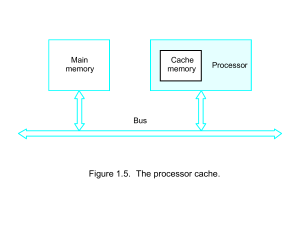
Computer Architecture and Operating Systems @ School of Computer Science for Business Management History of Computing Five generations of computer development • Pre-Computing • Electronics • Mini • Micro • Network PRE-COMPUTING sec IV B.C. – 1930 • The count is estimated to be invented in the VI century BC • Antikythera mechanism, a device used for recording and predicting the movement of stars and planets, is dated to the 1st century BC • The Arabic numerals were introduced into Europe in the 8th and 9th century AD • Leonardo da Vinci is supposed inventor of the first mechanical calculator around 1500. Evidence of Da Vinci's mechanism was found in his drawings until 1967. • John Napier of Scotland invented a set of tables to allow multiplication and division can be converted for addition and subtraction. • Wilhelm Schickard, a professor at the University of Tubingen, Germany builds a mechanical calculator in 1623 with a capacity of 6 digits. Calculating machines worked but never exceeded prototype stage. Napier's three-dimensional tables Da Vinci computer • Blaise Pascal builds a mechanical calculator in 1642 with a capacity of 8 digits. • Joseph-Marie Jacquard invented a loom controlled automatically with punch cards in the early 1800s. Calculating machine of Pascal Jacquard loom The first computing machine of Babbage • built at the beginning of 1800 • special purpose computer • used to calculate navigational routes Babbage difference engine The second computing machine of Babbage • General purpose Use binary and Ada Lovelace punched cards (first programmer) • The pieces were not sufficiently precise manufactured • Not finished analytical engine, 1834 • • • Samuel Morse invented the electric telegraph in 1837. George Boole invents Boolean algebra in the 1840s has not been used boolean algebra than a century later, a young student named until Claude E. Shannon acknowledged its relevance to the design of electronic components. In 1857, only twenty years after the invention of the telegraph, Sir Charles Wheatstone introduced the use of paper tape as a medium for preparation, storage, and transmission of data. Morse Code Wheatstone's Paper Tape • The first typewriter was developed by three inventors and American friends, Christopher Latham Sholes, Carlos Glidden, and Samual W. Soule. • They sold their project by Remington and Sons, who hired William K. Jenne to perfect the prototype, resulting in the launch of the first typewriter in 1874. The invention of the light bulb, 1878 • Sir Joseph Wilson Swan – English physicist – The first public exhibition of a light bulb in 1878 • Thomas Edison – American inventor, who worked independently of Swan – public exposure of a light bulb in 1879 – have a filament in a glass bulb which was evacuated leaving a vacuum air – heating filament producing electricity through its generating light by incandescence – vacuum prevents filament oxidation to occur • Edison continued to experiment with filament. • In 1883 found incandescent filament flow of electrons from a metal plate attached to the inside of the bulb, this phenomenon became known as the Edison effect, not further depth The invention of the diode (late 1800s) John Ambrose Fleming • English physicist • He studied the effect of Edison • to detect radio waves and convert them into electricity has developed a vacuum tube of two elements known as a diode • the flow of electrons inside the tube, moving to the negatively charged cathode to the positively charged anode • Today, a diode is used as a rectifier circuit Switching vacuum tube, 1906 • American inventor Lee de Forest has introduced a third electrode in a vacuum tube new vacuum tube was called triode • He was appointed a new electrode grid so the tube can be used as an amplifier and a switch many of the early radio transmitters were built using triode • Triodes revolutionized audio-visual • Their ability to act as switches had a special importance for binary calculations Switches used to binary calculation • early: – electromechanical relays • solenoid with mechanical contacts • The switch closes the circuit when electric current through a coil and generates a magnetic field • 1940's: – vacuum tube • Without physical contact form that can break or soil • Become available early 1900 • Originally used to manufacture radios • 1950 to present – transistors • Bell Labs patented invention in 1948 • Inventors: John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley • Nobel Prize 1956 Electromagnetic relay Electromagnetic relay The evolution of the transistor • The first transistor was made of various materials, including paper and a razor blade They were later integrated in small ICs Later they were widely integrated using semiconductor materials (Very Large Scale Integration) with millions of transistors / chip Integrated Circuit IC • invented separately by 2 people in 1958 • Jack Kilby from Texas Instruments • Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor Robert (1958-1959) 1974 • Intel introduces the 8080 processor one of the first microprocessors "single chip" Widely produced integrated circuits Schematic of a transistor Moore's Law • Offer a constant rate of miniaturization technology • Named after Intel co-founder Gordon Moore • Consider that the density of a chip doubles every 18 months Making the first computer • • • • • • • • microprocessors contain more transistors (ENIAC): 19,500 vacuum tubes and relays Intel 8088 processor (one PC): 29,000 transistors Intel Pentium II processor 7 million transistors Intel Pentium III Processor: 28 million transistors Intel Pentium 4: 42 million transistors Logically, each transistor acts as a switch transistors are combinations to implement Boolean operators AND, OR, NOT The electronic age 1900-1964 • In 1926, dr. Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in New York has filed a patent for a transistor. • Konrad Zuse, a German engineer, completes first general purpose programmable computer in 1941. • Colossus, a British computer used for code-breaking, is operational by the end of 1943. • ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer Analyze), developed by Research Lab in Maryland and the University of Pennsylvania built was completed in 1945. ENIAC Electrical Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), 1940 • One of the first computers • UPenn Development • Room size 10x15m • 18,000 vacuum tubes • 1500 relay • weighed 30 tons • Designers – John Mauchly – J. Presper Eckert • UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) is built in 1951 and can hold 12,000 digits. • ENIAC inventors John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert proposed building EDVAC in August 1944, and design work for the EDVAC commenced before the ENIAC was fully operational. The project implements a number of important architectural and logical improvements conceived during the ENIAC construction and includes a high-speed serial memory. • Like the ENIAC, EDVAC was built ballistic purpose of the US Army Research Laboratory at Aberdeen Proving Ground of the University of Pennsylvania. EDVAC MINI AGE (1959-1970) • Mini age was started by developing integrated circuit in 1959 by Texas Instruments and Fairchild Semiconductor. • Ivan Sutherland demonstrated a program called Sketchpad (sketch with a enlighted pen) on a mainframe TX-2 at MIT Lincoln Labs in 1962. • In 1965, a chip that cost $ 1,000 in 1959 cost less than $ 10. • Doug Engelbart demonstrates a word processor in 1968. • Also in 1968, Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce founded a company called Intel. • Xerox Palo Alto Research Center creates (Xerox PARC) in 1969. • Fairchild Semiconductor introduces a memory chip 256-bit RAM 1970. • At the end of 1970 Intel introduces a 1K RAM chip and 4004, a 4-bit microprocessor. Two years later, comes 8008, the 8-bit processor. Doug Engelbart MICRO AGE 1971-1989 • Bill Gates and Paul Allen founded tra-O-Data in 1971 to sell computers • Gary Kildall writes PL / M, the first high-level programming language for the Intel microprocessor. • Intel introduces the 8008, the first 8-bit microprocessor in April 1972.. Bill Gates Steve Jobs • Jonathan A. Titus designs the Mark-8 and presented in July 1974 • In January 1975 MITS Altair 8800 Popular Electronics completed, it is considered the first computer "personal". • Paul Allen and Bill Gates develop BASIC for the Altair 8800 and founded Microsoft The prototype Mark-8 • By 1980 Apple has captured 50% of the personal computer market. • Apple Apple II sold in 1977 for $ 1,195 including 16K RAM but no monitor. • Software Arts develops the first spreadsheet program, VisiCalc in spring 1979. 500 copies per month are delivered in 1979 with a sales increase to 12,000 per month in 1981. • By 1980 Apple grabbed 50% market share in personal computers. Apple II - 1977 • In 1980 Microsoft is approached by IBM to develop BASIC for its personal computer project. IBM PC is released in August 1981. • Apple Macintosh provides a simple graphical interface, using 8-MHz, 32-bit Motorola 68000 CPU and a built-in 9-inch B / W screen and starts in 1984. • Microsoft Windows 1.0 is released in November, 1985. Microsoft sales value in 1989 reached $ 1 billion. IBM PC - 1981 Age of Computer Networks (Late 50s - present) • Timesharing, the concept to link a large number of users from a single computer through remote terminals is developed at MIT in the late 50s and early 60s. • Paul Baran develops the concept of distributed networks with packet switching. • ARPANET is on-line in 1969. • Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn develop the basic ideas of the Internet in 1973. • In 1974, BBN launches first public packet switched network Telenet • University of North Carolina and Duke University established a connection USENET in 1979. • TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol) is set as the standard for ARPANET in 1982. • The number of hosts were more than 10,000 in 1987, two years later, the number of hosts exceeds 100,000. • Tem Berners-Lee developed the World Wide Web. • CERN launches first Web server in 1991. By 1992, the number of network hosts exceeds 1,000,000. • World Wide Web is appreciated with a growth rate of 341 634% traffic service in the third year - 1993.