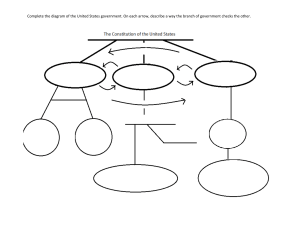
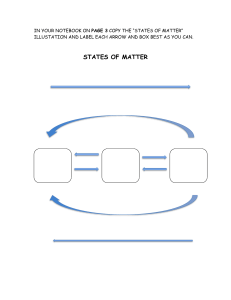
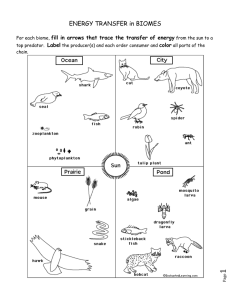
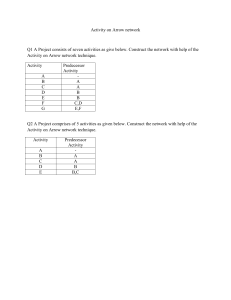
Year 11 Biology Semester 1 exam revision Plant Animal Prokaryote Protoctista Plantae Annelid Chordata Insecta A= Fungi B=Protoctista A= reproduce using spores / hyphae /mycelium/ chitin walls B=eukaryotic / single celled / membrane bound organelles Segmented body, jointed legs Class Arachnida, insect, crustacea Class Order Family Species Lemur catta Three species of bee were collected in a farmland area: Peponapis pruinosa, Andrena chlorogaster and Andrena piperi. What do these names suggest about the evolutionary relationships between these bee species? Three species of bee were collected in a farmland area: Peponapis pruinosa, Andrena chlorogaster and Andrena piperi. What do these names suggest about the evolutionary relationships between these bee species? A.chlorogaster and A. piperi are more closely related (to each other than to P. pruinosa); Because they are in the same genus Sam and Tina, keen biology students, spent a week on work experience in a microbiology laboratory studying and classifying bacteria. From the results of many observations, they constructed a key, which classified all the organisms they had observed. The key is shown below. Below is a diagram of one of the organisms they studied. According to the key, its name would be: Use the existing key above to draw a labelled diagram of Bacillus anthracis. Sam and Tina, keen biology students, spent a week on work experience in a microbiology laboratory studying and classifying bacteria. From the results of many observations, they constructed a key, which classified all the organisms they had observed. The key is shown below. Below is a diagram of one of the organisms they studied. According to the key, its name would be: Spirillum volutans Use the existing key above to draw a labelled diagram of Bacillus anthracis. Secondary succession Pioneer Climax community Seres GPP Pyramid of energy Finches are another organism in this ecosystem. These birds eat the seeds that the tree produces and the hawks and eagles eat the finches. Add this information to Fig 7.1. Suggest and explain two changes that might occur if the eagles in this ecosystem died out. Finches are another organism in this ecosystem. These birds eat the seeds that the tree produces and the hawks and eagles eat the finches. Add this information to Fig 7.1. Finch Suggest and explain two changes that might occur if the eagles in this ecosystem died out. Increase in hawks; as not eaten (by eagles/no predators) increase in hawks decrease in, everything eaten by the hawk/decrease in finch/crow decrease in crows/finches;as more hawks to eat them increase in finches;as fewer eagles to eat them; increase in aphids and locusts ;as fewer crows to eat them Inedible parts or egested faeces or respiration / as CO2 Eutrophication Bacteria decay organic matter / sewage / algae / dead plants (by) digestion bacteria respire aerobically or respire using oxygen (which) lowers oxygen concentration (in water) causing death of fish Using the results shown in Figure 5, discuss the succession of the sand dunes. Using the results shown in Figure 5, discuss the succession of the sand dunes. Beach grass is the pioneer (species) Pioneer species change the (abiotic)environment/habitat/ conditions/factors So less hostile / more suitable for shrub-bunchgrass Conifer/hardwood trees represent the climax community Beetles or spiders eating aphids Clover and Rhizobium (clover provides Rhizobium with shelter, Rhizobium provides the clover with nitrogen Lag Exponential / log Stationary Death / decline Draw an arrow labelled D on the solid line to show one phase where (Deaths + Emigration) exceeds (Births + Immigration). Explain the term carrying capacity. State two examples of density dependent factors that can affect the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. State one example of a density independent factor. Draw an arrow labelled D on the solid line to show one phase where (Deaths + Emigration) exceeds (Births + Immigration). Explain the term carrying capacity. The maximum size of population that can be maintained / supported. D State two examples of density dependent factors that can affect the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Availability of / competition for food / space / mates / light; predation; disease State one example of a density independent factor. Temperature / weather (extremes) / flood / fire / natural disasters What is the name of the processes represented by the arrows labelled 1 and 2? What general name is given to all the organisms responsible for the process represented by arrow 4? Name the term which describes the biochemical process represented by arrow 5. What is the general name given to the organisms carrying out the process shown by arrow 3? What process is indicated by arrow 6? What is the name of the processes represented by the arrows labelled 1 and 2? 1 Respiration 2 photosynthesis What general name is given to all the organisms responsible for the process represented by arrow 4? Decomposers Name the term which describes the biochemical process represented by arrow 5. Nitrogen fixation What is the general name given to the organisms carrying out the process shown by arrow 3? Nitrifying bacteria What process is indicated by arrow 6? Denitrification (mean per m2 =) 6 (field area =) 55 000 (m2) mean x area 6 × 55 000 = 330 000