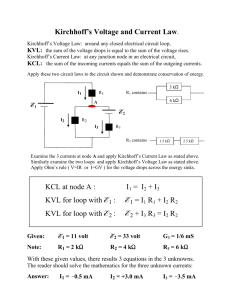
ACTIVITY 7 DATA SHEET Name: ____________________________________ Date Performed: __________________ Course Code & Section: _____________________________ DMM Model: _________________ DMM Type: __________________________________ KIRCHHOFF’S RULES A. GIVEN RESISTORS AND MEASURED VOLTAGES Resistors Measured Voltages 𝑅1 = 𝑉1 = volts 𝑅2 = 𝑉2 = volts 𝑅3 = B. CIRCUIT CALCULATIONS USING KVL AND KCL Figure A. Circuit with assumed currents KCL at node e: KVL around loop 1 (loop abgfea): KVL around loop 2 (loop efgdce): Solution for 𝐼1, 𝐼2, and 𝐼3. C. MEASURED CURRENTS Measured Currents (amperes) 𝐼1 = 𝐼2 = 𝐼3 = Figure B. Circuit with correct direction of currents D. COMPARISON Current Calculated Value (amperes) Measured Value (amperes) % difference 𝐼1 𝐼2 𝐼3 Manzano, Enrique (2020 December). For DLSU use only. NOT FOR CITATION, SALE, NOR REDISTRIBUTION. PHYSICS DEPARTMENT College of Science De La Salle University - Manila KIRCHHOFF’S RULES Guide Questions 1. Why must both batteries/power sources be connected when the terminal voltage across each of them was measured? 2. State the conservation laws that govern Kirchhoff’s Current Law and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law. 3. The terminal voltage of a battery is not in general equal to its emf when the battery is connected to a circuit. Why is this so? 4. Which battery in the circuit supplies power to the circuit? Which battery is being charged or absorbing power? 5. What is the significance of a negative calculated value for current in a branch? Manzano, Enrique (2020 December). For DLSU use only. NOT FOR CITATION, SALE, NOR REDISTRIBUTION.