Constructivism Theory: Subjective Reality & Knowledge Building
advertisement
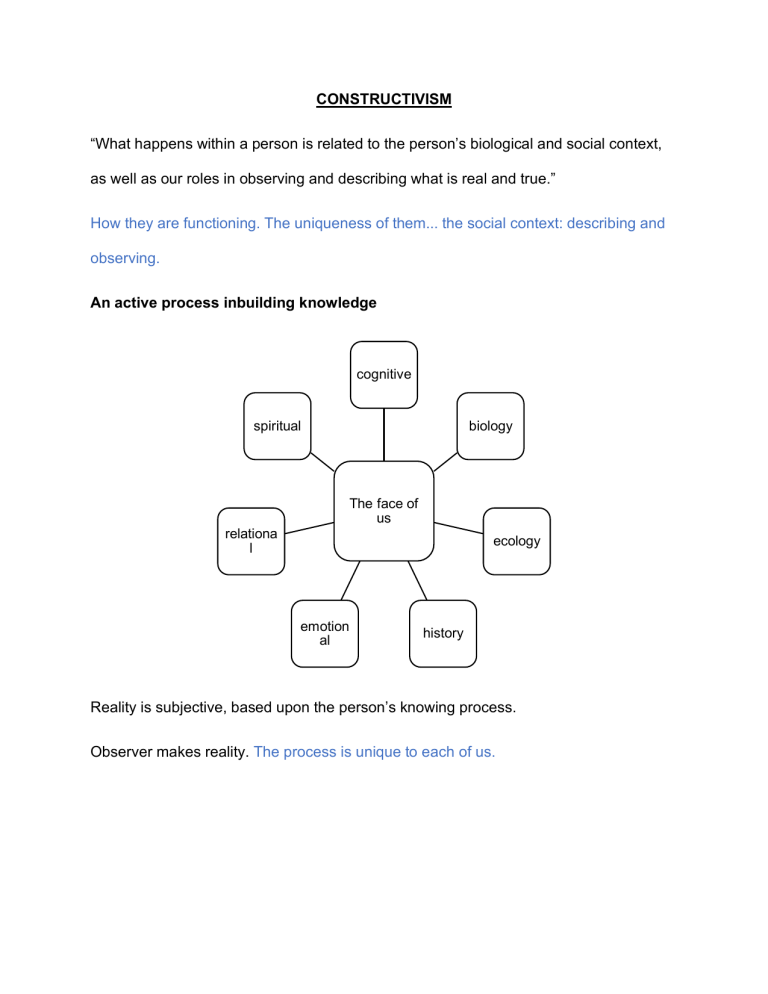
CONSTRUCTIVISM “What happens within a person is related to the person’s biological and social context, as well as our roles in observing and describing what is real and true.” How they are functioning. The uniqueness of them... the social context: describing and observing. An active process inbuilding knowledge cognitive spiritual biology The face of us relationa l ecology emotion al history Reality is subjective, based upon the person’s knowing process. Observer makes reality. The process is unique to each of us. • Knowledge is constructed, not discovered • Learning as an active process (not passively receiving information. You are creating your own understanding) • Truth is unknowable • Glaserfeld: “There is a world, but we are unable to acquire certainty of our representations of it as true to reality as we are unable to access any objective reality” • Knowledge from adaptation to viability, so not the environment produces structural changes but our fitness in relation to our experiences. “All communication and all understanding are a matter of interpretive construction on the part of the experiencing subject” CONSTRUCTIVISM: (second order cybernetics) what happens within a person is related to the person’s biological and social context as well as our role as observers in describing what is real and true. The knower creates the known Anti-realist: no independent reality Knower makes the reality rather than discovers it; creates reality, since reality is subjective, based upon the person’s knowing process. Environment effects are not predictable OBJECTIVISM: holds that there is a reality independent from the observer that can be known. The therapist would assume that there are objective facts waiting to be discovered and that a welltrained therapist can discover them. Objectivist position explains that there is an environmental determinism. Realist: an independent reality to be discovered. The knower discovers reality. Couse and effect relationships can be predictable, since the cause and the effect can be objectively known in advance. Environment has predictable effects on people Compare to other therapy models • Collaborative vs. totalitarian • Developmental vs. symptom oriented • Process vs content • Reflective vs psychoeducational • Interaction with the world • We (therapist) intervene in meaning “The focus of therapy from an assessment of what is- which would be an attempt to gain an objective truth of the situation- to an exploration of how the person, in this case the client (and, of course, the therapist), construct what they know.” Constructivists understand that we cannot help but influence other person, but we cannot say with certainty what the outcome of this influence/intervention will be. These non- predictable influences have come to be called perturbations. Life is not about how one conforms to the rigors of the outside world but, rather, how one transforms outside stimuli into a personal construct Essentially, constructivism is a family of theories and therapies: a. That humans are proactive (and not passively reactive) participants in their own experience- that is, in all perception, memory and knowing b. That the vast majority of the ordering process organizing human lives operate at tacit (un- or super- conscious) levels of awareness c. That human experience and personal psychological development reflect ongoing operation of individualized, self-organizing process that tend to favor the maintenance (over the medication) of experiential patterns. https://youtu.be//YozoZxblQx8 Von Glasersfeld proposed three essential epistemological tenets of constructivism to which a fourth has been added in light of recent writings. 1. Knowledge is not passively accumulated, but rather, is the result of active cognizing by the individual 2. Cognition is an adaptive process that functions to make an individual’s behavior more viable given a particular environment 3. Cognition organizes and makes sense of one’s experience, and is not a process to render an accurate representation of reality 4. Knowing has roots in both biological/neurological construction, and social, cultural and language based interactions. “An evaluation of radical constructivism results in radical constructivism being considered a “strong” form of constructivism, as it fully embraces three of the constructivist epistemological tenets and at least partially embraces the fourth. That is, radical constructivism is concerned with both the construction of mental structures, the position of cognitive constructivists, and the construction of personal meaning. In this sense, radical constructivism involves a greater degree of construction than does cognitive constructivism, involving two planes of construction, structure and meaning, rather than only one, structure” Radical constructivism- the knower can only know through his own experience, and this, there is no objective reality It is radical because it breaks with convention and develops a theory of knowledge in which knowledge does not reflect an “objective” ontological reality, but exclusively an ordering and organization of a world constituted by our experience. There is not a denial of events outside of us, but an understanding that what we experience are our own constructed models of what is. “The map is not the territory. Rather, the map is an individual’s construction of the territory that is out there”. “Anything said is said by an observer”. From a constructivist perspective, the self is based on an awareness of what one is doing and experiencing. FROM “I think, therefore I am” TO “I am aware of thinking, therefore I am”. The fundamental principles of radical constructivism: • Knowledge is not passively received either through the senses of by way of communication • Knowledge is actively built up by the cognizing subject • The function of cognition is adaptive, in the biological sense of the term, tending towards fit or viability. • Cognition serves the subject’s organization of the experiential world, not the discovery of an objective ontological reality. Video: What makes us different. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3WKlaMJaE0g Positivism- the idea that objective truth can be discovered by an observer who is neutral • desire to see • access reality • understand reality • desire to see Post-positivists understand that the observer inevitably influences that • responsability for observations is observed- that the observer is part of the observed, and that detached • observer's construction of reality neutrality is not possible. Biology of love accepting the legitimacy of the other Maturana defined violence as an act in which one person tries to negate the reality of another or replace it with his own reality. Love becomes defined as the opposite, an acceptance of the reality of the other. “For the constructivist therapist working with Frank and Stella, this leads to the conceptualization of each of them changing self rather than trying to change the other, since the self of each the source of their reality. When people accept that they construct their own reality, they are more readily available to accept responsibility for their actions” Autopoiesis: a system that self regulates A person is autopoietic in that he is a self- organizing and self-referential system. Further, the person has a structure, which determines how he functions. This functioning changes based on the interactions with various mediums (other systems). For therapists, perhaps one of the most important concepts is that the medium in which people interact is through language (both verbal and nonverbal) Ethical imperative- act always so as to increase the number of choices Consensual behavior- being in connection with one another, function based on their own organization but also change by being involved with one another. Frank and stella will each display behaviors that would not have existed if it were not for their being in relationship with one another. For each connection to a different person would lead to different consensual behavior. THERAPY CAN BE SEEN AS A PROCESS OF PERTUBING THE SYSTEM Structural drift: is the connection between how a system is organized and the system’s connection with the medium (another system). Structural drift happens in the moment based on the interactions between people. People in relationship are connected to one another through structural drift. Structural determinism: is the notion that people function in their internal and relational dynamics based on their structure. Maturana and Varela described that, in examining the organization of a system, one views the component parts not as separate entities but in terms of how they work in relation to the other components of system (what these authors call the unity) The actions of the environment are just the situation, which allows the system’s response to occur. These actions are called perturbations. We cannot help but influence the other person, and we cannot say with certainty what the outcome of our influence will be. When one part of a system change, it will change the consensual behavior, which is called orthogonal interactions. A change in one part of the system, can lead to system-wide change.







