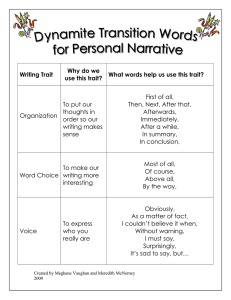
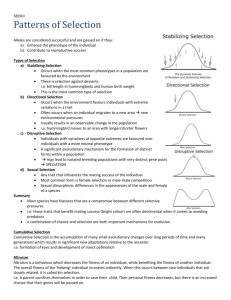
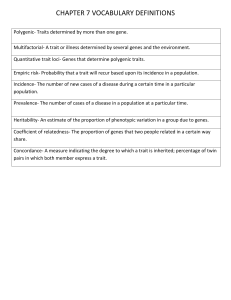
Comparative Psychology Flash Cards 1) Adaptation • A characteristic that confers higher inclusive fitness to individuals than any other existing alternative exhibited by other individuals within the population • A trait that has spread or is spreading or is being maintained in a population as a result of natural selection or indirect (kin) selection 2) Adaptionists • A behavioral biologist who develops and tests hypotheses on the possible adaptive value of a particular trait • Persons using an adaptationist approach test whether a given trait enables individuals to propagate their special genes more effectively than if they had an alternative trait 3) Adaptive Value • Contribution that a trait or gene makes to inclusive fitness 4) Alleles • Form of a gene • Different alleles typically code for distinctive variants of the same enzyme 5) Arms Race • Result of selection acting on two parties that are in opposition to one another, as in the increasing sophistication of defensive mechanisms in a species that is preyed upon by an increasingly sophisticated predator 6) Artificial Selection • Process that is identical to natural selection, except that humans control the reproductive success of alternative types within the selected population 7) Darwinian Puzzles • Trait that appears to reduce the fitness of individuals that possess it • Traits of this sort attract the attention of evolutionary biologists 8) Developmental Homeostasis • Capacity of developmental mechanisms within individuals to produce adaptive traits, despite potentially disruptive effects of mutant genes and suboptimal environmental conditions 9) Ethology • Study of the proximate mechanisms and adaptive value of animal behavior 10) Evolutionary change is inevitable if just three conditions are met: • VARIATION, with members of a species differing in some of their characteristic • DIFFERENCES IN REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS, with some individuals having more surviving offspring than others in their population, thanks to their distinctive characteristics • HEREDITY, with parents able to pass on some of their distinctive characteristics to their offspring Comparative Psychology Flash Cards 11) Fitness Benefits • Aspect of a trait that tends to raise the inclusive fitness of individuals 12) Fitness Costs • Aspect of a trait that tends to reduce the inclusive fitness of individuals 13) Fixed Action Pattern (FAP) • Innate, highly stereotyped response that is triggered by a well-defined, simple stimulus • Once the pattern is activated, the response is performed in its entirety 14) Genes • Segment of DNA, typically one that encodes information about the sequence of amino acids that makes up a protein 15) Genotype • Genetic constitution of an individual • Refers to either the alleles of one gene possessed by the individual or to its complete set of genes 16) Innate Releasing Mechanism • Hypothetical neural mechanism thought to control an innate response to a sign stimulus 17) Instinct • Behavior pattern that reliably develops in most individuals, promoting a functional response to a releaser stimulus the first time the behavior is performed 18) Learning • Durable and usually adaptive change in an animal's behavior traceable to a specific experience in the individual's life 19) Natural Selection • Darwin's theory that living species are the product of an unguided, unconscious process of reproductive competition among their ancestors 20) If in the past some individuals left more descendants than others because of their distinctive heredity attributes, then these reproductively dominant individuals would inevitably gradually reshape their species in their image 21) Neurons • Nerve cell 22) Operant Conditioning • Kind of learning based on trial and error, in which an action, or operant, becomes more frequently performed if it is rewarded Comparative Psychology Flash Cards 23) Phenotype • Any measurable aspect of an individual that arises from an interaction of the individual's genes with its environment 24) Polyphenisms • Occurrence within a species of two or more alternative phenotypes whose differences are induced by key differences in the environments experienced by individual members of this species 25) Proximate (immediate) Causes • Behavior changes that occur within the lifespan of individuals. • Immediate, underlying cause based on the operation of internal mechanisms possessed by an individual • How genetic-developmental mechanisms influence the assembly of an animal and its internal components, including its nervous and endocrine system • How neuronal-hormonal mechanisms control what an animal can do behaviorally 26) Sign Stimulus/Releaser • Effective component of an action or object that triggers a fixed action pattern in an animal 27) Ultimate (evolutionary) Causes • Behavior changes that occur across generations • Evolutionary, historical reason why something is the way it is • The evolutionary history of a behavioral trait as affected by descent with modification from ancestral species • The adaptive value of a behavioral trait as affected by the process of evolution by natural selection