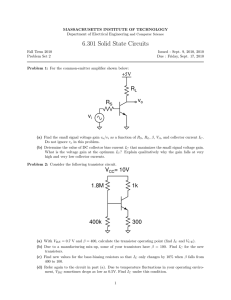
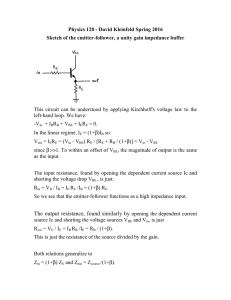
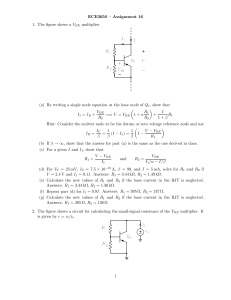
ANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 Biasing Using a Collector-to-Base Feedback Resistor • Figure shows a simple Biasing Using a Collector-to-Base Feedback Resistor Biasing Using a Collector-to-Base Feedback Resistor • The circuit employs a resistor RB connected between the collector and the base • Resistor RB provides negative feedback, which helps to stabilize the bias point of the BJT. Biasing Using a Collector-to-Base Feedback Resistor • Analysis of the circuit is shown in Fig., from which we can write Summary of the BJT Current–Voltage Relationships in the Active Mode Small-Signal Operation and Models • conceptual amplifier circuit shown in Fig. Cont… • Here the base–emitter junction is forward biased by a dc voltage VBE (battery). • The reverse bias of the collector–base junction is established by connecting the collector to another power supply of voltage VCC through a resistor RC. • The input signal to be amplified is represented by the voltage source vbe that is superimposed on VBE. Cont.. • We consider first the dc bias conditions by setting the signal vbe to zero. Cont.. • • • • IC = ISeVBE ⁄ VT IE = IC ⁄α IB = IC ⁄ β VCE = VCC – ICRC The Collector Current and the Transconductance • If a signal vbe is applied as shown in Fig. (a), the total instantaneous base–emitter voltage vBE becomes vBE = VBE + vbe • Correspondingly, the collector current becomes iC = IS evBE ⁄ VT =IS e (VBE + vbe) ⁄ VT ؞iC =ISeVBE ⁄ VT evbe ⁄ VT • Use of Eq. IC = IS eVBE ⁄ VT in iC =IS eVBE ⁄ VT evbe ⁄ VT yields iC = IC evbe ⁄ VT • Now, if vbe<<VT, we may approximate the above Eq. as Here we have expanded the exponential in Eq. iC = IC evbe ⁄ VT in a series and retained only the first two terms. This approximation, which is valid only for vbe less than approximately 10 mV, is referred to as the small-signal approximation. Under this approximation, the total collector current is given by the above Eq. and can be rewritten • Thus the collector current is composed of the dc bias value IC and a signal component ic , • This equation relates the signal current in the collector to the corresponding base–emitter signal voltage. It can be rewritten as where gm is called the transconductance The Base Current and the Input Resistance at the Base • To determine the resistance seen by vbe, we first evaluate the total base current iB using Eq. as follows: Thus, Base Current • where IB is equal to and the signal component ib is given by • The small-signal input resistance between base and emitter, looking into the base, is denoted by rπ and is defined as the Input Resistance at the Base • Using Eq. gives •Thus rπ is directly dependent on β and is inversely proportional to the bias current IC. •Substituting for gm in Eq. from Eq. and replacing IC /β by IB gives an alternative expression for rπ ,