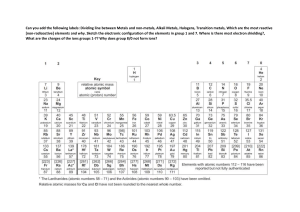
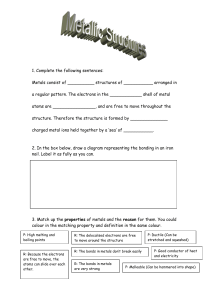
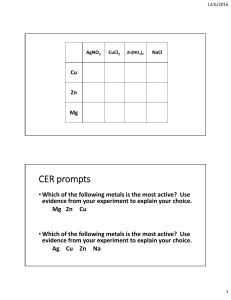
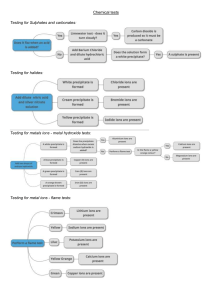
METAL Properties of metals The general physical properties of metals Other properties include: Malleable and ductile Conduct heat ✓ State ✓ Hardness ✓ Valency ✓ Density Conduct electricity luster ✓ Melting and Boiling Points METAL CRYSTALS explain many of the general physical properties of metals? Chemical Properties of Metals water Metals tend to have low ionization energies, and typically lose electrons . Alkali metals (IA) Nonmetal Metal Alkaline earth metals (IIA) acid Salt(aq) PERIODIC TABLE Trends in Metallic Character increase strength, increase corrosion resistance, or reduce costs properties superior to pure metals Making alloys with other metals is one of the commonest ways of changing the properties of metals. Alloys are formed by mixing the molten metals together thoroughly and then allowing them to cool and form a solid. ALLOYS Many different coins are made from cupro-nickel alloys a) The positions of atoms in a pure metal crystal before a force is applied. b) After the force is applied, slippage has taken place. The layers in a pure metal can slide over each other. c) In an alloy, slippage is prevented because the atoms of different size cannot slide over each other. ALLOYS REACTIVITY SERIES Reactivity series the metals with: ✓ water or steam ✓ dilute hydrochloric acid ✓ the reduction of their oxides with carbon The metals with: water or steam Metals from calcium upwards These react vigorously (and even more vigorously the higher up the series you go) with cold water to form the metal hydroxide and hydrogen. Metals from magnesium to iron These react with steam to give a metal oxide and hydrogen. Remember that the aluminium reaction is much slower than you would expect because of its stable oxide coating. Metals below hydrogen These don't react with water under any conditions. Reactions of metals with air, water and dilute acids THE EXTRACTION OF METALS ❖ A few metals are so unreactive that they occur in an uncombined state. These unreactive metals include copper, gold and silver. ❖ Most metals are too reactive to exist on their own in the ground. They exist combined with other elements as compounds called ores THE EXTRACTION OF METALS ✓ The moderately reactive metals such as iron, zinc, tin and lead occur either as oxide or as sulfide ores. ✓ The sulfide ores can easily be converted to the oxide by heating in air. ✓ The oxide must then be reduced to give the metal Metal displacement reactions In a displacement reaction, a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from solutions of salts of the less reactive metal For example: Metal displacement reactions Reactive metals are good reducing agents. The nature of the reaction taking place between zinc and copper sulfate can be explored in more detail by looking at the ionic equation: Aluminium, the more reactive metal, removes oxygen from the less reactive iron in iron(iii) oxide: In general, a reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal from its oxide. Thermal decomposition of metal compounds QUESTION 1) Write a word equation for the reaction of zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid. 2) Select from this list a metal that will not react with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen: magnesium, iron, copper. 3) Write a word equation for the reaction between magnesium and copper(ii) sulfate solution. 4) State two observations you would see when a piece of magnesium ribbon is placed in copper(ii) sulfate solution. 5) Write a balanced chemical equation and an ionic equation for the reaction between magnesium and copper(ii) sulfate solution QUESTION a) 𝐂𝐮 + 𝐙𝐧𝐒𝐎𝟒 → 𝐛) 𝐌𝐠 + 𝐙𝐧𝐒𝐎𝟒 → 𝐜) 𝐌𝐠 + 𝐇𝐂𝐥 → 𝐝) 𝐀𝐠 + 𝐇𝐂𝐥 → 𝐞) 𝐂𝐮 + 𝐀𝐠𝐂𝐥 → QUESTION a) Fe + … … … … → FeCl2 + … … … … b) Fe + Cl2 → … … … … c) Fe + ………. → FeS d) ……….. + ……….. → AlCl3 e) …………. + ………… → CaCl2 + CO2 ↑ +H2 O f) …………. + AgNO3 → Cu(NO3 )2 + ………… g) …………. → Al + ……………. h) Al + NaOH + H2O → ………….. + ……………. i) Fe3O4 + ……………→ Fe + ……………… Questions & answers Invite questions from the audience