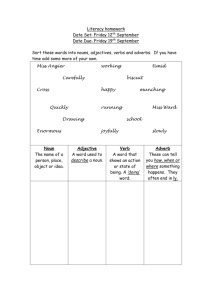
Noun Clause A noun clause is a dependent (or subordinate clause) that works as a noun. It can be the subject of a sentence, an object (DO, IO, and OP), a complement (PN) or Appositive. Like all nouns, the purpose of a noun clause is to name a person, place, thing, or idea. Sometimes when we want to name something, a single word won’t do – sometimes we need a group of words to name something. That is why we use noun clauses. Types of Noun Clauses a. Noun Clauses as Subjects Example 1 Whoever leaves last should turn off the lights. Example 2 That people need water to survive should be obvious to everyone. Example 3 In music, which note is played and how long it is played are both essential. In this example, the sentence is about two things: ‘which note is played’ and ‘how long it is played’. Therefore, both of these noun clauses are the subject of the sentence. b. Noun Clauses as Objects Direct objects Indirect objects Objects of prepositions Example 1 My dog will eat whatever food I give him. DO Example 2 The judges will award whichever painting they like the most the blue ribbon. IO Example 3 I want to play with whoever is a good sport. OP c. Noun Clauses as Complements (PN) A complement re-states or gives more information about a noun. It always follows a state-of-being verb (is, are, am, will be, was, were). Example 1 The winner will be whoever gets the most votes. Example 2 My hope is that everyone here becomes friends. d. Noun Clauses as appositive Her plan, that we improve the environment, has much support. Appositive III- Identify the function of each Noun Clause in each sentence (SUB, DO, IO, OP, PN, appositive) Example: I know what the answer is. ____DO_______________ 1. Do you know what happened? __ ___DO 2. Susan thinks that she will get the job at Martin's Store. _DO_ ___ 3. Whoever phoned us didn't let the phone ring long enough. _SUBJECT__ __ 4. Andy’s promise was that he'd be on time for the party. __ ___PN 5. Whether or not she should go camping worried Jane. _ ____SUB 6. Mr. Sims mentioned that he'd be late for the meeting. ____ _DO 7. Whoever sent us this letter should have signed his or her name. SUB_____ 8. Who your ancestors were makes no difference to me. _ ____SUB 9. Mr. Barnes wondered about what happened to Carl __ ___OP 10. That anyone else could be doing the same experiments has occurred to him. SUB___ __ 11. You can tell whomever you want the truth. ____ IO_______ 12. His idea, that people are equal, is central to American democracy. __APP___ ________ HINT: The noun clause cannot be removed unless it is an appositive IV- Identify the underlined clauses as Adjective, Adverb, or Noun. 1. What happened on June 30, 1973 will never be forgotten in our town. NOUN 2. We all believe that Jim will be elected class president. _NOUN__ __ 3. She can swim better than Bob can. __ADVERB _____ 4. Although I'd never been in the Martins' house before, I felt at home there. _ADVERB_ 5. When you listen to music on the radio, do you hum along with it? __ADVERB____ 6. Is this the letter that you were expecting? __ADJECTIVE _______ 7. Over there is the school that I attended. __ADJECTIVE___ ____ 8. Is that the antique show that you visited? ___ADJECTIVE _______ 9. The Harveys have a dog that is fourteen years old. ___ADJECTIVE_ _____ 10. We knew that we were in for a spell of hot, humid weather. _NOUN AS DO__ ____ 11. Mr. Norman regrets that he didn't travel more in his youth. __NOUN _______ 12. You may have the job if you will work hard at it. __ADVERB__ _____ 13. Whenever you make a promise, you must keep it. __ADVERB_ ______ 14. Mr. Hartman is a history teacher who also coaches track. __ADJECTIVE_________ 15. For dinner, we had chicken fried steak, which is my favorite dish. _ADJECTIVE_ ___ 16. Whoever sent us this Christmas card forgot to sign his or her name. _NOUN___ 17. Whoever visits us will be assured of a freshly painted room. _NOUN ____ 18. Since they left Cleveland, the Smiths have lived in three other cities. ADVERB Where, when, how, why, since, before: adverbs That: no function in a noun clause Who and whoever always subject Whom and whomever always DO or OP Whose: adjective If and whether : no function Which , whichever, and what, whatever: subject, DO,OP, and adjective My choice will be whichever ones she chooses. (Adjective) My choice will be whichever goes first. (Subject) My choice will be whichever he chooses. (DO) My choice will be whichever he looks for. (OP) What happened doesn’t concern me. (Subject) What he did doesn’t concern me. (DO) What he wrote about doesn’t concern me. (OP) What choice he made doesn’t concern me. (Adjective)