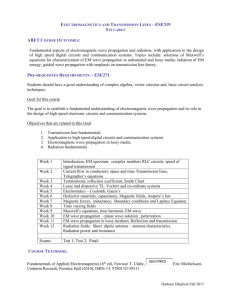
Course Title: Electromagnetic Field Theory Course Code: ECE301 Credit Units: 3 Level: UG L T 3 0 P/ S 0 SW/F W 0 TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 Course Objectives: This course provides a general introduction to the important physical concepts and mathematical methods used in treating all types of wave phenomena, but stresses electromagnetic signal propagation and issues of central importance in electrical engineering. As a core course in the Electrical Computer and Systems Engineering option of the Engineering Sciences concentration, it provides essential background and basic preparation for more advanced work in device physics, microwave and ultra-fast circuitry, antenna design, optics, optical communication and optoelectronics. Prerequisites: Applied Physics-I (Field & Waves) Weightage (%) Module I : Mathematical Basics 20% Coordinate Systems: Cylindrical and Spherical coordinates, differential length, area and volume, line surface and volume integral, Comparison and signifance of gradient, divergence , curl and Laplacian, Module II : Electrostatics and Magnetostatics 20% Gauss’s law, Poisson’s Equation, Laplace’s Equation, Electrostatic Boundary conditions, Faraday’s law, Biot Savart Law, Ampere’s law, Magnetostatics Boundary conditions, Magnetic Vector Potential. Module III : Electrodynamics 20% significance of Maxwell’s equations for time varying fields, Continuity equation Poynting theorem and power flow. Module IV: Electrodynamics Waves 20% Uniform plane wave, Wave Polarization, Propagation of wave in free space, lossy and lossless media, conducting medium Reflection and refraction at media interface, Module V : Transmission Lines 20% Equations of Voltage and Current on transmission line, Propagation constant, Characteristic Impedance and Reflection coefficient, Loss-less and Low loss Transmission line, VSWR, Power transfer on transmission line, Impedance and Admittance smith Chart, Impedance matching, lossy transmission line, Types of transmission Line, Problems on transmission line. Student Learning Outcomes: To define overall needs and constraints. The technical ability to analyze and design a prescribed communication sub-system Analyze and attract the vital resources required to turn a vision into reality. To identify and solve the technical requirements of the system and its impact on the global society Evaluate the opportunities involving technology, a product or a service required for developing a startup idea. The ability to develop and assess alternative RF system designs based on technical criteria Pedagogy for Course Delivery: The class will be taught using theory and numerical based method. The course instructor will spend considerable time in understanding of the concept and its application in real life problems. The instructor will cover the ways to think innovatively liberally using thinking techniques. Assessment/ Examination Scheme: Theory L/T (%) Lab/Practical/Studio (%) 100% Total NA 100% Theory Assessment (L&T): Continuous Assessment/Internal Assessment End Term Examination Components (Drop down) Mid-Term Exam S/V/Q HA Attendance 10% 8% 7% 5% Weightage (%) CT: Class Test, HA: Home Assignment, S/V/Q: Seminar/Viva/Quiz, EE: End Semester Examination; A: Attendance Text: M.N.O Sadiku,”Elements of Electromagnetics” . Griffiths: Introduction to Electrodynamics Fawwaz T. Ulaby: Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics Hayt, William H., Buck, John A. Hayt, William H., Buck, John A., Engineering Electromagnetics 70%