer Germany Leverkusen INEOS The UK Lyndhurst ExxonMobil the USA Irving, Texas DuPont the USA Wilmington Mitsubishi Chemical Japan Tokyo Sumitomo Chemical Japan Tokyo Air Liquide France Paris (b) Individual SS’ answers 9 Individual SS’ answers 10 1) g 2) h 3) I 4) a/c 5) b 6) a/c petrochemicals products of health care, nutrition and hightech materials chemicals, plastics chemicals, fuels, lubricants polymers, agricultural products, etc chemicals, plastics, etc chemicals, plastics, petrochemicals, agricultural products, pharmaceuticals chemicals, plastics, petrochemicals, medical gases, pharmaceuticals 7) d/e 8) d/e 9) f 11/12 (1) raw materials, (2) markets, (3) energy supply, (4) climate, (5) transportation facilities, and (6) water supply, etc. Professional Language Development 13 1) convert – conversion 2) chemical – chemically 3) undergo – undergoing 4) react – reactions 5) major – majority 6) industry – industries 7) chemistry – chemist 8) science – scientific 14 29 $35 $34,1 $33 $31,2 $28,5 $21,9 $14,1 $13 Technology of Basic Inorganic Synthesis Technology of Mineral Fertilizers Technology of Basic Organic and Petrochemical Synthesis Technology of Solid Energy Products Technology of Carbon and Composite Materials Technology of Oil and Natural Gases Technology of Biomedical Preparations Technology of Refractory Materials Chemistry and Technology of Bioactive Substances Corrosion and Protection of Metals water softening, cement, ceramics, glass, graphite, lime (industry), fertilizer biochemical engineering, explosive, petrochemical, petroleum processing and refining, plastics processing, polymer, rubber coal chemicals, coal gasification, coal liquefaction cement, ceramics, dyes, explosive, graphite, lime fuel gas biomedical chemical engineering ceramics distilled spirits electrochemical process Speaking 15 Individual SS’ answers 16 Individual SS’ answers Project work 17 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 18 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 30 UNIT 8 Functions and applications of chemical objects Starting up 1 a – glass b – rubber c – ceramics d – clay loam e – plastic f – organic and inorganic compounds g – clay ceramics h – oil products 2 Objects 1 2 Glasses and bottles Tyres Materials Properties glass Clear, hard, breaks easily rubber Elastic, water repellent and resistant to alkalies and weak acids, tough, impermeable, adhesive, and electrical resistant Ceramics (Metal high wear-resistant oxides (Al2O3, FeO, and hard, brittle recarbides and nifractory, trides) thermal insulating, electrical insulating, nonmagnetic, oxidation resistant, prone to thermal shock, and chemically stable. 3 Sink (wash bowl) 4 Bricks Ceramic material (Clay) Durable, brittle, having compressive strength and absorption 5 Toys plastic transparent, permeable, flexible, elastic, water absorption is low, electrical resistant. Some chemical properties: insoluble, 31 Material application Windows, bottles, glasses in transport, industrial, consumer, hygienic and medical sectors Porcelain, glass, bricks and refractory materials ( window glass, implantable components, cutting tools, valves, bearings, brake disks and chemicalprocessing equipment). are used for building and pavement, in the metallurgy and glass industries for lining furnaces, as silica, magnesia, chamotte and neutral (chromomagnesite) refractory bricks. Plastics are everywhere! Plastics are used from pillows and mattresses (cellular polyurethane or polyester) up to cars and hi-tech chemical resistant, thermal stable, no reactivity with water, inflammable, heat of combustion is high 6 Paint 7 See p. 4 Ceramics Oil products 8 Pigments(Titanium adhesive to dry paint dioxide (TiO2), films, high viscous, Magnesium silicate, scrub resistant Zinc oxide, Aluminum silicates (also called kaolin and china clay), binder, liquid (solventswater, oil, …) gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas. Fire and toxic hazards are high, evaporate quickly and leave little residue, most oils products are lighter than water, 32 computers. Since plastic is an insulator, plastic is used to cover almost all electric wires and cords. Painting, decorating, house painting, industrial coating In transport: private cars, company trucks, planes, diesel locomotives for the railways, etc. • In the home: heating oil, LPG or town gas, for heating and daily requirements such as cooking. In industry: industrial boilers, thermal electric power stations operating with gas or fuel oil. In the petrochemical industry: naphtha and gas for petrochemical processing to supply rawmaterials for the manufacture of plastics, textiles, etc.. In the public works sector: from local roads to motorways and on to aircraft runways. In agriculture: for tractors or other agricultural machines, greenhouse heating and drying. 3 Individual SS’ answers Reading 4 Basic chemicals, life sciences, specialty chemicals and consumer products. 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 Individual SS’ answers Professional language development 7 1 Aluminium 2 Aluminium, copper, mild steel 3 Copper, mild steel 4 Copper, mild steel, ABS, nylon 5 ABS 8 6 Copper 7 Acrylic 8 Polyester resin, urea formaldehyde 9 Aluminium, copper 10 Polyester resin 1 Aluminium 2 Epoxy resin and urea formaldehyde 3 High carbon steel 4 Brass 5 Nylon 6 ABS 7 Brass 8 Mild steel 9 Polyester resin 10 Copper Speaking 9 Individual SS’ answers 10 Individual SS’ answers Project work 11 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 12 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 33 UNIT 9 Chemical industry markets Starting up 1 Possible answers: money, trade, to buy/to purchase, to sell, goods, quality, competitor, consumer, etc. 2 3 Individual SS’ answers Individual SS’ answers 4 a) Individual SS’ answers b) 1) compromise 2) agreement 5 Individual SS’ answers Reading 6 1) c 7 2) e 3) strategy 4) priorities 3) f 4) b 5) g 6) d 7) a 1) ‘Soda – Chlorate’ limited company 2) industrial enterprise 3) a wide range of chemicals 4) complicated processes 5) unique 6) increase of competitiveness 7) a customer-oriented company 8) a reliable partner both in Russia and abroad 9) development of promising technologies 10) constant perfection of the existing productions 11) product quality improvement 12) establishment of new connections with domestic and foreign partners 8 SODIUM METASILICATE PENTAHYDRATE Chemical Name: sodium metasilicate pentahydrate Synonym & Trade Name: silicic acid, disodium salt; disodium trioxosilicate, pentahydrate; water glass Chemical Formula: Na2О • SiО2 • 5H2О (Na2SiO3 • 5H2О) Empirical Formula: Na2SiO8H10 Molecular Mass: 212.74 Specifications: Fine crystal white powder. The grayish tint is admissible. Appearance Mass fraction of alkalinity in terms of sodium dioxide, %, within 28–30 Mass fraction of silicon dioxide, %, within Module SiO2 / Na2O, within 26–28 0.9–1.0 34 Mass fraction of ferric in terms of ferric oxide, %, max 0.02 Mass fraction of water-insoluble impurities, %, within 0.01–0.06 Mass fraction of total moisture, %, max 45 Water solutions have alkaline reaction. Temperature of fusion from 40 up to 80 С. Application: in textile industry in cotton, flax and silk manufacture for cloth bleaching, in metallurgic and machine-building industry for neutralization and removing the hydrochloric acid from surfaces of metal, for oil regeneration, in technological processes of an oil recovery, in systems of water-supply, in vegetable oil refining. Packing: polypropylene bags of 5H3/Y type, 500-1000kg big bags of 13H3/Y type on pallets Transportation: railway cars, truck, 20" container Storage Warranty: 12 months. POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE Chemical Name: potassium hydroxide Synonym & Trade Name: potassium hydrate, caustic potash, potash lye Chemical Formula: К – О – Н Empirical Formula: КОН Molecular Mass: 56.10 Specifications: Appearance Caustic alkalies (KOH+NaOH) content in terms of KOH, %, min Potassium carbonate (К2СО3) content, %, max Chloride content in terms of Cl, %, max Sulphate content, %, max Iron content ,%, max Potassium chlorate content (КСIO3), %, max Silicone content, %, max Sodium content in terms of NaOH, %, max Calcium content, %, max Aluminum content, %, max Higher Grade Grade A Grade B flakes of green, lilac or grey color. flakes of light green or light grey color flakes of light green, light grey or light lilac color 95.0 91-93 93.5–95 1.4 1.4 1.4 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.025 0.03 0.025 0.03 0.025 0.03 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.01 0.01 0.1 1.5 1.5 1.5 0.01 0.003 0.01 0.003 0.01 0.003 35 Nitrate and nitrite content in 0.07 0.07 0.07 terms of nitrogen, %, max Application: In manufacture of fertilizers, technical detergents, synthetic rubber, potassium glass, electrolytes for accumulators, reagents and potassium salts; in oilextracting and gold mining industries, in machine – building industry, in manufacture of biodiesel fuel. Packing: 25kg polypropylene bags of 5H3/Y, 500-1000kg big bags of 13H3/Y type on pallets. Transportation: railway cars, truck, 20" container Storage Warranty: 36 months. POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE (liquid) Chemical Name: Potassium Hydroxide, liquid. Synonym & Trade Name: Potassium hydrate, caustic potash, potash lye Chemical Formula: К – О – Н Empirical Formula: КОН Molecular Mass: 56.10 Specifications: Higher Grade Solution of blue, green or grey colour, crysAppearance tallized residue is possible. Caustic alkalies (KOH+NaOH) content in 54.0 terms of KOH, %, min Potassium carbonate (К2СО3) content, %, 0.4 max Chloride content in terms of Cl, %, max 0.7 Sulphate content, %, max Iron content ,%, max Potassium chlorate content (КСIO3), %, max Silicone content, %, max 0.03 0.004 0.15 0.015 Sodium content in terms of NaOH, %, max 1.7 Calcium content, %, max 0.005 Aluminum content, %, max 0.003 Nitrate and nitrite content in terms of ni0.003 trogen, %, max Application: In manufacture of fertilizers, synthetic rubber, potassium glass, electrolytes for accumulators, reagents and potassium salts, antiicers; Transportation: railway cars, tank truck, ISO tank Storage Warranty: 36 months. SODIUM METASILICATE NONAHYDRATE 36 Chemical Name: sodium metasilicate nonahydrate Synonym & Trade Name: silicic acid, disodium salt; disodium trioxosilicate, nonahydrate; water glass Chemical Formula: Na2O· SiO2 · 9H2O (Na2SiO3 · 9H2O) Empirical Formula: Na2SiO12H18 Molecular Mass: 284.20 Specifications: Fine crystal powder of various hues of Appearance grey or yellow colour. Mass fraction of alkalinity in terms of sodium 20.5 oxide, %, min Mass fraction of silicon dioxide, %, min 19.0 Mass fraction of sodium carbonate in terms of 1.2 carbon oxide, %, max Mass fraction of sesquioxides (R2O5), %, max 0.2 Mass fraction of total moisture, %, max 59.0 Water solutions have alkaline reaction. Temperature of fusion from 40 up to 80 С. Application: In the textile industry in cotton, flax and silk manufacture for cloth bleaching; in metallurgical and a machine engineering industry for neutralization and removal of hydrochloric acid from a surface of metal; in manufacture household and washing-up liquids; for printed paints and for oil regeneration; in technological processes of extraction and transport of petroleum; in quality corrosion inhibitor in system of turnaround water supply; in disinfection. Packing: Polyethylene or polypropylene bags of 35 kg. Transportation: Railway cars, universal container. Storage Warranty: 12 months. POTASSIUM CHLORATE Chemical Name: Potassium chlorate moisten Synonym & Trade Name: Potassium salt chlornovatic acid, Berthollet`s salt Empirical Formula: KCIO3 Molecular Mass: 122.55 Specifications: First Grade Second Grade Crystals of white color tinged with Appearance yellow Potassium chlorate content in terms of dry sub99.8 99.7 stance,%, min Moisture,%, max 7.0 7.0 Substances nonsalute in water content, %,max 0.04 0.04 Chloride content in terms of calcium chloride 0.03 0.05 (CaC12), max, Sulphate content in terms of calcium sulphate 0.03 0.07 37 (CaS04), %, max Bromate content in terms of potassium bromate %, 0.008 0.025 max, Alkali content in terms of calcium oxide (CaO), %, 0.015 0.02 max, Organic substances content, %, max 0.005 0.01 Application: In chemical, metallurgical, pyrotechnical and match industries. Packing: 25kg polypropylene bags of 5H3/Y tupe on pallets/Polypropylene bags with polyethylene bags-inserts. Weight of 40 kg. Transportation: railway car, truck, 20" container. Storage Warranty: 6 months. POTASSIUM-LITHIUM ELECTROLYTE Chemical Name: potassium-lithium electrolyte alkaline, solid Synonym & Trade Name: chemical mixture hydroxides potassium and lithium Empirical Formula: KLiO2H2 Molecular Mass: 80.04 Specifications: Flakes form of grey-green Appearance or grey-lilac or grey colors. Caustic potash (KOH) content, %,min 88.0 Lithium hydrate content, %,min 3.4 Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) content,%,max 1.9 Chloride content in terms of chlorine-ion, %,max 0.75 Sulphate content in terms of sulphate-ion, %,max 0.03 Calcium content, %,max Nitrate and nitrite content in terms of nitrogen, %, max 0.005 Sodium content in terms of caustic soda, %, max 2.0 Iron content, %, max Aluminum content, %, max Silicone content, %, max 0.003 0.035 0.005 0.02 LiOH : KOH = 0.04 Application: for producing solutions with specific gravity of 1.19-1.21. The solutions are added into alkaline accumulators after the correction of their specific gravity, cooling and decantation. Packing: steel drums of 90 kg. Transportation: railway cars. Storage Warranty: 36 months. 38 CAUSTIC SODA GLASS Chemical Name: sodium silicate solution Synonym & Trade Name: sodium silicate solution, sodium metasilicate, water-soluble sodium silicate, sodium silicate. Chemical Formula: Na2O · n SiO2, where n=2.45 – 3.0 Physical and chemical properties: Viscous liquid of greenish-grey Appearance or brown color. Silicate module (molecular ratio SiO2 / Na2O) , not less 2.45 Density at , g/sm3 1.48 – 1.55 Mass fraction of water- insolubles, %, not more 1.8 Application: for silica gel, plumbum silicate, sodium metasilicate, synthetic detergents and household chemical goods production; as a chemical agent in technological process of oil production and transportation; for paper treatment as glue for cardboard and cardboard products; for production of heat resisting and refractory concretes, concrete structures and products; for soil stabilization at road laying, air field covering and foundation building, as a component in solutions for refractory masonry; fabric bleaching; for manufacture of forms and rods, dressings, welding electrodes, ceramic fluxes for arc welding; for vitrification of highly active nuclear wastes. Packing: 100 liter steel barrels, railway tanks Transportation: railway tanks, railway cars, trucks. Storage Warranty: 6 months after production. Certification information: sanitary and epidemiological certificate, certificate of conformity and certificate for application in technological processes of oil production and transportation. SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE Chemical Name: hypochlorous sodium Synonym & Trade Name: sodium hypochlorite. Chemical Formula: Na – O – CI Empirical Formula: NaCIO Molecular Mass: 74.44 Specifications: Appearance Liquid of sulphureous color Optical transmission factor, %, not less 20 Mass concentration of active chlorine, g/dm3 , not less 190 Mass concentration of alkali as NaOH, g/dm3 10-20 Mass concentration of ferrum, g/dm3, not more 0.02 Note: 10 days after shipment a maximum 30 % loss (compared with the initial content) of active chlorine and alteration of color (into reddish-brown) is allowed. 39 Application: in chemical industry, for chemical treatment of water, for drinking water disinfection and water disinfection of swimming pools and sewages, for disinfection and bleaching of fabrics and paper, for production of bleaching substance "Belizna" and other consumer goods. Packing: Special steel gummed railway and truck tanks or containers, up to 60 liter polyethylene canisters or barrels. Blacked out or dark painted glass lathed flasks. Transportation: by trucks according to transport rules for this type of vehicles. By railroad – in special gummed railway tanks with top discharge according to transport rules for this type of transport means. Storage: Special gummed or covered with corrosion-resistant material vessels with protection against direct sunshine. Storage with organic products, fuels or acids is not allowed. Certification information: sanitary-and-epidemiologic Certificate. POTASSIUM GLASS Chemical Name: potassium silicate solution Synonym & Trade Name: potassium silicate solution, potassium metasilicate, watersoluble potassium silicate. Chemical Formula: K2O · n SiO2 , where n=2.3 – 3.0 Specifications: Viscous liquid with greenish Appearance grey, grayish-brown or brown color. Silicate module (molecular ratio SiO2 / K2O) , not less 2.3 Density, g/sm3 1.4 – 1.56 Mass fraction of water-insolubles, %, not more 1.8 Application: for production of vanadic catalyst, granular catalyst for ammonia synthesis, silicate paints for household chemical goods, for paper treatment, as glue for cardboard and cardboard products; production of acid resistant and refractory concretes, concrete structures and products; for soil stabilization at road laying, air field covering and foundation building, as a component in solutions for refractory masonry; for manufacture of forms and rods, welding electrodes, ceramic fluxes for arc welding; for vitrification of highly active nuclear wastes. Packing: 100 liter steel barrels, railway tanks. Transportation: railway tanks, railway cars, trucks. Storage Warranty: 6 months after production. Professional language development 9 a) 1) e 2) d 3) f 4) b 5) g b) exporter? importer? To break into a market To place an order To meet a delivery date To quote a price 40 6) c 7) a exporter and importer? To carry out a market survey To arrange insurance cover 10 11 1) d 2) a 3) e 1) launched 2) orders 3) complaints 4) incomplete 4) b 5) f 5) in transit 6) careless 7) withdraw 8) inspection 6) g 7) c 9) tests 10) modified 11) relaunched 12) failed to deliver 13) cancelled 14) durability 15) reliability 16) long-lasting Listening 12 1) technical characteristics 5) 30% 2) liquids with low viscosity 6) 3 days 3) power 7) methods of payment 4) discount system 8) insurance Tapescript - So you would like to buy our pumps. What information exactly would you like to know? - Firstly I’d like to ask you about technical characteristics of your product. - Well, we have 2 main types of pumps. The pumps of type A are intended to pump over liquids with low viscosity. Their capacity is about 3 kW. The pumps of type B are used to for viscous liquids and soles and their capacity is 5 kW. - That’s wonderful! Could you tell about discounts? Does your company have any discount system? - Certainly. If you buy 50 pumps you will get 10% discount, and if you buy more than 100 pumps you’ll get 30% discount. - And what about dispatch? - You will get pumps in 3 days. - What about methods of payment? Should I pay by letter of credit or by bank draft? - You may choose any way you like. But if you pay by banker’s draft you will get insurance free. - OK. I’ll buy 100 A-pumps. - All right. It’s nice to deal with you. 13 Individual SS’ answers Speaking 14 Individual SS’ answers 15 Individual SS’ answers 16 Individual SS’ answers Project work 17 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 18 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 19 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling and punctuation, register and format. 41 UNIT 10 Materials in chemical industry Starting up 1 a Benzene Extraction Plant b Hydrogen Plant c Borosilicate Glass/ Soda Lime Plant d Sewage Treatment Plant 2 a Benzene Extraction Plant (benzene – oil) b Hydrogen Plant (hydrogen) c Borosilicate Glass/ Soda Lime Plant (Borosilicate Glass/ Soda Lime/cooking glass) d Sewage Treatment Plant (clearing, e.g. water) Reading 3 Individual SS’ answers 4 Individual SS’ answers Possible answers: 1) material characterization/industrial applications of materials science; 2) metal alloys; 3) polymers; 4) composite materials 5 processing techniques – the process of converting raw materials into a final product extraction of materials – the act of extracting or the extraction condition of being extracted conversion – a change or adaptation in form, character, or function metal alloy – a metallic material, such as steel, brass, or bronze, consisting of a mixture of two or more metals or of metallic elements with nonmetallic elements additive – any substance added to something to improve it, prevent deterioration, etc concrete – a construction material made of a mixture of cement, sand, stone, and water that hardens to a stonelike mass 6 1) processing techniques 2) electrolytic extraction 3) industrial applications 4) materials science 5) foundry techniques Possible answers: metal alloys steel, stainless steel, cast iron, tool steel, alloy steels, low, mid and high carbon steels, aluminium, titanium, copper (bronze, brass) and magnesium alloys 6) stainless steel 7) cast iron 8) tensile strength 9) copper alloys 10) electromagnetic shielding 7 8 polymers plastics, polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC (polyvinyl-chloride), polystyrene, nylon, polyester, acrylic, polyurethane, polycarbonate Individual SS’ answers 42 composite materials steel-reinforced concrete, plastic casing, thermoplastic matrix, acrylonitrilebutadiene-styrene (ABS), calcium carbonate chalk, talc, glass fibre, carbon fibre 9 10 1C Product steel diamonds energy polymers 11 2A 3E 4G 5B 6D Technological Product uses conditions At high temperatures, carbon sheet steel and tools; used for automocombines with iron bile and aircraft engine parts; used for transportation equipment and structural beams; Stainless steel for engine parts or kitchen utensils; synthesis; at high temperature gem cutters, surgeons, and manufacturand pressure ers use diamond knives and drills; used as abrasives; cutting tools People burn fossil fuels to -anthracite (containing the most carbon) generate energy. Burning or is valuable coal; combustion, is the reaction of - a lignite (containing the least amount a substance with oxygen to of carbon) is the least valuable; produce new substances and energy (in the form of heat). When coal burns, carbon reacts with oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and heat. The higher the carbon content, the greater the energy released in combustion. Burning releases energy when bonds between the atoms break and when carbon and hydrogen atoms recombine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. synthesis Pharmaceuticals, pesticides, paints, synthetic fiber, synthetic rubber, and plastics, synthetic fibers, nylon, rayon, and polyester. All the plastics, from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in soft drink bottles to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in window frames to styrene in car parts, depend on the properties of carbon. Individual SS’ answers Professional Language Development 43 12 1 inorganic 2 organic 3 inorganic 4 inorganic 5 organic 6 inorganic 7 inorganic http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inorganic_compound 13 1) substances 2) production 3) manufacturing 4) buildings 5) art 6) stars 14 1) i 2) e 3) a 4) g 7) computers 8) raw material 9) finishing 10) distribution 11) construction 12) consumption 5) b 6) c 7)h 8) d 13) cotton 14) cloth 15) garment 16) steelmaking 17) ore 18) steel 9) f http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Materials_science Speaking 15 Individual SS’ answers 16 Product description (H2SO4) Chemical name Trade names Chemical formula Molecular weight Packaging/ Delivery Properties Product description (HCl) Chemical name Chemical nature Trade name Ingredient Chemical formula Relative molar mass Form supplied and packaging Properties Storage Applications Safety Storage Applications Safety Project work 17 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 18 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 44 UNIT 11 Technological process in chemical industry: tools & equipment Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 A boilers B reactor C mixer D centrifuge E furnace F heat exchanger G extruder H fraction distillation column 3 Individual SS’ answers 4 Boiler – a closed vessel or arrangement of enclosed tubes in which water is heated to supply steam to drive an engine or turbine or provide heat; Reactor – a vessel, esp. one in industrial use, in which a chemical reaction takes place; Mixer – a kitchen appliance, usually electrical, used for mixing foods, etc; Centrifuge – rotating machines that separate liquids from solids or dispersions of one liquid in another, by the action of centrifugal force; Furnace – an enclosed chamber in which heat is produced to generate steam, destroy refuse, smelt or refine ores, etc; Heat exchanger – a device for transferring heat from one fluid to another without allowing them to mix; Extruder – to extrude, press, squeeze, squeeze out; Fraction distillation column/rectifying column – to rectify, distillate, separate Reading 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 1e 2b 3h 4а 5g 6с 7b 8f 7 design – a plan, scheme, or project solid – a substance in a physical state in which it resists changes in size and shape appropriate equipment – right or suitable; fitting unit operation – production unit economic cost – expenses assembly-line – a sequence of machines, tools, operations, workers, etc., in a factory, arranged so that at each stage a further process is carried out automatic control – self-operated control 8 distillation – the process of evaporating or boiling a liquid and condensing its vapour; purification or separation of mixture by using different evaporation rates or boiling points of their components crystallization – conversion of liquid into solid dissolution – the resolution or separation into component parts; disintegration; destruction by breaking up and dispersing filtration – the act or process of filtering extraction – the act of extracting or the condition of being extracted 45 9 1) B 2) A 3) D 4) C 5) F 6) E 7) J 8) G 9) H 10) I Professional Language Development 10 1) d 4) a 7) j 10) h 13) n 2) i 5) k 8) e 11) c 14) m 3) f 6) g 9) b 12) o 15) l 11 mixer, compressor, mill, kiln, dryer Cement Equipment boiler, briquetter, centrifuge, separator, compressor, dryer, dust colChemical lector, evaporator, filter, furnace, heat exchanger, kettle, mill, reEquipment frigeration, screen, solvent distillation Food Processing blancher, briquetter, dicer, pulper, ribbon blender, ribbon mixer, tank, Raymond mill heat exchanger, boiler, industrial evaporator, reactor, conveyor Industrial Processing grinding mill, crusher, ball mill, spiral separator/classifier, magnetic Mining Equipseparator, mixer, dryer, vibrating screen, belt conveyor, Raymond ment mill Pharmaceutical conveyor, capsule filler, centrifuge, compressor, dryer, dust collector, mixer, kettle, reactor, evaporator Equipment filter, boiler, centrifuge, evaporator, heat exchanger, kettle, reactor, Water screen, screw press, belt press, sludge separator, tank Treatment 12 1 building 2 gas 13 1) indicator 2) applications 3) measurement 4) variety 3 valves 4 specialists 5 assurance 6 quality 5) replacement 6) removing 7) configurations Speaking 14 b) Individual SS’ answers 15 Individual SS’ answers 16 № 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Equipment CARBIDE HOPPER ACETYLENE GENERATOR L.P. DRYER PURIFIER AMMONIA SCRUBBER ACETYLENE COMPRESSOR H.P. DRYER CYLINDER FILLING MANIFOLD ACETONE PUMP FLAME PROOF MOTORS 46 7 petroleum 17 Individual SS’ answers Project work 18 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 19 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 47 UNIT 12 Safety at work Proverb Get the SS to read the proverb at the head of the page Elicit SS’ understanding of the proverb Put SS in pairs or small groups and tell them to think of some examples to prove the proverb Starting up 1 Possible answers: fire, spilt chemicals, splashes from acid; injuries: burns, cuts, electrical shock, fractures, poisoning (intoxication), etc. 2 Before working To see warning symbols; To check equipment; To put safety wear on; To know safety rules During working After working Wearing hard hat, safety glass- Using First Aid Kit es, respiratory mask, ear defenders; using flashlight, transmitter, etc.; Following safety rules 3 1) ear defenders: they protect from high sound effect 2) safety glasses/goggles: they protect from eye injury and other harmful effect 3) respiratory mask: it protects human’s respiratory tract from harmful effect 4) safety gloves: they protect skin of hands from injuries 5) lab coat (safety wear/clothing) 6) safety footwear 7) hard hat protects a head from injuries 4 Individual SS’ answers (a) highly flammable – burning easily harmful – causing or likely to cause harm explosive – able to explode corrosive – gradually making smth weaker and possibly destroying it oxidizing – making smth combine with oxygen, especially in a way that causes rust toxic – containing poison or caused by poisonous substances environmental – concerning or affecting the air, land or water on Earth biohazard – dangerous for living things radioactive – containing substanses which are able to emit ionizing radiation (=a form of energy that can harm living things) (b) 1) b 2) d 3) c 4) a 5) I 6) f 7) e 8) h 9) g 48 Reading 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 1) B 2) D 3) F 4) H 5) A 6) C 7 1) D 2) B 3) C 4) D 8 1) a 9 – The following information is not mentioned in the report: sex of injured worker, date/time of accident, witness(es) – name and department. – The delay is more than 24 hours 5) D 6) D 2) c 7) D 8) D 9) I 9) D 10) D 3) b Professional Language development 10 1) C 3) H 5) I 2) E 4) A 6) G 11 1) corrosive 2) flammable 3) toxic 12 A Electrical Hazard Sign B No Open Flames C Fire Extinguisher Sign 13 (a) a) assistant b) coat c) supervisor d) blanket e) extinguisher (b) Individual SS’ answers 14 1) b 2) d 15 Noun 1 explosion 2 flame 3 chemistry 4 hazard 7) E 8) G 7) F 8) D 4) radiation 7) electricity 5) biohazard 8) combustible 6) No Open Flames 9) functional 3) e 9) B 10) nonpotable 11) explosive 12) chemical containers D Nonpotable Water Sign E Chemistry Hazard Label f) sign g) rules h) equipment i) fumes j) materials 4) a Adjective explosive flammable chemical hazardous 5) c Verb/adjective 1 radiate 2 electrical 3 extinguish 4 save Speaking 16 Individual SS’ answers 17 Individual SS’ answers 18 Individual SS’ answers 49 Noun radiation electricity extinguisher safety 19 20 Individual SS’ answers Individual SS’ answers Project work 21 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 22 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 50 UNIT 13 Resource saving Starting up 1 A energy B land C biota D minerals 2 Individual SS’ answers E water Reading 3 Individual SS’ answers 4 1) Humans appropriate 24 per cent of the Earth's production capacity that would otherwise have gone to nature. Resources consumed: fossil fuels, carbon, land, tropical rainforests. 2) The result is a gradual depletion of species and habitats, devastating effects on the climate 3) growing more plants like palm oil and rapeseed for biofuels to ease our reliance on fossil fuels; producing food more efficiently; intensifying agriculture on roughly the same amount of land as we use now. to gobble up – to eat or swallow (food) hastily and in large mouthfuls species – any group of related animals or plants to appropriate – to take for one's own use, esp illegally or without permission depletion – exhaustion habitat – the environment in which an animal or plant normally lives or grows consumption – the act of consuming or the state of being consumed, esp by eating, burning, etc annually – every year to cope – to deal successfully with or handle a situation; manage to expand – to make or become greater in extent, volume, size, or scope; increase fertile – capable of producing offspring rainforest – dense forest found in tropical areas of heavy rainfall. The trees are broad-leaved and evergreen, and the vegetation tends to grow in three layers (undergrowth, intermediate trees and shrubs, and very tall trees, which form a canopy) Also called: selva full-scale – universal, all-embracing, total, complete implication – the act of implicating or the state of being implicated to foresee – to see or know beforehand to wipe out – to destroy completely devastating – extremely effective in a destructive way evaporation – vaporization 5 6 1) based on figures 7) to expand production of biofuels 2) gradual depletion of species and habitats 8) tropical rainforests 3) palm oil 9) full-scale replacement 4) to ease reliance on 10) dramatic implications for ecosystems 5) fossil fuels 11) to meet the biofuel targets 6) fires lit by humans 12) devastating effects on the climate 51 Professional Language development 7 1) raw materials 2) valuable 3) natural 4) petroleum extraction 5) forestry 8 1) valuable minerals 2) geological 3) ore 4) base metals 5) precious metals 6) coal 7) diamonds 8) agricultural 9) artificially 10) laboratory 9 1) reason – reasonably 2) explore – exploring 3) consider – considerable 4) produce – products 5) efficient – efficiency 6) renewable 7) fossil fuels 8) coal 9) natural gas 10) tax on consumption 11) factory 12) natural gas 13) water 14) art 15) science 16) wood 17) wildlife habitat 18) landscape 19) biodiversity 20) carbon dioxide 6) compete – competition 7) strict – stricter 8) innovate – innovation 9) competition – competitive 10) friend – friendly Speaking 10 a) Individual SS’ answers b) Individual SS’ answers 11 Individual SS’ answers Project work 12 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 13 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 52 UNIT 14 Waste disposal Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 A (2) Sanitary Landfill B (4) Ocean dumping C (1) Incineration D (3) Hazardous waste containers E (5) Recycling F (6) Open dumping/landfill 3 1) Sanitary landfill – disposal of waste material by burying it under layers of earth 2) Incineration – disposal method that involves combustion of waste material. 3) Ocean dumping – disposal of waste material by burying it under water 4) Recycling – to reclaim (packaging or products with a limited useful life) for further use 5) Open dumping/landfill – disposal of waste material without burying it under earth but 6) Hazardous waste containers – disposal of waste material without burying, combustion or dumping Reading 4 Possible headlines: 1) Hazardous waste 2) Waste minimization and recycling 3) Disposal options 5 1) a liquid, solid, sludge, or containerized gas waste substance 2) quantity, concentration, or chemical properties 3) when it is corrosive, flammable, unstable, or toxic 4) Sources of hazardous waste may include industry, research, medical, household, chemical producers, agriculture, and mining, as well as many others. 5) The recycling of waste through waste exchanges is one aspect of industrial ecology. Waste exchange also promotes the use of one company's waste as another company's raw material. 6) The ideal disposal method is the destruction and conversion of hazardous waste to a non-hazardous form. 7) The most common form of hazardous waste disposal in the United States is landfilling. 6 Method of waste disposal Landfill Principle of working burying hazardous waste under layers of earth Examples (if mentioned) – Injection well Injecting hazardous – 53 Problems associated with the method Toxic substances leak into surrounding groundwater which is a major source of drinking water worldwide and once it is contaminated, pollutants are extremely difficult and costly to remove. See “landfill” point Incineration Bioremediation Transportation off-site 7 waste under layers of earth with the help of well A way to convert hazardous waste into a nonhazardous form while greatly decreasing its volume; A way to convert hazardous wastes to nontoxic by-products using microorganisms and natural degradation processes; hazardous waste is to be transported offsite for disposal The waste is burned and converted into carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic byproducts. Phytoremediation, the process by which plants absorb and in some cases degrade hazardous substances in the environment. – a) RCRA – The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act EPA – The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency b) Individual SS’ answers Professional Language development 8 1) which/that 6) before 2) rid 7) few 3) into/to 8) with 4) a 9) of/for 5) than 10) all/any 9 1) attract – attracted 2) install – installed 3) house – household 4) extract – extraction 5) like – unlike 11) not 12) on 13) and 14) so 15) other 6) package – packaging 7) less – unless 8) second – secondly 9) sell – sold 10) great – greater Speaking 10 Individual SS’ answers 11 Individual SS’ answers 12 Individual SS’ answers Project work 54 high capital and operating costs; the disposal of ash, which may contain hazardous substances; incinerating wastes can cause mercury and dioxin air pollution It requires very long treatment times and it may be difficult to control or enhance natural degradation processes. – 13 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing 14 Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 55 UNIT 15 Innovations in chemical engineering Starting up 1 Individual SS’ answers 2 1) D 3) F 2) A 4) E 3 Individual SS’ reports 5) C 6) B Reading 4 Individual SS’ answers 5 Individual SS’ answers 6 factor dosimeter indicator acid-release agent pigment material radiation effective solution 7 1. contributing factor 2. skin cancer 3. sun exposure 4. acid-release agent 5. colour change 8 (a) Individual SS’ answers (b) Individual SS’ answers 6. a tin oxide photocatalyst 7. pigment materials 8. UV radiation 9. academic science 10. greatest challenge 9 A–7 C–1 E–6 G–3 B–5 D–2 F–4 (The interview with a professor at Queen's University Belfast, UK – A Prasanna de Silva.) (Chem. Technol., 2009,6. T25-T32 T29) What led you to specialise in supramolecular chemistry? The philosophical breadth of supramolecular chemistry, especially in the hands of JeanMarie Lehn and Seiji Shinkai, was clear to see during the early 1980s. Around this time, I had just completed my PhD research in organic photochemistry at Queen's University Belfast under Jim Grimshaw. Combiningphotochemistry with supramolecular chemistry permitted the fluorescence signalling of alkali metal ions-a virgin field at the time. Your research helped develop blood diagnostic cassettes. How does this chemistry work? Fluorescent molecular sensors can gather information about atomic or molecular behaviour from environments of nanometre dimensions. We developed sensors which contain a fluorescent unit and a receptor unit joined through a spacer module. This supermolerale loses its fluorescence capability owing to an inter-module photoinduced electron transfer (PET) quite similar to that seen in green plant photosynthesis. This PET 56 process is stopped the moment the receptor module captures its target, for example a sodium ion, thereby switching the suppressed fluorescence back on. Thus the fluorescence signal measures the concentration level of the target species. In collaboration with Roche Diagnostics (now Optimedical), we produced fluorescent PET sensors held inside small plastic cassettes. These sensors respond to various blood gases and electrolytes and are used in hospital critical care units, ambulances, general practice surgeries and even veterinary environments. The cassettes have had sales of over 55 million US dollars so far. You have said in the past that you persuade molecules to perform arithmetic operations. What you mean by this? Conventional silicon-based logic devices use electric voltages as the inputs and outputs. The first examples of molecular logic gates used chemical species such as protons and sodium ions as inputs along with fluorescence as the output. Nathan McClenaghan and I designed molecules which could perform the computation of adding one and one to get two. Though elementary, this computation is understandable to virtually everyone on the planet. So, persuading molecules to do arithmetic was an important early step on the journey of molecular logic and computation. What is the next bigt hing that you would like to tackle in your lab? Molecular logic and computation is a young field with a need to prove itself in different ways. Demonstratingreal-life applications which conventional silicon-based computingcannot do would be one such avenue. We have already shown an application where a population of small micrometric objects are given identification tags made up of molecular logic gates. This is a bit like faces on people or number plates on cars except everything is a lot smaller. Such molecular computational identification (MOD) can address far smaller objects than those handled conveniently by the popular RFID (radiofrequency identification) technology. We now need to generalize this MCID technique and broaden its applicability. What is hot at the moment in your research area? Molecular computingor data processingin small spaces is the hot topic. These molecular devices will reach where silicon devices cannot easily go, whether it be inside living cells, on the surface of plastic beads or inside detergent micelles. Which scientist, current or historic, do you most admire and why? Thomas Andrews was the first professor of chemistry at the then Queen's College of Belfasi 150 years ago. Even1 time water turns to vapou г о г ice, I am reminded of this man's work on the effects of temperature and pressure on materials. Also at that time, George Boole at University College Cork. Ireland laid the foundations of modern computing with his ideas on logic and algebra. These two giants in the north and the south of a small island changed the way the world worked. If you weren't a scientist, what would you do? I would have to be a percussionist. I have pi ayed all my life and, like many Sri Lankan kids, I got my grounding in rhythm at a young age. Northern Ireland, with its rich musical tradition, was a great place to put that rhythm to use. It was a just matter of 57 timebefore I was introduced to a band where a Sri Lankan percussionist could blend with Irish fiddles, flutes, banjos, bodhrans and voices. We have enjoyed playing together for the last 13 years, even though I have been advised to hold onto my day job! 10 Individual SS’ answers Professional Language development 11 verb noun (thing) develop development design invent innovate produce create pioneer patent design invention innovation production creation patent noun (person) developer designer inventor inventor producer creator pioneer patentee adjective developed developmental developing Inventive/invented innovative productive Creative/created pioneering Patent/patented 12 positive negative Efficient, brilliant, ingenious, revolution- Ridiculous, uneconomical, impractical, ary, viable, beneficial, ground-breaking, useless, pointless clever, marketable, feasible 13 1 ultraviolet 2 light 3 bugs 4 photochemistry 5 hydrogen 6 sewage 7 bug-killing 8 germ-free 9 domestic 10 chemicals 14 http://altachemical.com/index.php?page=techno&pid=290 1) innovation 6) generating 2) chemists 7) developed 3) production 8) developments 4) marketing 10) successfully 5) working 11) commercial Speaking 15 Individual SS’ answers Project work 16 Criteria to assess SS’ presentations : stage presence, interactive communication, visual aids, grammar and vocabulary correctness, language use, coherence, structure of presentation, timing). Writing Criteria to assess SS’ writing tasks : content, structure, vocabulary, grammar, spelling, register and format. 58 Учебное издание АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК ДЛЯ ИНЖЕНЕРОВ-ХИМИКОВ Книга для преподавателя Учебное пособие Авторы-составители ПЕТРОВСКАЯ Татьяна Семеновна РЫМАНОВА Ирина Евгеньевна МАКАРОВСКИХ Александра Викторовна Издано в авторской редакции Научный редактор кандидат филологических наук, доцент А.В. Диденко Дизайн обложки А.И. Сидоренко Отпечатано в Издательстве ТПУ в полном соответствии с качеством предоставленного оригинал-макета Подписано к печати 13.11.2012. Формат 60×84/16. Бумага «Cнегурочка». Печать XEROX. Усл. печ. л. 3,43. Уч.-изд. л. 3,1. Заказ 1264-12. Тираж 100 экз. Национальный исследовательский Томский политехнический университет Система менеджмента качества Издательства Томского политехнического университета сертифицирована NATIONAL QUALITY ASSURANCE по стандарту BS EN ISO 9001:2008 . 634050, г. Томск, пр. Ленина, 30 Тел/факс: +7 (3822) 56-35-35, www.tpu.ru 59