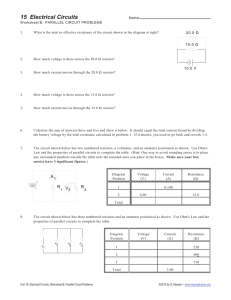
Science Notes → Circuits Learning Intentions ● Calculate the effective resistance of a series or parallel circuit ● Explain the role of effective resistance in circuits ● Calculate the current and voltage across individual elements in series and parallel circuits Series Circuits ● Voltage is shared between all elements according to their resistance ● Current remains constant for elements in series Parallel Circuits ● Each parallel branch receives the same amount of voltage ● Current splits at junctions so that the required amount flows through each branch Effective Resistance ● The power source provides enough current for all connected elements to work as predicted by Ohm’s Law ● Current splits at junctions but the total current moves through the battery ● Effective resistance is the resistance a single resistor would need to have the same current flow through the battery as the overall circuit ● V = I x R → Voltage = Current x Resistance ● Series: RT = R1 + R2 + … + RN ● Parallel: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/RN Example 1 Calculate the effective resistance of the circuit ● RT = 30 + 45 = 75 ohms How much voltage does the 45 A(amps) resistor use? ● I = V/RT = 12/75 = 0.16 A ● V = IR = 0.16 x 45 = 7.2 V Terms & General Knowledge ● Ω → Ohms ● A → Amps ● V = I x R → Voltage = Current x Resistance ● Long bar (in battery) is positive charge ● Currents generally flow from positive to negative