English Verb Tenses: Present Simple, Progressive, Perfect, Past
advertisement

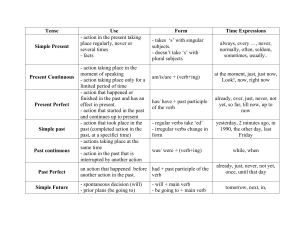
Al Farahidi University. College of Education . English language department Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past By\Hashim . S . Ameer Stage\Third Group\ -4- Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 The first verb tenses an English student learns are the present simple and the present continuous, partly because they are the most simple but also because they are the most commonly used. Here is a guide on how to create and use both tenses. The Present Simple We use the present simple tense for the following situations: 1. to describe permanent or long-term facts. For example: Lions live in Africa. 2. to describe habits and routines. For example: I usually get up at 7am. 3. to express general preferences and opinions. For example: She loves music. 4. to refer to the schedule of transport or events. For example, Our flight leaves at 12:30. The Structure To make sentences with the present simple there are only two forms for almost all verbs. For example, for the verb ‘to play’ in the present simple affirmative form is as follows: As you can see, we simply use the base form of the verb ‘play’ for all the subjects, except the third person singular, where we add -s. For example: They work here. She likes tennis. You have a beautiful car. We want a sandwich. I live in the city center. The conference starts tomorrow. Al Farahidi University Page 1 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 To create negative sentences we add ‘don’t’ for I/you/we/they and ‘doesn’t’ for he/she/it: For example: We don’t have time. They don’t come from this city. He doesn’t often play football. You don’t speak Chinese. I don’t like tea. You and your brother don’t eat fish. And to make questions we add ‘do’ for I/you/we/they and ‘does’ for he/she/it: For example: Do we need to make a reservation? Do you think it’s a good idea? Does it rain much here? Do I have time for a coffee? Do they want something to eat? Al Farahidi University Page 2 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 The exception to this structure is the verb ‘to be’ which is irregular and forms negatives and questions in a different way. To make negatives in the verb ‘to be’ we add ‘not’, and to make questions we invert the subject and verb: Here are some examples: Are you tired? We’re not hungry. Is he ready? They’re from Rome. You’re not a student, are you? It’s really hot here today. The Third Person Singular Having such a simple structure for most subjects can make you think it’s very easy to use the present simple, and it is in many ways. But it’s really important to remember the one subject that is different because forgetting to use the -s for verbs in the third person singular is very noticeable. So it’s a really good idea to focus on learning and practicing it to be a good English speaker. There are three ways to add -s to verbs in the present simple, according to the spelling of the verb: Al Farahidi University Page 3 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 For example: He studies very hard. My Dad fixes things in our home. She does ballet. Your house looks beautiful. The weather always gets worse in November. He doesn’t want to go out. She doesn’t need any more clothes. The Present Continuous The present continuous (also known as the Present Progressive) is used in these situations: 1. to describe an action in progress 2. to describe a short-term or temporary situation Al Farahidi University Page 4 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 The Structure To create the present continuous we use the verb ‘to be’ and the gerund (or -ing form) of the main verb. The affirmative form of the verb ‘to play’ is as follows: To create the negative form we simply change the verb ‘to be’ into the negative: To make questions with the present continuous we invert the subject and the the verb ‘to be’. Al Farahidi University Page 5 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 Here are some examples: We’re going out. See you later. Ted’s working in the garden. What are the children doing? They’re doing their homework. How are you feeling? The machine isn’t working properly. Why are you wearing a sweater? It’s hot in here. Giulia is staying with her sister at the moment. EXCEPTION! There are some verbs that we never use in the present continuous tense because they are states and cannot have a progressive form. These verbs are preference and state verbs, such as: know, have (for possession), like, love, prefer, hate, want, believe, own, cost. For these and similar verbs, we use the simple tenses. The Present Continuous for the Future When we talk about a fixed event in the future we often use the present continuous. It’s particularly common when you refer to appointments in your agenda, For example: I’m going to the dentist on Tuesday at 10am. We’re meeting my sister for lunch today. He’s having a haircut this afternoon. What time are you leaving? They’re taking the seven o’clock train. Al Farahidi University Page 6 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 You’re looking after the kids tonight. Present Simple or Present Continuous? When you are not sure whether to use the present simple or the present continuous, ask yourself these questions: Is it a long-term situation? If so, use the present simple Is it a state verb? (For example, like) If so, use the present simple Is it an action verb happening in this moment? If so, use the present continuous Is it an action verb that is a temporary situation? If so, use the present continuous Is it a fixed plan in the future? If so, use the present continuous As you can see, we use these two tenses in many daily situations so they’re really useful to learn as well as you can. Try to practice them a lot until they become natural, and pay special attention to the third person singular form because it will really make a difference in your accuracy in conversation. Present Perfect (Simple / Continuous) Perfect Simple: Subject + have/has+ verb (p.p) + complement Perfect Continuous: Subject +have/has+ been+ verb -ing + complement Present perfect (simple or continuous) has three uses: 1- Unfinshed (An activity that occurred in the past and was not completed in the past, that is, it continued to the present) past Examples: - We have lived in this house for twenty years. - I have been playing video games since I was a kid. The difference between the present perfect simple and the present perfect continuous is that the perfect continuous is temporal (limited to a period) while the simple seems permanent 2- Present results ( an activity that happened in the recent past and leaves results that can be sought in the present) Examples: Al Farahidi University Page 7 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 - I have lost some weight. - I have been doing some exercises. The difference between Present Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Continuous is that the Present Perfect Continuous is used to express An activity that happened repeatedly for a period of time, while the simple is used to express a completed activity. In both cases we see the results in the present. Headway: Upper- Intermediate Student's Book An activity that happened at an indefinite time, where the focus is on the event and not the time past Indefinit-3 Examples: - Have you ever taken Karate classes? - Have you ever been flying in a plane when it's hit an air pocket? The similarity between Present Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Continuous is both used to focus on A specific event without paying attention to time.. In the first sentence, focus on taking karate lessons and in The second sentence focuses on the experience of flying in an airplane and exposes it to an air pocket. Notes: 1 - There is a group of verbs that we find suitable for the present perfect simple and others for the present perfect continuous Present Perfect Simple Start, find, lose, begin, stop, break, die, decide, and cut Example: We have decided to get married. Present Perfect Continuous Al Farahidi University Page 8 Present simple Present progressive (ing) Present perfect Past 2020\2021 Wait, rain, snow, learn, sit, lie, play and stay Example: It has been raining all day. 2- There is a group of verbs to which we must add ing - and it is called verbs state and therefore it is Use the present perfect simple only Believe, think, understand, agree, like, love, want, have, look, hear, state, smell, feel, know…etc Example: I have known him for years I have been knowing him for years. I've/ as, have for '(ve) and she's /he's/ it's as, has for '(s) 3- Abbreviations They've/ we've/ you've Al Farahidi University Page 9