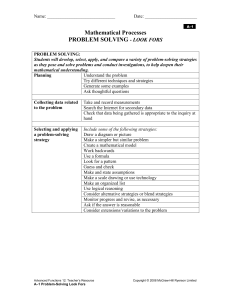
Differentiated Instruction: Look Fors in the Classroom TKES Performance Standard 4: Differentiated Instruction The teacher challenges and supports each student’s learning by providing appropriate content and developing skills which address individual learning differences. The lists below are not all encompassing. These are examples of what can be seen in a classroom with differentiated instruction. ************************************************************************************* Pre-­‐Assessment Look-­‐Fors with DI: A way to determine what students know of a topic before it is taught or the skill level before instruction begins. This will allow the teacher to determine flexible grouping patterns and different levels of instruction. ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Guess box Place mats Teacher prepared pre-­‐test KWL / graphic organizers Thinking Maps Writing prompts Prediction Teacher observation/checklist Student demonstrations / discussions Initiating activities Informal surveys/ questionnaires/inventories ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Student interviews Student products & work samples Self evaluations Portfolio analysis Game activities Show of hands – every student responds Drawing related to topic/content Reader response survey Anticipation journals ****************************************************************************** Content Look-­‐Fors in DI: Ideas, concepts, descriptive information and facts, rules and principles that are presented to the learner. Content is differentiated through depth, complexity, novelty, and acceleration. Strategies for Differentiating by Content: ü Readiness testing ü Concept based teaching ü Learning Contracts ü Multiple and/or supplementary texts ü Small groups to re-­‐teach or extend ü Materials on tape Ways to Differentiate by Content: ü Reading partners / reading buddies ü Read / summarize ü Read / Question / Answer ü Visual Organizer / Summarizer ü Parallel Reading with Teacher Prompt ü Choral Reading / Responsive Reading ü Split Journals (Double Entry – Triple Entry) ü Flip Books ü ü ü ü ü Learning styles & multiple intelligences Interest based mini lessons Curriculum compacting Technology Varying rate of learning and complexity (spelling, vocabulary, questioning, readability levels of text) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Highlights with Tape Digests / Cliff Notes / Teacher Notes Note-­‐Taking Organizers Varied Texts Varied Supplementary Materials Highlighted Texts Think-­‐Pair-­‐Share / Preview-­‐Midview-­‐Postview Books of Tape Process Look-­‐Fors in DI: The presentation of content, including the learning activities for students, the questions that are asked, as well as the teaching methods and thinking skills that are used. Strategies for Differentiating by Process: ü Student Choice ü Tiered Curriculum / Activities ü Interest Centers ü Cubing ü Learning Stations ü Similar Readiness Groups ü Varying length of time to complete task ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Mixed Readiness Grouping Learning Contracts Choice of Work Arrangement Anchor Activities Varied Journal Prompting Manipulatives & Hands-­‐on Support Encourage students to take greater depth in topics Ways to Differentiate by Process: ü Fun and Games ü RAFTS ü Cubing ü Think Dots ü ü ü ü Centers Choice Boards (Intelligences) Tiered Lessons Contracts ****************************************************************************** Product Look-­‐Fors in DI: The outcomes of instruction that consolidate learning and communicate ideas. Strategies for Differentiating by Product: ü Tiered Products ü Student Choice ü Interest Based Investigations ü Rubrics that extend varied skills Ways to Differentiate by Product: ü Choices based on readiness, interest, & learning profile ü Clear expectations ü Timelines ü Independent Study – create own product assignment ü Mentors ü Allowing students to work alone or small groups ü ü ü ü Agreements Product Guides Rubrics Evaluations ****************************************************************************** Learning Environment Look-­‐Fors in DI: The way the classroom looks and/or feels. The types of interactions that occur, roles and relationships between students and teacher, expectations for growth and success, and the sense of mutual respect, fairness and safety in the classroom. Strategies for Differentiating the Learning Environment: ü Class Meetings ü Responsibility for Learning ü Shared Decision Making ü Established Protocols ü Response Journals