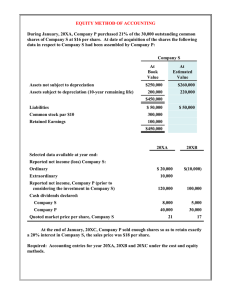
ASSIGNMENT NO - 01 Name: Reg No: Subject: Rohail Ahmad 19bnele0938 Engineering Economics Submitted to: Eng. Bilal Pirzada Semester: 5th Department: Electrical Engineering November 21, 2021 University of Engineering & Technology Peshawar Campus III Bannu External Source of Finance: External sources of finance are equity capital, preferred stock, debentures, term loans, venture capital, leasing, hire purchase, trade credit, bank overdraft, factoring, etc. By external sources, we mean the capital arranged from outside the business, unlike retained earnings which are internally generated out of the activity of a business. A source or sources of finance, refer to where a business gets money from to fund their business activities. A business can gain finance from either internal or external sources. External sources of finance are those sources of finance that come from outside the business. For example, retained earnings are an internal source of finance whereas bank loan is an external source of finance. We can segregate external sources of funds between longterm sources of finance and short-term sources of finance. Family and friends - businesses can obtain a loan or be given money from family or friends that may not need to be paid back or are paid back with little or no interest charges. A bank loan is money borrowed from a bank by an individual or business. A bank loan is paid off with interest over an agreed period of time, often over several years. Overdrafts - are where a business or person uses more money than they have in a bank account. This means the balance is in minus figures, so the bank is owed money. Overdrafts should be used carefully and only in emergencies as they can become expensive due to the high interest rates charged by banks. Venture capital and business angels - refers to an individual or group that is willing to invest money into a new or growing business in exchange for an agreed share of the profits. The venture capitalist will want a return on their investment as well as input into how the business is run. New partners - is when an additional person or people are brought into the business as a new business partner. This means they would provide money to then own part of the business. Share issue - a business may sell more of their ordinary shares to raise money. Buying shares gives the buyer part ownership of the business and therefore certain rights, such as the right to vote on changes to the business. Long-Term Sources of Finance: Long-term Financing plays an important role in financial management for every firm. It is defined as the credit facility given to the firm for more than 5 years. Long-term Sources of Finance are required for firms to manage their Long-term Liabilities. It comprises of financing the fixed capital required for the investment in fixed assets. It involves the financing decisions for the long periods of time that also has more risk. That’s why Long-term Sources of Finance is also known as the Capita Budgeting Decisions. Equity Shares: Equity shares are a common source of finance for big companies. Not all businesses can use this source as it is governed by a lot of legislation. A key feature of equity share is the ‘sharing of ownership rights’ and therefore, the current shareholders’ rights are diluted to some extent. It is considered costly compared to debt finance because the return in the form of a dividend or bonus shares offered to shareholders is not tax-deductible. Also, it’s not easy to raise this capital as it requires a lot of legal formalities to be complied with, and above all, the investors should have faith in the company. Debentures: Debentures are another common means of finance used by companies who prefer debt over equity. Debt is considered to be the cheaper mode of finance compared to equity. It does not share control with investors. It is because the interest paid to debenture holders is tax-deductible. The rest of the process of debentures issue is similar to the equity issue. It is offered to the common public and therefore necessary legislations need to be complied with. Debentures also involve some cost of issuing and they are collateralized by some assets of the company. Term Loan: The characteristics of a term loan are very similar to debentures except that it does not include too much cost of issuing because it is given by some bank or financial institutions. The common public is not involved in it. A rigorous analysis of the company’s financials and future plans is done by the bank to judge the debt servicing capacity of the company. These loans are also secured by some assets. Preferred Stock: The preferred stock shares characteristics of both common equity stocks and debt. They are called preferred because they have got priority over common equity shares in terms of payment of dividends and the capital also at the time of liquidation. A special kind of preferred shares called cumulative preference shares has its dividend accumulated till it is not paid. The payment of such dividends can be delayed but cannot be ignored. Venture Capital: It is the same as equity shares except that the investors are a different set of people. Commonly known as venture capitalists, they normally invest in a new company at an initial stage and do a rigorous analysis of a company before investing. Venture capitalists exit the firm once it starts getting a good valuation. Leasing and Hire Purchase: Choosing hire purchase or lease as an option over paying the full amount to the supplier of goods can help businesses delay their cash payment which is equal to having its goods financed. Normally, the hire purchase option is provided by suppliers of big machinery or bank becomes an intermediary at times. Both lease and hire purchase provide the buyer with an option to purchase the asset at the end of its term. External Sources as a Long-term sources: When a company needs a lot of money and its internal sources of Finance are exhausted, the company tries out the external options. Under the long-term External Source of Finance, companies fund their requirements by looking into options that are almost permanent and can offer them a huge amount in a go. We can handle all these external sources as a long-term source but these required a special technique that every business industry can handle for their own proposes. Share Capital: Share capital is the money a company raises by issuing common or preferred stock. The amount of share capital or equity financing a company has can change over time with additional public offerings. The term share capital can mean slightly different things depending on the context. Accountants have a much narrower definition and their definition rules on the balance sheets of public companies. It means the total amount raised by the company in sales of shares. Understanding Share Capital: Share capital is reported by a company on its balance sheet in the shareholder's equity section. The information may be listed in separate line items depending on the source of the funds. These usually include a line for common stock, another for preferred stock, and a third for additional paid-in capital. Common stock and preferred stock shares are reported at their par value at the time of sale. In modern business, the "par" or face value is a nominal figure. The actual amount received by a company in excess of par value is reported as "additional paid-in capital." The amount of share capital reported by a company includes only payments for purchases made directly from the company. The later sales and purchases of those shares and the rise or fall of their prices on the open market have no effect on the company's share capital. A company may opt to have more than one public offering after its initial public offering (IPO). The proceeds of those later sales would increase the share capital on its balance sheet. Types of Share Capital The term "share capital" is often used to mean slightly different things depending on the context. When discussing the amount of money, a company can legally raise through the sale of stock, there are several categories of share capital. Accountants have a much narrower definition. Authorized Share Capital: Before a company can raise equity capital, it must obtain permission to execute the sale of stock. The company must specify the total amount of equity it wants to raise and the base value of its shares, called the par value. The maximum amount of share capital a company is allowed to raise is called its authorized capital. This does not limit the number of shares a company may issue but it puts a ceiling on the total amount of money that can be raised by the sale of those shares. For example, if a company obtains authorization to raise $5 million and its stock has a par value of $1, it may issue and sell up to 5 million shares of stock. Issued Capital: Generally, a part of the authorized capital is issued to the public for subscription which is known as issued capital, i.e., it is the nominal value of the shares which are offered to the public for subscription. Usually, a company does not issue all its capital at a time, i.e., issued capital is less than the authorized capital. If all shares are issued, issued capital and authorized capital will be the same. Subscribed Capital: A part of the issued capital which is subscribed by the public is known as subscribed capital. It does not necessarily mean that all the shares which have been issued will be taken over by the public. In other words, the share capital of the number of shares which are taken over by the public is called subscribed capital, i.e., the portion of issued share capital which is paid/subscribed by the shareholder is known as subscribed capital. Called-Up Capital: Generally, the shareholders pay the price of the shares by installments, viz., application, allotment, First call, Final call etc. Therefore, the portion of the face value of the shares which the shareholders are called upon to pay or the company has demanded to pay is called Called-up capital. Uncalled Capital: The unpaid portion of the subscribed capital is called Uncalled Capital. In other words, it is the remainder of the issued Capital which has not been called. However, the company may call this amount at any time but that must be subject to the terms of issue of shares. Paid Up Capital: The amount actually paid by the shareholders is known as Paid-up Capital. Reserve Capital: According to Sec. 99 of the Companies Act, 1956, Reserve Capital is that part of uncalled capital of a company which can be called only in the event of its winding-up. A limited company may, by special resolution, determine that any portion of its share capital which has not been called-up, shall be called up, except in the event of the company being wound-up, such capital is known as Reserve Capital. It is available only for the creditors on the winding-up of the company. Conclusion: So, this was about the Long-term and Short-term Sources of Finance. Both these Sources of Finance plays an important role in Business. On one side, Short-Term Sources of Finance helps in managing the working capital of the Business. On the Other side, Long-Term Sources of Finance helps in providing the fixed capital for the investment in the fixed assets. The organization should make the balance of both these sources for smooth operations of the business.