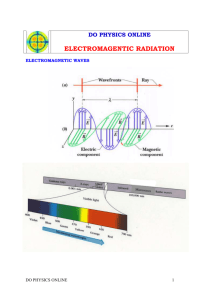
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION PHYSICS S.PANNEER SELVAM, Associate Professor of Medical Physics, Sri Ramachandra Medical College & Research Institute, Porur, Chennai. Electromagnetic radiation (often abbreviated E-M radiation or EMR) is a phenomenon that takes the form of self-propagating waves in a vacuum or in matter. It comprises electric and magnetic field components, which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation. EM radiation carries energy and momentum that may be imparted to matter with which it interacts. Electromagnetic waves are produced by the motion of electrically charged particles. These waves are called as "electromagnetic radiation" because they radiate from the electrically charged particles. They travel through empty space as well as through air and other substances. Electromagnetic radiation has a dual "personality." Besides acting like waves, it acts like a stream of particles (called "photons") that have no mass. WAVE CONCEPT • Wavelength : Distance between the peaks ( λ ) • Frequency : Number of cycles passes per second , a fixed point ( ν ) • Velocity : Distance travelled per second by a point ( V ) V=νxλ Lower frequency : Longer wavelength Higher frequency : Shorter wavelength PARTICLE CONCEPT ▪ Electromagnetic waves, may react with matter as if they were particles rather than waves ▪ These particles are discrete bundles of energy ▪ Each of these bundles of energy is called a Quantum or Photon ▪ Frequency doubled , energy of the photon doubled ▪ The photons with the highest energy correspond to the shortest wavelengths Electromagnetic radiation is classified into several types according to the frequency of its wave; these types include (in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength): radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. SOURCES OF EMR There are both natural and man-made sources of electromagnetic radiation ▪ Natural Sources Ultraviolet rays , Visible light ▪ Man made sources X-Rays , Microwaves and Radio waves They also classified electromagnetic radiation into Ionizing and Non Ionizing radiation ▪ Non Ionizing Visible radiation, infrared radiation, low-energy radio waves and microwaves ▪ Ionizing X-Rays & Gamma Rays COMMON PROPERTIES OF EMR ▪ It travels through free space as straight lines ▪ The speed of EMR is constant in space. All forms of EMR have the same speed of 299,800 kilometers/second (~ 3 x 108 m/s) in space ▪ According to quantum theory of EMR, the energy associated with a photon is given as E = hυ ▪ Electromagnetic radiation on passing through a medium gets attenuated ▪ EMR obeys Inverse square law Binding Energy ▪ Electrons held in their orbits by electrostatic attraction ▪ This force of attraction is Binding Force ▪ Binding force is > in K Shell Bound / Free electrons ▪ In high atomic number : Electrons in the orbits close to the nucleus are Bound electrons and electrons far from the nucleus are Free electrons ▪ In low atomic number : All the Electrons considered to be Free Electrons IONIZATION • An atom as a whole is normally Electrically Neutral • When one or more of the orbital electrons are removed from the Atom, the remainder of the atom is left positively charged and is known as Positive ION • This process of removal of orbital electrons is known Ionization • The energy required to produce ionization may be supplied to the atom by means of Ionizing Radiation – e.g. x-ray, alpha, beta, gamma, etc., EXCITATION • Sometimes energy given to the atom is less than the binding energy & an orbital election receives insufficient energy to enable it to leave the atom as in ionization • Instead, electron may move from its original shell to the outer shell • Then the atom has more energy than normal state • It is said to be in excited state and this process is known as excitation IONIZING RADIATION • Ionizing radiation is the radiation that can produce charged particles (ions) in materials that it strikes. Types of Ionizing Radiation ▪ Alpha radiation ▪ Beta radiation ▪ Gamma radiation ▪ Neutrons ▪ X-rays – discovered by W. C. Roentgen, 1895 RADIOACTIVITY • It is the property possessed by certain nuclides of undergoing spontaneous transformation of their nuclei accompanied by emission of particles or radiation • Isotopes are nuclides which have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in their nuclei Types of Radiation • Alpha ( Helium nucleus ) • Beta ( electron ) • Gamma Rays ( Photon ) Half Life ▪ Is the time taken for the radioactive nuclide to decay to one half of its original value Units of Radioactivity ▪ Becquerel : one disintegration / sec ▪ Curie : 3.7 X 1010 disintegrations / sec Inverse Square Law • The intensity of the radiation from a point source varies inversely as the square of the distance from the source, provided there is no absorption (or) scattering by the medium.