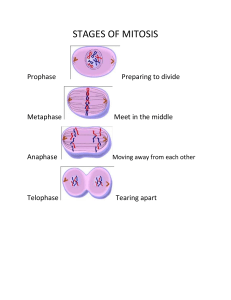
CELL DIVISION Reading Comprehension COLOR & BW CELL DIVISION Living organisms are required to constantly make new cells to replace old dead cells. This process is known as cell division is constantly occurring. In the average human body about two trillion cell divisions occur daily. Types The three main types of cell division are: binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis. Simple organisms, like bacteria, use binary fission. Other cells that are more complex use either mitosis or meiosis to gain new cells. Mitosis When a cell needs to be replicated into an exact copy of itself, the process of mitosis is used. Everything in a cell is duplicated, so the two new cells have the same DNA, function, and genetic code. The mother cell is the original cell, and the two new cells are known as the daughter cells. Cells produced through mitosis include skin, blood, and muscle cells in the human body. Mitosis Cycle There are different phases of the cell cycle. Interphase The “normal” state of a cell is known as “interphase.” Genetic material is duplicated during the interphase stage. When a cell receives the signal to duplicate, it enters the first state of mitosis, called “prophase.” Prophase The chromatin condenses into chromosomes during the prophase stage. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus break down. Metaphase The chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell during metaphase. ©Teaching to the Middle Anaphase The separation begins in anaphase. Half of the chromosomes are pulled to one side, while the other half go the other way. Once they reach the side of the cell, it is time for telophase. Telophase The cell division finishes up during the telophase. The cell forms two nuclear membranes around each set of chromosomes during telophase. Then the chromosomes uncoil and the cell walls pinch off and split down the middle. The daughter cells, or two new cells, are then formed. Cytokinesis The splitting of the cells is known as cytokinesis or cell cleavage. Meiosis When an entire organism needs to reproduce, the meiosis process occurs. There are two major differences between mitosis and meiosis. The meiosis process has two divisions. Upon completion, meiosis produces four new cells instead of only two. Another difference is that the new cells only have half of the DNA of the original cell in meiosis. This is vital for Earth’s living organism that require new genetic combinations and a variety of life. Diploids and Haploids Cells produced during mitosis are known as diploids since they have two complete sets of chromosomes. Cells produced from meiosis are called haploids because they contain half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Binary Fission Simple organisms, like bacteria, go through a cell division process known as binary fission. The DNA replicates and the cell grows to twice its normal size. Duplicate strands of DNA then move to opposite sides of the cell. The cell wall then “pinches” off in the middle to form two separate cells. ©Teaching to the Middle Name_________________________________________ Cell Division Identify: Use the word bank to identify each term described. mother cell interphase cytokinesis prophase meiosis mitosis daughter cells binary fission anaphase diploids metaphase telophase 1. The chromosomes separate and move to the opposite sides of the cell in this phase of mitosis 2. The “normal” state of a cell 3. The splitting of the cells in mitosis 4. Process that makes an exact copy of a cell 5. Process used when it is time for an entire organism to reproduce 6. Original cell 7. The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle during this phase of mitosis 8. The new cells produced 9. Cells produced from mitosis because they have two complete sets of chromosomes 10. First step of mitosis 11. Part of mitosis when the chromosomes line up 12. Cell division process for simple organisms ©Teaching to the Middle Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer. 13. A. B. C. D. Which of the following is NOT a main type of cell division? Mitosis Meiosis Interphase Binary Fission 14. A. B. C. D. Which step of mitosis is illustrated to the right? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 15. A. B. C. D. What type of organisms mainly undergo binary fission? Humans Plants Animals Bacteria 16. How often do living organisms make new cells? A. Never B. Sometimes C. Frequently D. Constantly 17. Which of the following is NOT a difference in mitosis and meiosis? A. Mitosis produces new cells, while meiosis does not. B. Mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the mother cell, while meiosis produces four daughter cells. C. Cells produced during mitosis are known as, while cells produced from meiosis are called haploids. D. Chromosome numbers remain the same in mitosis, while they are reduced by half in meiosis. 18. What mainly occurs during the telophase part of mitosis? A. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. B. Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. C. Chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. D. The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle. ©Teaching to the Middle CELL DIVISION Living organisms are required to constantly make new cells to replace old dead cells. This process is known as cell division is constantly occurring. In the average human body about two trillion cell divisions occur daily. Types The three main types of cell division are: binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis. Simple organisms, like bacteria, use binary fission. Other cells that are more complex use either mitosis or meiosis to gain new cells. Mitosis When a cell needs to be replicated into an exact copy of itself, the process of mitosis is used. Everything in a cell is duplicated, so the two new cells have the same DNA, function, and genetic code. The mother cell is the original cell, and the two new cells are known as the daughter cells. Cells produced through mitosis include skin, blood, and muscle cells in the human body. Mitosis Cycle There are different phases of the cell cycle. Interphase The “normal” state of a cell is known as “interphase.” Genetic material is duplicated during the interphase stage. When a cell receives the signal to duplicate, it enters the first state of mitosis, called “prophase.” Prophase The chromatin condenses into chromosomes during the prophase stage. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus break down. Metaphase The chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell during metaphase. ©Teaching to the Middle Anaphase The separation begins in anaphase. Half of the chromosomes are pulled to one side, while the other half go the other way. Once they reach the side of the cell, it is time for telophase. Telophase The cell division finishes up during the telophase. The cell forms two nuclear membranes around each set of chromosomes during telophase. Then the chromosomes uncoil and the cell walls pinch off and split down the middle. The daughter cells, or two new cells, are then formed. Cytokinesis The splitting of the cells is known as cytokinesis or cell cleavage. Meiosis When an entire organism needs to reproduce, the meiosis process occurs. There are two major differences between mitosis and meiosis. The meiosis process has two divisions. Upon completion, meiosis produces four new cells instead of only two. Another difference is that the new cells only have half of the DNA of the original cell in meiosis. This is vital for Earth’s living organism that require new genetic combinations and a variety of life. Diploids and Haploids Cells produced during mitosis are known as diploids since they have two complete sets of chromosomes. Cells produced from meiosis are called haploids because they contain half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Binary Fission Simple organisms, like bacteria, go through a cell division process known as binary fission. The DNA replicates and the cell grows to twice its normal size. Duplicate strands of DNA then move to opposite sides of the cell. The cell wall then “pinches” off in the middle to form two separate cells. ©Teaching to the Middle Name_________________________________________ Cell Division Identify: Use the word bank to identify each term described. mother cell interphase cytokinesis prophase meiosis mitosis daughter cells binary fission anaphase diploids metaphase telophase 1. The chromosomes separate and move to the opposite sides of the cell in this phase of mitosis 2. The “normal” state of a cell 3. The splitting of the cells in mitosis 4. Process that makes an exact copy of a cell 5. Process used when it is time for an entire organism to reproduce 6. Original cell 7. The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle during this phase of mitosis 8. The new cells produced 9. Cells produced from mitosis because they have two complete sets of chromosomes 10. First step of mitosis 11. Part of mitosis when the chromosomes line up 12. Cell division process for simple organisms ©Teaching to the Middle Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer. 13. A. B. C. D. Which of the following is NOT a main type of cell division? Mitosis Meiosis Interphase Binary Fission 14. A. B. C. D. Which step of mitosis is illustrated to the right? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 15. A. B. C. D. What type of organisms mainly undergo binary fission? Humans Plants Animals Bacteria 16. How often do living organisms make new cells? A. Never B. Sometimes C. Frequently D. Constantly 17. Which of the following is NOT a difference in mitosis and meiosis? A. Mitosis produces new cells, while meiosis does not. B. Mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the mother cell, while meiosis produces four daughter cells. C. Cells produced during mitosis are known as, while cells produced from meiosis are called haploids. D. Chromosome numbers remain the same in mitosis, while they are reduced by half in meiosis. 18. What mainly occurs during the telophase part of mitosis? A. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. B. Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. C. Chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. D. The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle. ©Teaching to the Middle Name_________________________________________ Cell Division Identify: Use the word bank to identify each term described. mother cell interphase cytokinesis prophase meiosis mitosis daughter cells binary fission anaphase diploids metaphase telophase 1. anaphase The chromosomes separate and move to the opposite sides of the cell in this phase of mitosis 2. interphase The “normal” state of a cell 3. cytokinesis The splitting of the cells in mitosis 4. mitosis Process that makes an exact copy of a cell 5. meiosis Process used when it is time for an entire organism to reproduce 6. mother cell Original cell 7. telophase The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle during this phase of mitosis 8. daughter cells The new cells produced 9. diploids Cells produced from mitosis because they have two complete sets of chromosomes 10. prophase First step of mitosis 11. metaphase Part of mitosis when the chromosomes line up 12. binary fission Cell division process for simple organisms ©Teaching to the Middle Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer. 13. A. B. C. D. Which of the following is NOT a main type of cell division? Mitosis Meiosis Interphase Binary Fission 14. A. B. C. D. Which step of mitosis is illustrated to the right? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 15. A. B. C. D. What type of organisms mainly undergo binary fission? Humans Plants Animals Bacteria 16. How often do living organisms make new cells? A. Never B. Sometimes C. Frequently D. Constantly 17. Which of the following is NOT a difference in mitosis and meiosis? A. Mitosis produces new cells, while meiosis does not. B. Mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the mother cell, while meiosis produces four daughter cells. C. Cells produced during mitosis are known as, while cells produced from meiosis are called haploids. D. Chromosome numbers remain the same in mitosis, while they are reduced by half in meiosis. 18. What mainly occurs during the telophase part of mitosis? A. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. B. Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. C. Chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. D. The cell walls pinch off and split down the middle. ©Teaching to the Middle Thank you for your purchase! www.Ducksters.com www.biology4kids.com www.kidsdiscover.com Tutorial How to Make PDFs Editable for Google Classroom *If you don't already, Follow Me! I add new products almost daily.