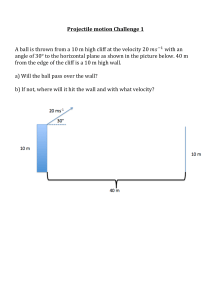
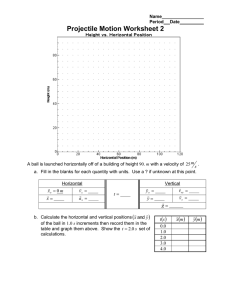
MOTION IN TWO DIMENSION 1. If a person can throw ball to a minimum height h (vertically) then the maximum distance up to which they can throw the ball is a) h b) 2h c) 3h d) 4h 2. When a particle is thrown up, it will have a) different speed at the same heights during ascent and during descent b) same speed at the same heights during ascent and during descent c) same speed at different heights during ascent and during descent D) Different speed at different heights during ascent and during descent 4. 3. The path of a projectile is a a) triangle b) circle c) ellipse d) parabola 4. The horizontal range (R) of a projectile is maximum when projectile’s angle is a) 90◦ b) 75◦ c) 60◦ d) 45◦ 5. Planets move around the sun due to a) centrifugal force c) Gravitational pull b/w them b) centripetal force d) none of the above 6. A car sometimes overturns while taking a turn. When it overturns. It is a) The inner wheel which leaves the ground first b) the outer wheel which leaves the ground first c) Both the wheel which leaves the ground simultaneously d) Either wheel leaves the ground first 7. A bullet is dropped from the same height when another bullet is fired horizontally. They will hit the ground a) one after the other c) Depends on the observer b) Simultaneously d) none of the above 8. A bomb is dropped from an aero plane moving horizontally at constant speed. When air resistance is taken into consideration, the bomb a) Falls to earth exactly below the aeroplane b) Falls to earth behind the aeroplane c) Falls to earth ahead of the aeroplane d) files with the aeroplane 9. A man projects a coin upwards from the gate of uniformly moving train. The path of coin for the man will be a) parabolic b) Inclined straight line c) vertical straight line d) Horizontal straight line 10. A particle in a plane with constant acceleration in a direction different from the initial velocity. The path of the particle will b a) A straight line 11. b) An arc of a circle c) A parabola d) An ellipse In the motion of a projectile freely under gravity, its a) total energy is conserved b) momentum is conserved c) Energy and momentum both are conserved d) none is conserved 12. The range of a projectile for a given initial velocity is maximum when the angle of projection is 45◦. The range will be minimum. if the angle of projection is a) 90◦ b) 180◦ c) 60◦ d) 75◦ 13. A ball is thrown upwards and it returns to ground describing a parabola path. Which of the following remains constant a) kinetic Energy of the ball b) speed of the ball c) Horizontal components of velocity d) Vertical components of velocity 14. An object is thrown along a direction inclined at the angle of 45 with the horizontal direction. The horizontal range 0f the particle is equal to a) vertical height c) Thrice the vertical height b) Twice the vertical height d) four times the vertical height 15. Galileo writes that for angle of projection of a projectile at angles (45+θ) and (45θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of (if θ≤45). b) 2:1 b) 1:2 c) 1:1 d) 2:3 A projectile thrown with a speed v at an angle has a range R on the surface θ of 16. earth. For same v and a) R/6 . its range on the surface 0f moon will be b) 6R c) R/36 d) 36R 17. The horiz0ntal range is four times the maximum height attained by a projectile. The angle of projection is a) 90◦ b) 60◦ c) 45◦ d) 30◦ 18. Two bodies are projected with the same velocity. If one is projected at an angle of 30◦ and the other at an angle of 60◦ to the horizontal, the ratio of the maximum heights reached is a) 3:1 b) 1:3 c) 1:2 d) 2:1 19. At what point of a projectile motion acceleration and velocity are perpendicular to each other a) At the point of projection b) At the point of drop c) At the topmost point d) Anywhere in b/w the point of projection and topmost point A particle is revolving in a circle of radius r. It’s displacement after completing half of the revolution will be: a) π r b) 2r c) 2πr d) r/2 20. 21. A circular disc start slipping without rolling down an inclined plane then its velocity will be: a) g h c) √gh b) 2gh d) √2gh 22. If a particle moves in a circle describing equal angles in equal times, its velocity vector a) Remains constant c) Changes in direction b) changes in magnitude d) changes both in magnitude and direction 23. If the over bridge is concave instead of being concave, the thrust on the road at the lowest position will be a) mg+mv2/r b) mg_mv2/r c) m2v2g/r d) v2g/r 24. A particle revolves round a circular path. The acceleration of the particle is a) Along the circumference b) Along the tangent c) Along the radius d) Zero 25. A cyclist turns around a curve at 15 miles/hour. If he turns at double the speed, the tendency to overturn is a. b. c. d. Doubled Quadrupled Halved Unchanged 26. A body moves with a constant speed in a circular path is moving in a circular path with a constant speed. It has a. b. c. d. Acceleration of constant magnitude Constant velocity Constant acceleration An acceleration which varies with time 27. A motorcyclist going with a constant speed in a circular track has a. b. c. d. Linear velocity is constant Constant acceleration Angular velocity is constant Constant force 28. What could be the reason a car moving on a horizontal road gets thrown out of the road while taking a turn a. b. c. d. Due to the reaction of the ground Due to rolling frictional force between tyre and road By the gravitational force Due to lack of sufficient centripetal force 29. A stone tied to a string is rotated in a circle. If the string is cut, the stone flies away from the circle because a. b. c. d. A centrifugal force acts on the stone Of its inertia A centripetal force acts on the stone The reaction of the centripetal force 30. A tachometer is a device to measure a. b. c. d. Gravitational pull Speed of rotation Surface tension Tension in a spring