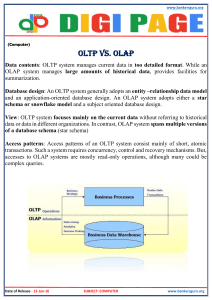
Lectures 6,7 Business intelligence technologies and tools. OLAP technologies 1 Instructor assoc. prof. Sembina G.K. BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE (BI) Business intelligence (BI) is a set of theories, methodologies, architectures, and technologies that transform raw data into meaningful and useful information for business purposes. Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis of business information. BI helps to transform: Data into information Information into knowledge Knowledge into decisions Finally, decisions to action 2 THE BI GOAL BI is about using data to help enterprise users make better business decisions 3 FUNCTIONS OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE Common functions of business intelligence technologies include reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI technologies can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic 4 business opportunities. BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE TOOLS 5 DATA WAREHOUSING Data warehouse (DW or DWH) is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and Extract, load, transform (E-LT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. 6 THE ETL PROCESS 7 BUSINESS PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT (BPM) AND DATA MINING BPM is a set of performance management and analytic processes that enables the management of an organization's performance to achieve one or more pre-selected goals. Data mining is a process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems.8 PROCESS MINING, QUERYING, AND REPORTING Process mining is a family of techniques relating the fields of data science and process management to support the analysis of operational processes based on event logs. The goal of process mining is to turn event data into insights and actions. Querying: a request for specific data or information from a database Reporting: sharing operating and financial data analysis with decision-makers so they can draw 9 conclusions and make decisions DECISION ENGINEERING AND DASHBOARDS Decision engineering is applying relevant knowledge to design, build, maintain, and improve systems for making decisions. A dashboard is a type of graphical user interface which often provides at-a-glance views of key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to a particular objective or business process. In other usage, "dashboard" is another name for "report" and considered a form of data visualization. The “dashboard” is often accessible by a web browser and is usually linked to 10 regularly updating data sources. BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE BENEFITS Improved decision making Integrating architecture Common user interface for data reporting and analysis Common data repository fosters single version of company data Improved organizational performance 11 THE BEST BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE TOOLS FOR 2020 https://synergytop.com/blog/top-10-businessintelligence-tools-in-2020/ 12 ONLINE ANALYTICAL PROCESSING (OLAP) OLAP is a category of software that allows users to analyze information from multiple database systems at the same time. It is a technology that enables analysts to extract and view business data from different points of view. Analysts frequently need to group, aggregate and join data. These operations in relational databases are resource intensive. With OLAP data can be pre-calculated and preaggregated, making analysis faster. 13 OLAP CONCEPTUAL DATA MODEL An OLAP cube is a multidimensional dataset built from the data warehouse. Goal of OLAP is to support ad-hoc querying for the business analyst. Business analysts are familiar with spreadsheets. Extend spreadsheet analysis model to work with warehouse data. 14 THE OLAP PROCESS 15 HOW DOES OLAP WORK? • • • • There are multiple steps of OLAP: First, data is first extracted from various data sources and formats, like text files and spreadsheets. This data is then stored in the Data Warehouse. Next, the data is cleaned, transformed, and stored in OLAP Cubes . Once in the OLAP cubes, information is then precalculated and pre-aggregated in advance for further analysis. Lastly, the user gets the data from the OLAP cubes by running queries against them. 16 OLAP CUBE OLAP databases are divided into one or more cubes. At the core of the OLAP, concept is an OLAP Cube. The OLAP cube is a data structure optimized for very quick data analysis. The OLAP Cube consists of numeric facts called measures which are categorized by dimensions. OLAP Cube is also called the hypercube if the number of dimensions is greater than 3. OLAP contains multidimensional data, with data usually obtained from a different and unrelated sources. Using a spreadsheet is not an optimal option. The cube can store and analyze multidimensional data 17 in a logical and orderly manner. OLAP CUBE Date sum 2Qtr 3Qtr 4Qtr sum Portugal Spain Germany Country TV PC VCR 1Qtr sum 18 DIMENSIONS Dimensions are how people like to segment, or slice, the data. Dimensions are how you want to see the data You usually want to see data by product, country, date, account, employee, … Almost anytime someone asks a question, they describe how they want to see it. For example, sales by store by month. Dimensions are made up of attributes and may or may not include hierarchies Year – Semester – Quarter – Month – Day 19 Product Category – Product Subcategory - Product MEASURES Measures are what you want to see They are almost always numeric They are often additive Dollar sales, unit sales, profit, expenses, and more Some measures are not additive Date of last shipment Inventory counts and number of unique customers Measures may be KPIs 20 ATTRIBUTES Attributes represent different ways of looking at something in a dimension. Attributes are individual values that make up dimensions A Time dimension may have a Month attribute, a Year attribute, and so forth A Geography dimension may have a Country attribute, a Region attribute, a City attribute, and so on A Product dimension may have a Part Number attribute, a size attribute, a color 21 attribute, a manufacturer attribute, and more HIERARCHIES Most dimensions contain hierarchies which allow users to drill down on data. You can put attributes into a hierarchical structure to assist user analysis One of the most common functions in BI is to “drill down” to a more detailed level For example, Time hierarchy might be to go from Year to Quarter to Month to Day Another Time hierarchy might go from Year to Month to Week to Day to Hour 22 BASIC ANALYTICAL OPERATIONS OF OLAP Four types of analytical operations in OLAP are: Roll-up Drill-down Slice and dice Pivot (rotate) 23 1. ROLL-UP Roll-up is also known as "consolidation" or "aggregation." In this example, cities New jersey and Los Angeles rolled up into country USA. The sales amount of New Jersey and Los Angeles are 440 and 1560 respectively. They become 2000 after rollup. In this aggregation process, data is location hierarchy moves up from city to the country. In this process at least one or 24more dimensions need to be removed. In this example, Quarter dimension is removed. Quarter Q1 is drilled down to months January, February, and March. Corresponding sales are also registering. 2. DRILL-DOWN In drill-down data is fragmented into smaller parts. It is the opposite of the rollup process. 25 3A. SLICE Here, one dimension is selected, and a new sub-cube is created. 26 3b. Dice is similar to a slice. The difference in dice is you select 2 or more dimensions that result in the creation of a sub-cube.27 4. In Pivot, you rotate the data axes to provide a substitute presentation of data. In the following example, the pivot is based on item types. 28 TYPES OF OLAP SYSTEMS OLAP Hierarchical Structure 29 TYPES OF OLAP SYSTEMS ROLAP works with data that exist in a relational database. Facts and dimension tables are stored as relational tables. It also allows multidimensional analysis of data and is the fastest growing OLAP. MOLAP uses array-based multidimensional storage engines to display multidimensional views of data. Basically, they use an OLAP cube. Hybrid OLAP is a mixture of both ROLAP and MOLAP. It offers fast computation of MOLAP and higher scalability of ROLAP. HOLAP uses 30 two databases. TYPES OF OLAP SYSTEMS WOLAP. Web OLAP which is OLAP system accessible via the web browser. WOLAP is a three-tiered architecture. DOLAP. In Desktop OLAP, a user downloads a part of the data from the database locally, or on their desktop and analyze it. MOLAP. Mobile OLAP helps users to access and analyze OLAP data using their mobile devices SOLAP. Spatial OLAP is created to facilitate management of both spatial and non-spatial data in a Geographic Information system (GIS). 31 ADVANTAGES OF OLAP OLAP is a platform for all type of business includes planning, budgeting, reporting, and analysis. Information and calculations are consistent in an OLAP cube. This is a crucial benefit. Quickly create and analyze "What if" scenarios Easily search OLAP database for broad or specific terms. OLAP provides the building blocks for business modeling tools, Data mining tools, performance reporting tools. Allows users to do slice and dice cube data all by various dimensions, measures, and filters. It is good for analyzing time series. Finding some clusters and outliers is easy with OLAP.32 It is a powerful visualization online analytical process system which provides faster response times DISADVANTAGES OF OLAP OLAP requires organizing data into a star or snowflake schema. These schemas are complicated to implement and administer You cannot have large number of dimensions in a single OLAP cube Transactional data cannot be accessed with OLAP system. Any modification in an OLAP cube needs a full update of the cube. This is a time-consuming process What is Business Intelligence and an OLAP Cube? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yoE6bgJv08E&feat 33 ure=youtu.be Thank you for your attention! 34