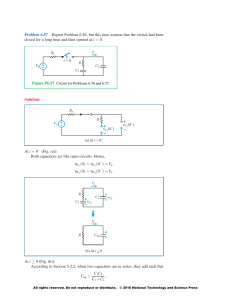
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press 1. CIRCUIT TERMINOLOGY CIRCUITS by Ulaby & Maharbiz All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Chapter 1: Circuit Terminology Electronics Devices – active vs. passive Circuits Systems All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Cell-Phone Architecture All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Units, Multiples, Notation All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Tech Brief 1: Micro- and Nanotechnology All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Tech Brief 1: Moore’s Law All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Tech Brief 1: Micro- and Nanotechnology Tech Brief 1: Heat power Density by CPU All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Circuit Representation All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Common Circuit Elements All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Circuit Topology Branch: single element, such as a resistor or source Node: connection point between two or more branches Extraordinary Node: connection point between at least 3 branches Loop: closed path in a circuit node branch loop All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Terminology All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Planar Circuits Planar circuits: can be drawn in 2-D without branches crossing each other Whenever possible, re-draw circuit to simplify! Charge & Current Unit of charge = coulomb All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Electron Drift Response time = 0.2 microsecond Actual travel time = 10 days!! All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Current All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Example 1-1: Charge Transfer Given: Determine: (a) q(t) (b) Solution: All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Example 1-1: Charge Transfer (cont.) (b) All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Voltage & Power Reference/Gro und Choose reference point for potential Assign potential at reference = 0, called ground Now all potentials are relative to ground terminal All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Measuring Voltage & Current Voltmeter: measures voltage without drawing current Ammeter: measures current without dropping voltage All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Open Circuit & Short Circuit Open circuit: no path for current flow (R = ) Short circuit: no voltage drop (R = 0) All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Power Rate of expending or absorbing energy dw dw dq P= = = vi dt dq dt Energy P = 0 conservation Units: watts One watt = power rate of one joule of work per second. 1 W = 1 A x 1 V Passive Sign Convention All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Example 1-4: Energy Consumption Given: Resistor consuming 20 W before switch turned off at t = 0. Also Determine: Total energy consumed by resistor after t = 0. Solution: (before t = 0) All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Circuit Elements: Independent Sources All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Circuit Elements: Dependent Sources I-V for Sources Current/voltage fixed for independent sources What does a non-ideal source look like? Dependent sources vary with reference voltage/current What are units for slope? All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Equivalent Circuit Using Dependent Source All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Example 1-5: Dependent Source Given: Source is CCVS Determine: Solution: All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Switches All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Summary All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press