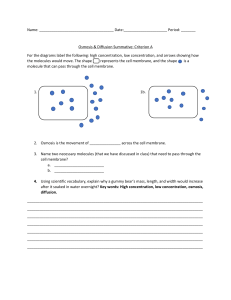
B.4(B) Everything you need to know about… Homeostasis Water Nutrients Extracellular space (Outside the cell) Membrane Intracellular space (Inside the cell) Gases Wastes Cells must maintain a steady balance of water, nutrients and energy. The cell membrane helps maintain homeostasis by controlling what enters and exits the cell. Diffusion Small, uncharged particles move along their concentration gradient from high concentration to low concentration through the cell membrane High concentration Low concentration Diffusion does NOT Facilitated Diffusion require cells to use energy! High concentration Low concentration Proteins help move large and charged particles from high concentration to low concentration across the cell membrane Osmosis High concentration Osmosis is the diffusion of water. Water moves from high concentration to low concentration Low concentration Osmosis is always the diffusion of WATER! Plant Cells Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Red blood cells Osmosis causes water to enter or leave cells Active Transport Low concentration Cells use energy to move particles against their concentration gradient from low concentration to high concentration. High concentration Active transport requires cellular ENERGY in the form of ATP! Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transports molecules to different parts of the cell. It is like the circulatory system of the cell! Vesicles Vesicles are tiny packages of molecules that travel between organelles and can transport molecules across membranes.