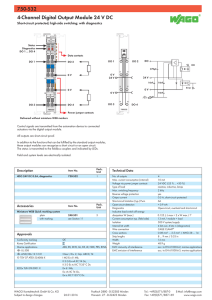
ATTACHMENT 2H 60439-1 © IEC:1999+A1:2004 – 91 – 7.5.2.2 For an ASSEMBLY having several incoming units which are unlikely to be in operation simultaneously, the short-circuit withstand strength can be indicated for each of the incoming units in accordance with 7.5.2.1. 7.5.2.3 For an ASSEMBLY having several incoming units which are likely to be in operation simultaneously, and for an ASSEMBLY having one incoming unit and one or more outgoing units for high-power rotating machines likely to contribute to the short-circuit current, a special agreement shall be made to determine the values of the prospective short-circuit current in each incoming unit, in each outgoing unit and in the busbars. 7.5.3 Relationship between peak current and short-circuit current For determining the electrodynamic stresses, the value of peak current shall be obtained by multiplying the short-circuit current by the factor n. Standard values for the factor n and the corresponding power factor are given in table 4. Table 4 – Standard values for the factor n RMS value of short-circuit current kA cos ϕ n I≤ 5 0,7 1,5 5< I≤ 10 0,5 1,7 10 < I ≤ 20 0,3 2 20 < I ≤ 50 0,25 2,1 0,2 2,2 50 < I NOTE Values of this table represent the majority of applications. In special locations, for example in the vicinity of transformers or generators, lower values of power factor may be found, whereby the maximum prospective peak current may become the limiting value instead of the r.m.s. value of the short-circuit current. 7.5.4 Co-ordination of short-circuit protective devices 7.5.4.1 The co-ordination of protective devices shall be the subject of an agreement between manufacturer and user. Information given in the manufacturer's catalogue may take the place of such an agreement. 7.5.4.2 If the operating conditions require maximum continuity of supply, the settings or selection of the short-circuit protective devices within the ASSEMBLY should, where possible, be so graded that a short circuit occurring in any outgoing branch circuit is cleared by the switching device installed in the faulted branch circuit without affecting the other outgoing branch circuits, thus ensuring selectivity of the protective system. 7.5.5 7.5.5.1 Circuits within an ASSEMBLY Main circuits 7.5.5.1.1 The busbars (bare or insulated) shall be arranged in such a manner that an internal short circuit is not to be expected under normal operating conditions. Unless otherwise specified, they shall be rated in accordance with the information concerning the short-circuit withstand strength (see 7.5.2) and designed to withstand at least the shortcircuit stresses limited by the protective device(s) on the supply side of the busbars.