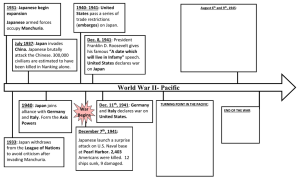
History Department: IB History Curriculum Map IB History Curriculum Map Prescribed Subject: The Move To Global War Japanese expansion in East Asia (1931–1941); German and Italian expansion (1933–1940) World History Topic 1: 10: Authoritarian states (20th century): Hitler and Mao World History Topic 2: 11: Causes and effects of 20th-century wars: FWW, SWW, Spanish CW, Chinese CW &2nd Italo-Abyssinian War Higher Level Regional Option 1: 9: Early modernization and imperial decline in East Asia (1860–1912) Higher Level Regional Option 2: 12: China and Korea (1910–1950) Higher Level Regional Option 3: 14: The People’s Republic of China (1949-2005) IB Requirements: P1 Prescribed Subject P2 World History Units P3 HL Regional Option Units IA: Historical Investigation SL: 150 HL 240 SL: 40 HL: 40 SL: 90 HL: 90 HL: 90 SL: 20 HL: 20 Allocations: 160 hours 86 hours 20 hours Year 12 = 36 weeks Total hours: 164 hours SL: 110; HL: 51 The Move to Global War: 40 hours Early Modernization and Imperial Decline in East Asia 1860-1912: 30 hours Choice of topic to be taken from the SL or HL course Year 13 = 24 weeks Total hours: 105 SL Hours: 70; HL Hours: 35 SL Total Hours: 180 (+30) HL Total Hours: 86 (-4) Total Hours: 271 Total = 60 weeks Total = 14 weeks Authoritarian States: 45 hours Mao Hitler Chiang Kai Shek/Mussolini Causes and Effects of 20thC Wars: 45 hours FWW SWW SS-JW CCW SCW SI-AW Total = 30 weeks (15 weeks per module) China and Korea (19101950): 30 hours The People’s Republic of China 1949-2005): 30 hours Total = 60 weeks Total = 8 weeks 1 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map HISTORY COURSE OUTLINE IB YEAR 1: 36 weeks TERM 1: 16 weeks Term 1a: 6 weeks Paper 1 Paper 2 th Paper 3 UNIT The Move to Global War: German and Italian expansion (1933–1940) 20 Century Conflicts: The effects of the FWW P3 Early Modernization and Imperial Decline in East Asia 1860-1912 CONTENT Causes of expansion Impact of fascism and Nazism on the foreign policies of Italy and Germany Effects The successes and failures of peacemaking Territorial changes: Paris Peace Conference Political repercussions; Economic, social and demographic impact; changes in the role and status of women Post war conflicts and the World order 1920-1929 League of Nations 1920’s Collective Security 1930’s 3 weeks: 10 lessons Half Term 6 weeks: 9 lessons The Move to Global War: Japanese expansion in East Asia (1931–1941) The Causes of the Second World Asia P3 Early Modernization and Imperial Decline in East Asia 1860-1912 Causes of expansion nationalism militarism, foreign policy P2 approach/review and essay SWW Asia Causes Economic, ideological, political, territorial and other causes, Short- and long-term causes Estimated time 2 weeks: 6 lessons Term 1b: 10 weeks The Move to Global UNIT War: German and Italian expansion (1933–1940) CONTENT Impact of domestic economic issues on the foreign policies of Italy and Germany Tongzhi (T’ung-chih) Restoration and SelfStrengthening Movement (1861‑94) Impact of defeat in the Sino–Japanese War (1894‑5); Guangxu (Kuang-hsu) and the Hundred Days Reform (1898) Boxer Rebellion (1900‑01); the late Qing (Ch’ing) reforms Sun Yixian (Sun Yat-sen) and the 1911 “Double Ten” Nationalist Revolution Meiji Restoration (1868) in Japan; the 1889 Constitution 2 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map Estimated Time Changing diplomatic alignments in Europe; the end of collective security; appeasement Events German challenges to the post-war settlements (1933– 1938) Italian expansion: Abyssinia (1935– 1936); Albania; entry into the Second World War German expansion (1938–1939); Pact of Steel, Nazi–Soviet Pact and the outbreak of war Responses International response to German aggression (1933– 1938) International response to Italian aggression (1935– 1936) International response to German and Italian aggression (1940) Japanese domestic issues Instability in China Events Manchuria and northern China (1931) Sino-Japanese War (1937–1941) The Three Power/Tripartite Pact; the outbreak of war; Pearl Harbor (1941) Responses League of Nations China—the Second United Front International response, 4 weeks: 12 lessons 6 weeks: 18 lessons 1 week: 3 lessons The impact of the First World War and the post-war conferences Taisho democracy: the growth of liberal values and the two-party system Reasons for, and impact of, the rise of militarism and extreme nationalism: increasing influence of the army in politics; political coups and assassinations Invasions of Manchuria (1931) and China (1937), and impact on relations with the West; Three Party/ Tripartite Pact (1940); US embargo (1940) Japan and the Pacific War (1941–1945): decision to attack Pearl Harbor; Social, cultural and economic developments in Meiji Japan Commitment to military power; victory in the Sino– Japanese War (1894‑5) and in the Russo–Japanese War (1904‑5) 10 weeks: 15 lessons Christmas holiday 3 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map Assessment Knowledge Test, Research Essay, Controlled Assessment P1/P2/P3, Blog Entries TERM 2: 11 weeks Term 2a: 2 weeks Paper 1 Paper 2 th Paper 3 UNIT 20 Century conflicts An introduction to conflict Early Modernization and Imperial Decline in East Asia 1860-1912 CONTENT Estimated Time Definitions of War: What is war? Types of conflicts: Total, Interstate, Guerrilla, Civil Causes of conflicts: Themes Developments of conflicts: Technology, government, society, ‘ways of war’ Theories/Analysis of conflicts: Thucydides, von Clausewitz, Mao, TE Lawrence, Historians, Max Boot, Max Hastings 2 weeks: 6 lessons Korean isolation: opening (1876); rebellions; annexation (1910) 2 weeks: 3 lessons Holiday Term 2b: 8 weeks UNIT Interstate: The causes and practices of the FWW China and Korea (1910-1950) (Europe) and SWW (Asia) CONTENT FWW Europe Causes Causes of the First World War: short- and long-term causes; relative importance of causes; the Alliance system; the decline of the Ottoman Empire; German foreign policy; Austria-Hungary, Russia and Balkan nationalism; the arms race and diplomatic crises; the July Crisis of 1914 Practices Rise of national identity in China: Yuan Shikai; Sun Yixian; 21 Demands (1915); new culture movement; Treaty of Versailles (1919); May Fourth movement (1919); effects of warlordism Nationalist rule of China: Guomindang leadership and ideology; Jiang Jieshi; successes and failures of domestic policy during the Nanjing decade (1927–1937) Rise of communism in China: Chinese Communist Party (CCP) ideology; First United Front; Shanghai massacre (1927); Yan’an; Jiangxi Soviet; Long March; Mao Zedong 4 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map Types of war: civil wars; wars between states; guerrilla wars; Technological developments; theatres of war— air, land and sea; The extent of the mobilization of human and economic resources; The influence and/or involvement of foreign powers Effects Impact of the First World War on civilian populations of two countries from the region between 1914 and 1918 Factors leading to the defeat of Germany and the other Central Powers, and to the victory of the Entente Powers: strategic errors; economic factors; entry and role of the US; domestic instability in the Central Powers Impact of Japanese invasion of China; Manchuria (1931); Second United Front; Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945); Chinese Civil War (1946–1949); nature of conflict; reasons for communist victory SWW Asia Practices Types of war: wars between states; guerrilla wars Technological developments; theatres of war—air, land and sea; The extent of the mobilization of human and economic resources; initial successes; SE Asia Burma, Island Hopping and the Pacific War reasons for defeat Effects The successes and failures of peacemaking; Territorial changes; Political repercussions; Economic, social and demographic impact; changes in the role and status of women in Japan, US and Australia The Japanese Empire Treaty of San Francisco The US occupation of Japan(1945–1952): social, political and cultural changes Early Cold War in Asia 1945-1950 Estimated Time 8 weeks: 24 lessons 5 weeks 6 lessons Spring Break 5 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map Assessment Knowledge Test, Research Essay, Controlled Assessment P1/P2/P3, Blog Entries TERM 3: 9 weeks Term 3 Paper 1 UNIT CONTENT Paper 2 Paper 3 Cause Course and Effects of the Spanish Civil War Cause Course and Effects of the Chinese Civil War China and Korea (1910-1950) Causes Practices Effects Estimated time 5 weeks 17 lessons 8 weeks 17 lessons Impact of Japanese rule of Korea: social, political and economic effects of annexation (1910); impact of the SinoJapanese War on Korea: Japanese use of forced labour, conscription and comfort women; division of Korea at 38th parallel (1945); Syngman Rhee; Kim Il-Sung Taiwan and Republic of China (ROC): nature of Jiang Jieshi’s rule: martial law (1949); White Terror (1950); beginnings of Taiwanese independence movement 10 weeks 14 lessons Summer Holiday Assessment Knowledge Test, Research Essay, Controlled Assessment P1/P2/P3, Blog Entries 6 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map IB YEAR 2: 24 Weeks TERM 1: 16 weeks Term 1a Paper 1 UNIT CONTENT Estimated Time weeks Paper 2 Paper 3 weeks weeks weeks weeks weeks Half Term Term 1b UNIT CONTENT Estimated Time weeks weeks Christmas Holiday Assessment Knowledge Test, Research Essay, Controlled Assessment P1/P2/P3, Blog Entries, IA TERM 2: 11 weeks ( -2 weeks for mock examinations) Term 2a Paper 1 UNIT CONTENT Estimated Time Mock Exam No lessons 2 weeks Paper 2 Paper 3 Mock Exam No lessons 2 weeks Holiday Term 2b 7 History Department: IB History Curriculum Map UNIT CONTENT Estimated Time Spring Break Revision for examinations Revision, Final Examinations Assessment TERM 3: 1 week Term 3 Paper 1 UNIT CONTENT Estimated time 1 week Paper 2 Paper 3 1 week 1 week Exam Leave Assessment Revision, Final Examinations Notes/Points to consider 8