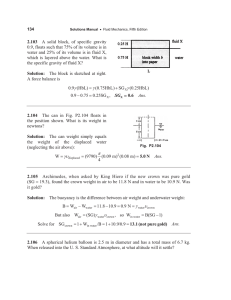
BUOYANCY A S H O R T L E S S O N O N W H Y T H I N G S F L O AT BUOYANCY • Upward net force on objects within a liquid • Occurs because pressure in a fluid increases with depth • Since the bottom is deeper, more force is pushing up than force on the bottom pushing down • Net upward force pushes objects up ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE • The buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object FB = Fw = mg ρ = M/V M = ρV FB = ρVg It is NOT the object that exerts the buoyant force, it is the fluid that the object displaces that causes it FB = ρfluidgVsubmerged Sink or Float • The difference between the buoyant force and the object’s weight determines whether an object sinks or floats. WHAT IS THE BUOYANT FORCE ON THIS OBJECT? EXAMPLE • A 70kg statue lies at the bottom of the sea. Its volume is 3.0 x 10-2 m3. How much force is needed to lift it? • When a crown of mass 14.7kg is submerged in water, an accurate scale reads only 13.4kg. Is the crown gold? FLOATING • An object floats on a fluid if its density is less than that of the fluid • When floating FB = FW • ρfVdispg = ρoVog • ρfVdisp = ρoVo • Fraction of an object submerged is given by the ratio of the density of the object to the fluid EXAMPLE • A rectangular block of wood (1.0m x 2.0m x 0.25m) floats so that 0.15 cm of its height is above the water level. a) find the density of the wood b) find the mass of the wood