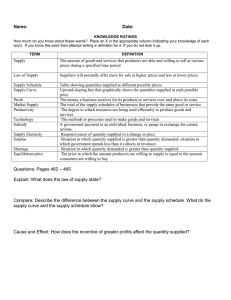
Good morning, I will continue the discussion about the shift in supply versus movements along a supply curve. SLIDE 2: if the amount supplied is affected by anything other than a change in price, there will be a shift in supply. a movement along the supply curve will occur when the price of the good changes and the quantity supplied changes in accordance to the original supply relationship. In other words, a movement occurs when a change in quantity supplied is caused only by a change in price, or a movement occurs when a changed in price is caused by the change in quantity supplied. In thinking about the factors that affects supply, remember what motivates a firm: it is the profit that motivates the firm which is the difference between revenues and costs. SLIDE 3: This are the factors affecting the supply curve: 1. A decrease or increase in costs of production – a decrease in the costs of production means business can supply more at each price. Lower costs could be due to lower wages or lower raw material costs 2. Productivity of workers - If workers become more motivated and work hard, then there will be significant increase in the output and the supply 3. Technological improvements - Improvements in technology, e.g. computers or automation, reducing firms costs, equipments, machinery ganon 4. Tax - Lower direct taxes (e.g. tobacco tax, VAT) reduce the cost of goods 5. Government subsidies - Increase in government subsidies will also reduce the cost of goods, e.g. train subsidies reduce the price of train tickets. SLIDE 4: Shift in supply – the graphic representation of the effect of a change in a factor other than price on supply. If the shift in demand is represented by a change in the quantity demand at every price, a shift in supply means that there is a change in the quantity supplied at every price. SLIDE 5: To better understand the idea of shift in supply, there’s a graphical representation of it in this slide. So here at the right side, the vertical line represents the price (per unit) and sa ibaba naman, the horizontal line represents the quantity supplied. So for example, a courier company that delivers packages around the city. Syempre if you are delivering a package, one of the main costs or expense non is buying of gasoline for the vehicles that is being used. If you are in a courier company and magpapagasolina ka, it became a costs of the company. If for instance bumaba yung price ng gasoline, it will result to a lower costs and mas mataas na profit ng company which leads to an increase of supply. So kagaya dito sa graphical presentation, The S1 represents the old supply which has a 250 quantity supplied at 20 price per unit while the S2 represent the new supply which has a 400 quantity supplied with the same price which of 20 per unit. So makikita natin dito that there is a shift in supply. Nagkaroon ng shift of the curve in supply by the increase of the supply from 250 to 400. If there is an increase in the shift of supply, then that is called as the forward shift in supply. SLIDE 6: The next one is the backward shift in supply From the example ulit kanina dun sa courier company, kung kanina ang scenario is bumaba yung price ng gasoline and nagresult siya into a lower costs and mas mataas na profit that leads to an increase of supply. Ngayon naman is yung kabaliktaran, if for instance na tumaas yung price ng gasoline, nagreresult siya to a higher costs and a decrease of the supply na napoproduce ng company. So eto kung kanina 250 to 400, ngayon naman is 400 to 250. meaning from an old supply to the new, pabawas or decrease yung nangyayari. And If there is an decrease in the shift of supply, then that is called as the backward shift in supply.