Review on exponential
𝑥
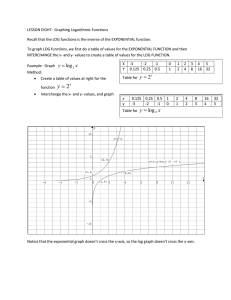
For exponential function 𝑦 = 𝑐 𝑐 > 0
Properties of standard exponential
𝑥
functions 𝑦 = 𝑐
𝑐 > 0, 𝑐 ≠ 1
Domain: 𝑥 ∈ ℝ
Range: {𝑦 > 0|𝑦 ∈ ℝ}
Y-intercept: 1
Horizontal asymptote: y=0
Increasing if c>1; decreasing if 0<c<1
Of course, if you have an application question,
the domain could be limited.
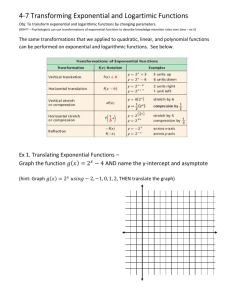
Transformation of exponential
functions
• 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑓 𝑏(𝑥 − ℎ) + 𝑘 = 𝑎 × 𝑐 𝑏
• Domain: 𝑥 ∈ ℝ
• Range:
– If a>0: 𝑦 > 𝑘 𝑦 ∈ ℝ
– If a<0: 𝑦 < 𝑘 𝑦 ∈ ℝ
• Horizontal asymptote: y=k
• Intercepts: Please calculate them
𝑥−ℎ
+𝑘
Find the domain, range, asymptote and all intercepts of
𝑦=
1
−
3
3
1
𝑥
2
+5
Domain: 𝑥 ∈ ℝ
Range: 𝑦 < 5 𝑦 ∈ ℝ
Horizontal asymptote: 𝑦 = 5
Intercepts:
14
Y-intercept (x=0):
3
x-intercept (y=0): We need some tests for now
1
1
0 = − 3 2𝑥 + 5
3
1
1
−5 = − 3 2𝑥
3
1
2𝑥
15 = 3
1
𝑥 = 2.47
2
𝑥 = 4.94
32 = 9
33 = 27
1
𝑥 is between 2 and 3
2
32.5 = 15.6
32.4 = 14.0
32.47 = 15.1 (𝑐𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒)
How to graph an exponential function?
• Identify the base function (no a, b, h or k)
• Make a table of values for the base function
• Apply transformations
• 𝑦=
1
−
3
3
1
𝑥
2
+5
• Base function: 𝑦 = 3𝑥
Solving exponential equations without
log
Write everything using the same base.
1
𝑥
2 =
128
Recall the exponential rules.
Write down the domain and range of