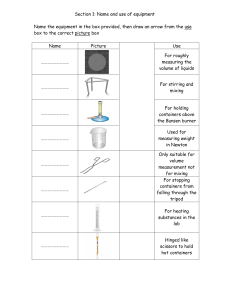
MECHANICAL SYSTEM DESIGN MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM -Chaitanya Narendra Damle PRN: 1806096 INTRODUCTION TO MATERIAL HANDLING: Definition: ⁻ Material handling is the movement, protection, storage and control of materials and products throughout manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption and disposal. ⁻ Materials handling is the art and science of conveying, elevating, positioning, transporting, packaging and storing of materials. As a process, material handling incorporates a wide range of manual, semi-automated and automated equipment and systems that support logistics and make the supply chain work. Any Material handling process includes: 1. Picking up the load 2. Transporting the load 3. Setting up the load Material handling is to move the materials around. Material handling does not add any value. It adds to the cost of product; therefore it should be eliminated or at least reduced as much as possible. It applies to the movement of raw materials, parts in process, finished goods, packing materials, and disposal of scraps EFFECT OF MATERIAL HANDLING ON COST: In a typical factory handling accounts for ⁻ 25% of all employees, ⁻ 55% of all factory space, and ⁻ 87% of production time. Material handling is estimated to represent between 15 and 70% of the total cost of a manufactured product. Material handling is one of the first places to look for cost reduction & quality improvements. SYSTEM CONCEPT FOR MATERIAL HANDLING: Any solution to the material handling problem must satisfy the following conditions: 1. The solution to material handling problem should not transfer the problems into other areas of the product cycle. 2. The solution should not only resolve the immediate problems, but also take care of problems for a reasonably long period of time. It should be able to account for future expansion or modification without unreasonable cost. 3. The solution should not be prone to rapid obsolescence. 4. The solution should be as simple as possible and easy to adopt. 5. The solution should be such that, the initial cost as well as operational costs should be minimum. 6.The rate of return on investment should justify the solution. TYPES OF LOAD HANDLED BY MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM: Load is classified into two types: 1. Bulk Load: Bulk load consists of a large number of homogenous particles or lumps of any material. Examples: coal, minerals, sand very small steel components, etc. 2. Unit Load: Unit load is a rigid mass which is handled and transported as one single piece. Examples: machines, large boxes, containers, etc. CONTAINERIZATION: The use of containers for the handling of bulk loads and small sized products is done for bringing convenience the material handling. Depending upon the size of the containers, one container may be treated as a unit load or number of containers together may be treated as a unit load. The process of converting the bulk loads or small units into a unit load by using the containers, is known as Containerization. Types: wire–mesh, steel, wooden, plastic. CONSIDERATIONS IN CONTAINERIZATION: Limit the number of container sizes and shapes. Design the container size and shape based on the load to be handled. Size the containers taking into account the space available in material handling equipment. Design the containers for stacking arrangement. Design the containers for flexibility and maximum utilization. Keep the containers painted. Color-code the containers by function. Wire-mesh and solid steel containers are preferred over wood or plastic containers for the sake of cleanliness, fire protection and long life. In many applications, wire-mesh containers are preferred over solid steel containers due to following reasons: Wire-mesh containers are self-cleaning. When parts are dropped into the container, the wire-mesh containers produce less noise as compared to the solid steel containers. Wire-mesh containers are used for washing parts without removing them from the container. Parts will dry and cool faster in wire-mesh containers than in solid steel containers.