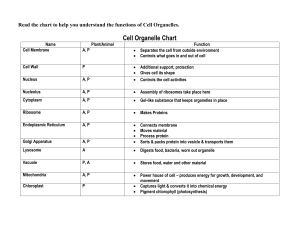
Biology: UNIT 3Vocabulary – Cells NAME: _______ ______________ DATE: _______________ BLOCK: _____ Match the vocabulary term to the correct definition. 1. _C___ All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and new cells come from pre-existing cells. 2. _A___ The basic unit of structure and function of all living things. 3. _D___ Have very few organelles (parts), they don’t have a nucleus, and they are primitive cells (bacteria). 4. _B___ Have many organelles (parts), they have a nucleus, and they are modern cells (Plants and animals). 5. _H___ A membrane bound cell structure that performs a specific function. 6. __F___ An organelle that converts the radiant energy of the sun into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. 7. __I___ The rigid, porous outer layer of a plant cell. 8. __M___ A small body in the nucleus where ribosomes are synthesized. 9. __J___ A round body in the center of the cell that contains DNA and directs the cells. 10. __E___ A double layer that surrounds the cell and protects the cell and regulates what enters and leaves the cell. 11. __O___ Short and numerous hair-like projections from the cell membrane that aid in locomotion of the cell. 12. __G___ Long activitiesprojections or tail that is composed of microtubules that help propel cells and organisms by a whip-like motion. 13. __P___ The aqueous component of the cytoplasm of a cell within various organelles and particles are suspended. 14. __K___ A small sac, or vesicle, that contains digestive chemicals. 15. __N___ A tiny structure where proteins are synthesized. 16. __L___ A type of vesicle that stores water, nutrients, and other chemicals. 17. __T___ An organelle that, using oxygen, converts nutrients into energy that can be used by the cell. 18. __R___ A network of passageways is formed, which chemical compounds are manufactured, processed, and transported. 19. __S___ An organelle that converts the radiant energy of the sun into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. 20. __U___ A stack of membranes that collects, modifies, and packages chemical compounds (ribosomes). 21. __AA___ A term referring to the cell membranes individual phospholipids and proteins that can move side-to-side as if they are in a liquid and the collection of the components that make it up. 22. __Y___ can change shape and bond to molecules to move them from one side to the other. 23. __V___ Feature of the plasma membrane that maintains homeostasis with a cell by allowing some molecules to pass through the cell membrane while keeping others out. A. Cell B. Eukaryote C. Cell Theory D. Prokaryote E. Cell Membrane F. Chloroplast G. Flagella H. Organelle I. Cell Wall J. Nucleus K. Lysosome L. Vacuole M. Nucleolus N. Ribosome O. Cilia P. Cytoplasm/Cytosol Q. Centriole R. Endoplasmic Reticulum S. Chloroplast T. Mitochondria U. Golgi Apparatus V. Selectively Permeable W. Hypertonic X. Endocytosis Y. Carrier Protein Z. Diffusion AA. Fluid Mosaic Model BB.Passive Transport CC.Facilitated Diffusion DD.Phagocytosis EE. Dynamic Equilibrium FF. Pinocytosis Biology: UNIT 3Vocabulary – Cells 24. __HH___ Molecules move from low concentration to high concentration with energy (ATP), and against the concentration gradient. 25. __BB___ The movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration without energy. 26. __Z___ the movement of small and the large hydrophobic, or lipid soluble molecules from an area of high to low concentration without energy. 27. _CC____ the movement of large or small hydrophilic, or ion molecules from an area of high to low concentration through transport proteins without energy. 28. __EE___ an even distribution of molecules on the outside and inside of the cell. 29. _X____ molecules move in the cell. 30. _GG____ takes out large molecules from the cell that are manufactured in the cell. 31. __DD___ when large molecules such as food, bacteria, etc. are taken into the cell through vesicles and referred to as “Cell Eating” 32. __FF___ The most common form of endocytosis, that takes in dissolved molecules in water through a vesicle. “Cell drinking” 33. _JJ___ movement of water molecules from an area of high to low concentration without energy. 34. __II___ an equal amount of solute (salt) outside and inside the cell. 35. _W____ have a greater amount of solutes (salt) on the outside of the cell compared to the inside. 36. __KK___ have less amount of solute (salt) outside of the cell compared to inside. GG. Exocytosis HH.Active Transport II. Isotonic JJ. Osmosis KK.Hypotonic