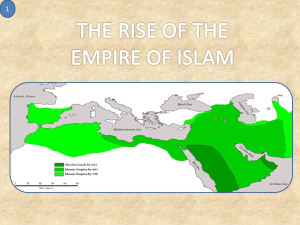
Draw a map of the world. Label 0 latitude and 0 longitude. Draw and label the continents. Label the oceans. Draw and label a major mountain range on each continent. Draw and label one major river on each continent. Draw and label one country on each continent. Draw and label one capital city on each continent. Unit 3 Arabia Mostly desert except for coasts Most people were herders and traders called Bedouins Cities developed around trade including Mecca Religious Diversity in Arabia Many religions were present in Arabia in the early 600s Christianity Orthodox Coptic Jews Zoroastrians Polytheistic faiths Muhammad Born in 570 C.E. into a powerful clan Started working as a caravan trader at an early age Around 40 years old Muhammad was visited by the angel Gabriel Gabriel revealed a new prophecy which Muhammad memorized and began preaching Spread of Islam Muhammad's ideas quickly spread across the region His ideas made the elites in Mecca nervous He fled from Mecca to Yathrib to avoid persecution from authorities This was known as the “hijrah” or flight A few years later Muhammad and 10,000 followers reentered Mecca Faith of Islam Islam – “Submission to the will of Allah” Muslim – “ One who has submitted” Holy book of Islam Qur’an Muslims consider the Arabic text to be the literal word of God Muslims try to memorize the Qur’an in Arabic Even if they don’t speak the language Foundations of Islam Muslims must follow the Five Pillars There is only one God and Muhammad is His messenger Muslims must pray five times daily toward Mecca Must pay “Zakat” a tax for the poor Muslims must fast during the holy month of Ramadan Muslims must make a pilgrimage to the holy site of Mecca The Kaaba in Mecca Life for Muslims Live a humble life Be tolerant and generous Do not eat pork or drink alcohol Jihad – Struggle to defend the faith Greater Jihad – Internal struggle to live well and overcome base desires Lesser Jihad –Struggle to defend Islam Dar al-Islam – House of Islam Dar al-Harb – House of War May be violent or not Most Muslims see this as requiring a group consensus and focus more on the House of Islam Holy Texts The most important text to Muslims is the Qur’an This is the direct revelation from God recited to Muhammad Hadith – Traditions of the prophet Sayings and other stories attributed to the prophet or his followers There are four major collections and they are not universally accepted by all Muslims Crash Course Islam World Religions Notebook Create an entry for Judaism in your World Religions Notebook Include the following Origins (Location and story of how the religion began) Important symbols of the faith Prophet (Describe three major prophets of this faith Map (Map at the time of this religion’s beginning and height. Shaded for each) Demographics (How many people in the world follow this faith? List the top three countries and how many followers are in that country) What are the major beliefs of this faith What are the major sects or divisions in this faith (How did they split and what are their differences in belief) Koran By Heart Qur’an and Hadith Writing Assignment You will explore passages in the Qur’an and Hadith to better understand the diversity present in Islam Choose one of the Five Pillars or another topic (marriage, dress, food, etc…) Find passages from the Qur’an and passages from the Hadith that address this topic Use the University of Southern California Center for Muslim-Jewish Engagement http://cmje.usc.edu/religious-texts/home/ Answer the following How does the Qur’an treat this topic? How does the Hadith complement it? Are there differences between the two? How do you understand the difference between the Qur’an, which Muslims consider the revealed word of God, and the Hadith, which are the sayings of God’s messenger, Muhammad, who Muslims believe is an exemplar of proper Muslim behavior? Place the treatment of the subject by these texts within the context of what we have learned about Islam. Why would these rules and laws exist given the world Muslims lived in? Islam Expands Expansion 622-632 Expansion 632-661 Expansion 661-750 Muhammad’s successors Muhammad did not appoint a successor Muslims selected Abu-Bakr “Caliph” The next 3 caliphs are known as the Rightly Guided Caliphs Expansion Muslim armies were well organized and powerful They were also fighting weakened neighbors such as the Byzantines and Sassanids People were sick of persecution by previous state religions and Muslims were very tolerant to conquered peoples Crisis When the last rightly guided Caliph died different groups fought for control of the Muslim community Two branches of Islam were created after the Umayyad family took power Schism Sunni Party of the Umayyad family Believe Muslims should follow Muhammad’s example Muslim rulers do not need to be related to Muhammad Shi’a Believe that Caliphs should be related to Muhammad Feel that Ali should have been the second leader of Islam See divinity in the ruler of the community What do the following words have in common? Algebra Cotton Guitar Lemon Soda Sofa Trade Muslims expanded trade throughout the middle East and into Europe Textiles, Metalwork, Jewelry, Perfume, and spice were a few goods Muslims traded Ideas were also exchanged and the Muslim world was seen as a center of learning Islamic World C.E. 814 Govt. and Society The Islamic Empire split into 3 parts Baghdad (Iraq) Cairo (Egypt) Cordoba (Spain) Qur’an discouraged slavery Women's Roles “Men are the managers of the affairs of woman” Each family member had specific roles Men provided for the family Women maintained the home and raised the children Women could own property and go to school Modern practices concerning women vary widely across the Muslim world Marriage Marriages were arranged Men could have several wives Over time some Muslims have begun limiting the rights of woman while others have expanded them Scientific Achievements Medicine - knowledge among the best in the world Dissection, drugs, study of disease Geography – Due to experience in trade Muslims had good maps and tools Compiled maps from abroad Used astrolabe Muslims continued the old Greek and Roman philosophical and scientific tradition Mathematics – Base 10 number system still used today Invented Algebra “Al-Jabr” Arts Most art focused on geometric designs and patterns instead of people Architecture – Mosques became more elaborate and built minarets The Thousand and One Nights Collection of Muslim stories told around the world Byzantine Empire After the fall of Rome, Byzantium remained in the east 650 CE Justinian Emperor 527-567 C.E. Led a revival of Byzantium Expanded Borders of the Empire Ruled with absolute power and authority A massive revolt broke out over taxes and harsh rule which he brutally suppressed by luring rebels into the hippodrome and having them killed by the army Justinian Code Justinian enacted the “Codex Justinianus” in the early 6th century This was based on the recorded laws of Rome Became the Basis of English Civil Law Emblem of the Emperor Theodora Justinian’s wife Rose from humble beginnings to become Empress Expanded the rights of woman Exercised tremendous power over the Empire Military The empire had a powerful military force General Belisarius was responsible for the expansion of the empire Strong navy using “Greek Fire” Church Strong differences between Western Church (Pope) and east (Constantinople) Byzantines were against veneration of idols Iconoclastic controversy – Argument between east and west which resulted in the split of the church Great Schism The Pope and the Emperor of Byzantium excommunicated each other In 1054 the Orthodox and Catholic churches split apart in the Great Schism Culture Constantinople – One of the greatest cities in the world Hagia Sophia – “Church of Holy Wisdom” built in 532 C.E. Architectural triumph Created many religious paintings Constantinople Hagia Sophia Decline Over time the Empire began to weaken Seljuk Turks began conquering lands in Asia Minor, and Christian crusaders looted and pillaged the city In 1453 C.E. Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks 1180 CE Ch 11 Sec 2 Geography Russia extends from Europe to Asia and encompasses the Carpathian and Ural mountains. Grassy plains called steppes – good for farming Kievan Russia Kiev and Novgorod lay among major trade routes Trade flourished on the route between Constantinople and the Baltic Sea Government Boyars – Nobles who ruled the region Yaroslavl the Wise – Created the Pravda Russkia a law book based on tribal customs and traditions Religion Christianity spread in the 800s C.E. Ruler Vladamir I converted to Orthodox Christianity The Mongols Kiev began to decline and was eventually sacked by raiders This weakness allowed eastern invaders known as the Mongols to capture the area in 1240 C.E. In the late 1400s the Mongols began to weaken Moscow Ivan III “The Great” United the region around Moscow to claim independence from the Mongols Ivan IV “The Terrible” – Took title “Czar” Had many people including his son killed, and beat his pregnant daughter-in-law to miscarriage Church The Russian church over time became powerful and took large amounts of land When Constantinople fell the center of the Orthodox church moved to Moscow Rise of the “third Rome” The Mongols Tang and Sung Dynasties China With the fall of the Han dynasty China was ruled by the Sui dynasty (581-618) Short lived Created the Grand Canal Fell quickly due to disastrous military campaigns and peasant revolts Grand Canal Built to link northern and southern China Tang (618-907) China began expanding under the Tang Tang Literature • Li Bo and Du Fu became poets • Wrote about Daoism and Confucianism Religion • Zen Buddhism spread into China • When Buddhism became too powerful it was restricted and Confucianism returned Xian • New Capital of China Sung (960-1279) During Sung rule China was invaded by Jin tribes from the north Civil Service System • Improved fairness of the CSS Inventions • Gunpowder • Movable type City and Rural life • Population rose along with taxes on peasants • Woman in cities began foot binding