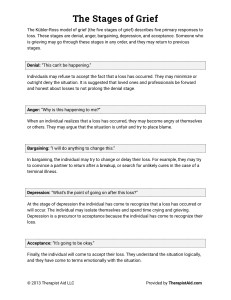
Ch.2 Power Point Notes Wellness is the quality or state of being in good health What are components of wellness: Physical, mental, emotional and spiritual What are consequences of poor nutrition: Obesity, Cardiac illness, Type 2 diabetes What are the four main food groups: Fruits & Veggies, Meats, Grains and Dairy Products The AHA’s “Simple 7”: Get active, control cholesterol, eat better, manage blood pressure, lose weight, reduce blood sugar and stop smoking. What does the USDA’s 2010 Dietary Guideline encourage: Lower calorie intake, Increase physical activity and make wiser food choices. What should your exercise program be targeted at maintaining or improving: Cardiovascular endurance, flexibility and physical strength How much physical activity should adults engage in every day: 30 mins of vigorous activity What are options for quitting smoking: Acupuncture, hypnotism, counseling, medications, instructions What is Circadian: Your body’s natural timing system How to avoid throwing off your circadian rhythm: avoid caffeine, eat healthy, keep regular sleep schedule. What are the most common hereditary health risk factors: Heart disease and Cancer What are proper lifting habits: Minimize the number of total body lifts you have to perform Coordinate every lift prior to performing the life What are the two common categories of stress: Eustress(Positive stress that motivates), Distress(Negative stress that overwhelms) When a person is subjected to stress, what is activated: “The fight or flight” system. Any event that causes us to react physically, emotionally or mentally is considered: Stress What does a stress response often times begin with: Events that are perceived as threatening or demanding The three reactions to stress: Acute(During the event), Delayed(After the event), or Cumulative(When exposed to prolonged or excessive stress) Initial management Techniques on how to control stress: Controlled breathing, Professional assistance and progressive relaxation. Prolonged or excessive stress is a strong contributor to: Heart disease, Hypertension, Cancer, Alcoholism and Depression Common reactions or responses to emergencies are: Fear, Anxiety, Depression, Anger and Confusion Psychological defense mechanisms of patients to illness/injury are: Denial (Early response to a medical emergency), Regression (returning to childish behavior while under stress), Projection (blaming others) and Displacement (putting emotion from yourself to someone else); ex. Pt angry at the medic. Blind Panic: Fear reactions when a person when a person’s judgement disappears Depression: Sitting or starring in a numb state Conversion Hysteria: When a person converts anxiety into a body function dysfunction. Ex. Person temporarily can’t see or hear OR if they become paralyzed. Early warning signs of stress: Heart palpations, Rapid breathing, Chest tightness or Sweating. Burnout: The exhaustion of physical or emotional stress(*Develops because the way a person reacts to stress) Signs/ Symptoms of burnout: Chronic Fatigue, Cynical or negative attitudes, Emotional instability, Changes in sleep pattern Encounters with life and death are an honor(most private moment/holy time in someone’s life) The 5 stages of grieving: Denial, Anger, Bargaining, Depression and Acceptance. Grieving Child Ages: up to 3yrs old(will be aware), 3-6yrs old(believe death is temporary), 6-9yrs old(may mask their feelings), 9-12yrs old(may want to know details) What caution does EMS follow when dealing with diseases: “Standard Precaution”- approach all body fluids as potentially infectious At minimum, each ambulance should have: Gloves, Facial protection, Gowns and N-95 Respirators. Communicable Disease: Any disease that can be spread from person to person or animal to person. Infectious Disease: Can be transmitted by contact (direct or indirect) or they are airborne. What calls are your “most dangerous” ones: Your “everyday” calls because you become comfortable with them and may let down your guard.