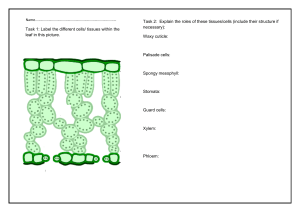
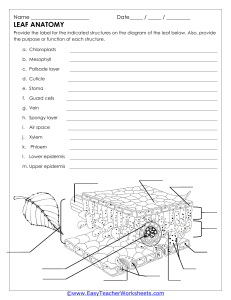
Some definitions Leaves – definition and structure. What is a leaf? When is a leaf not a leaf? Plant Anatomy: Some technical words Parts of a leaf Names for Leaf shape Names for leaf edges Veins of leaves Demonstrating leaf shape Apiacaea leaves Lamiaceae family Asteraceae family Hairy and Smooth Lets look at flowers Anatomy and function, using our four families as examples. Rose Family Celery family Anatomy of a flower Celery family (more!) Ray florets Mint family Anatomy of mint flowers Pollination Daisy family Capitulums Anatomy of Capitulums Important plant structures: Transportation. Plant tissues that transport useful things. Vascular Tissues Tissues are specialised groups cells that perform a function. Xylem and Phloem are two types of tissue that transport liquids and nutrients around a plant. Cross section of a stem Comparison Phloem Transports food (sugars) and nutrients (proteins) Two-directional Present in roots, stem and leaves Living tissue Not star shaped in cross section Xylem Transports water and minerals from the roots. One direction –up! Present in root, stem and leaves Once mature is hollow Star shaped cross section Xylem and Phloem Microscope image Congratulations! You have now seen how a plant germinates from seed. You have seen images of cotyledons, leaves and leaf anatomy, leaf shapes, leaf edges, hirsute and glabrous, even leaf veining! You have seen different kinds of flowers, and their basic anatomy. You have seen how plants transport water and nutrients. Now you can observe these anatomical parts in any plant you choose to study!